
The genesis and classification of mountains are fascinating subjects that unveil the dynamic geological processes shaping the Earth’s surface. Mountains are born through intricate tectonic forces and exhibit diverse forms, each telling a unique geological story. By employing suitable sketches, this exploration seeks to illustrate the genesis of mountains and highlight various types found across the globe. From towering fold mountains formed by converging tectonic plates to volcanic peaks emerging from the Earth’s interior, the world’s mountain systems present a rich tapestry of geological history. Examples from iconic mountain ranges like the Himalayas, the Andes, the Alps, and the Rockies will be woven into this narrative, providing insights into the distinct characteristics and origins of these majestic landforms. As we delve into the sketches and examples, we embark on a visual and informational journey to comprehend the intricate processes that have sculpted some of the most awe-inspiring features on our planet.
Answer
Mountains are formed through various complex geological processes leading to the formation of different types of mountain systems on the surface of the earth.
Different types of mountains and their genesis Fold mountain System
- when two tectonic plates converge and Earth’s Crust is subjected to intense pressure and compression and is pushed upward.
- Tectonic convergence can be:
- Continental-Continental convergence:Himalayan type mountains,among highest fold mountains in the world,eg.The Himalayas,Urals,Alps.
- Ocean-Continent convergence:Cordilleran collision,formation of extensive mountain systems eg.The Rockies and The Andes.
- Ocean-Ocean convergence:Formation of Island arcs instead of fold mountains,eg Japanese Archipelago.
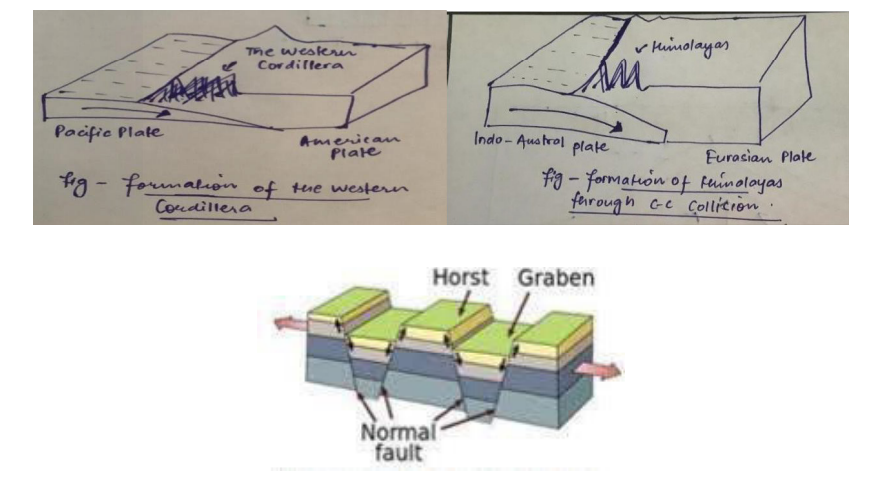
Block mountains
- Created when large blocks of the Earth’s Crust are pushed up or down along the fault lines. Example The Sierra Nevada Mountains in the USA.
Volcanic mountains
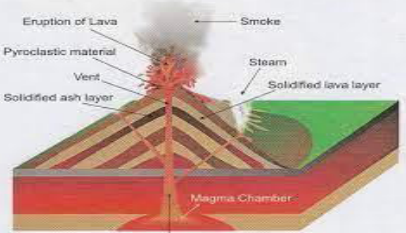
- Formed by the accumulations of lava, volcanic material such as volcanic ash, and other pyroclastic Material.

Types of volcanic mountains based on structure:
- Shield Volcano: Shield volcanoes are not so steep therefore lava flows to a great distance, wider, resemble warrior shields and hence its name, the largest of all types of volcanoes.
- Cinder Volcanoes: formed when upcoming lava of shield mountains moves in the form of shield mountains and comes out explosively, a steep slope, a crater on the top.
- Composite volcanoes: do not have one but many vents, lava flows with a mixture of volcanic rocks called cinders, and material accumulates in the form of layers over layers.
- Caldera: created as a large depression due to an explosion in the volcano, which collapses it.
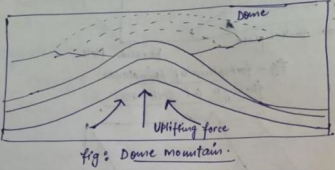
Dome mountains
- Formed when molten magma pushes up the Earth’s surface but doesn’t erupt as a Volcano Example The Black Hills in South Dakota USA.
Residual mountains
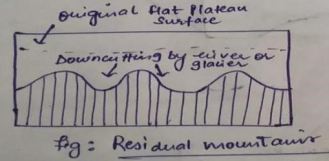
- Formed through erosion of existing land forms leaving behind elevated remnants Example The Appalachian mountain in North America
Mid-Oceanic Ridges
- A mid-ocean ridge (MOR) is a seafloor mountain system. It typically has a depth of about 2,600 meters and rises about 2,000 meters above the deepest portion of an ocean basin. This feature is where seafloor spreading takes place along a divergent plate boundary.
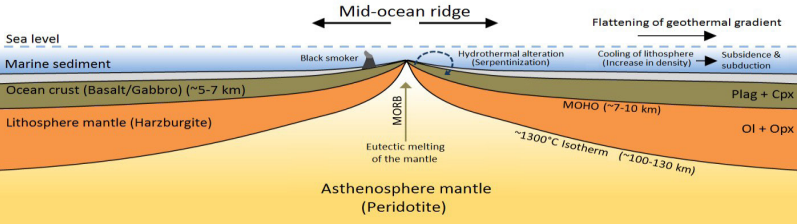
- Mountains are important second-order relief features on the surface of the earth. They hold special significance in understanding the complex geology of the earth’s crust and thus are important in the field of economic geology as they indicate the type of resources found in a region.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here

