Million plus cities, cities with a population of one million or more, are urban areas characterized by a high concentration of people, infrastructure, and economic activities.
These are often hubs of economic, social, and cultural activities, attracting a large population due to employment opportunities, educational institutions, and various amenities.
The problems faced by million-plus cities can be attributed to several factors:
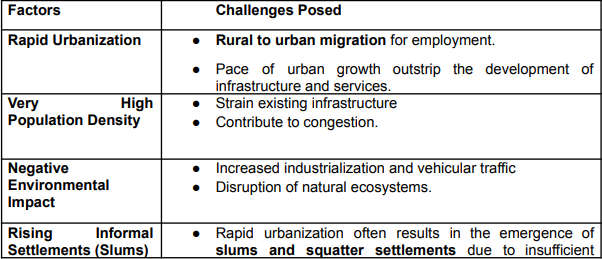


Problems faced by million-plus cities can be summarized as follows:
- Problems due to very high Population Density:
- Congestion, strain on infrastructure, and other essential resources like drinking water, electricity, etc.
- For example, Mumbai, with over 20 million people in an area of around 600 square kilometers, faces challenges of congestion, housing shortages (leading to very high real estate prices), and pressure on infrastructure.
- Problems due to Limited Infrastructure:
- For example, Bangladesh experienced rapid population growth, facing issues with traffic congestion, inadequate public transport, and a lack of proper waste management.

- Problems due to negative Environmental Impact:
- Rapid industrialization and increased vehicular traffic negatively impact the environment.
- For example, Beijing, China, often records high levels of particulate matter, impacting air quality and public health.
- Problems due to Slums:
- Lack of proper infrastructure, sanitation facilities, and access to clean water also pose administrative challenges.
- People often have a low quality of life and face challenges of inequality.
- For example, Kibera in Nairobi, Kenya, is one of the largest slums in Africa, lacking proper infrastructure, sanitation facilities, and access to clean water, highlighting the challenges associated with informal settlements in million-plus cities.
- Problems due to Resource Scarcity:
- High population pressure causes challenges of overconsumption of urban resources well beyond the carrying capacity of the urban ecosystem.
- For example, São Paulo, Brazil, faced a severe water crisis in 2014-2015, with reservoirs reaching critically low levels.
These issues and challenges can be managed by adopting a multipronged approach incorporating these factors:
- Spatial Planning: Land-use zoning and urban planning can help manage overcrowding by strategically allocating space for residential, commercial, and industrial purposes. This promotes balanced development and reduces the strain on infrastructure.
- Environmental Impact Assessment: Conducting environmental impact assessments of urbanization and industrial activities can better inform policies and regulations in mitigating air and water pollution, emission controls, management of green spaces, and water conservation strategies.
- Establishing counter magnets: Developing tier 2 and tier 3 cities in terms of infrastructure and employment opportunities will help in the diffusion of urbanization away from the million-plus cities.
- Establishing functional transportation routes: Connecting urban areas with nearby semi-urban landscapes via fast and congestion-free transportation arteries will help in the diffusion of people away from prime urban spaces.
- Better Transportation Planning: Implementing measures such as public transportation improvements, road infrastructure upgrades, and promoting non-motorized modes of transport can help alleviate congestion and reduce air pollution.
Adopting sustainable urbanization techniques like AMRUT, SMART city programs, Aspirational district programs, and developing satellite towns with functional transportation arteries (like RRTS) are progressive steps taken by the Indian government to fulfill SDG 11 (Sustainable Cities) in India.
Contents
To get free counseling/support on UPSC preparation from expert mentors please call 9773890604
- Join our Main Telegram Channel and access PYQs, Current Affairs and UPSC Guidance for free – Edukemy for IAS
- Learn Economy for free- Economy for UPSC
- Mains Answer Writing Practice-Mains Answer Writing
- For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here

