Explore the current demographic landscape of India, focusing on age structure and workforce availability. Analyze population trends, highlighting the proportion of working-age individuals relative to dependents and elderly. Understand the implications of India’s demographic dividend, with a large youthful population driving economic growth and development opportunities. Delve into challenges posed by an aging workforce and dependency ratios, affecting labor supply, healthcare, and social security systems. Examine regional disparities in workforce distribution and skill levels, shaping employment patterns and human capital development initiatives. Gain insights into policy implications for harnessing demographic advantages, ensuring inclusive growth, and addressing socio-economic disparities in India’s evolving demographic scenario.
Contents
Answer:
Introduction:
Currently, India has a diverse age structure, with a significant portion of its population in the working-age group.
Body:
Present Status of Age Structure:
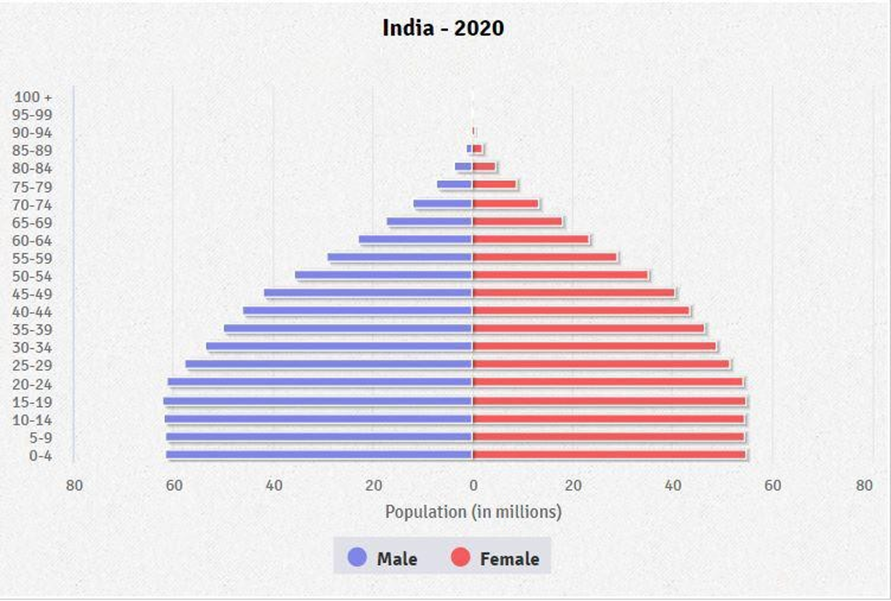
- High Proportion of Working Age Adults: As of 2022, approximately 67.8% of the population falls under the 15-64 age group, considered the prime working age . This translates to a large workforce potential.
- Declining Child Population: The share of children below 14 years has been steadily decreasing. From a peak of 42% in 1971, it reached 25.3% in 2022 . This trend is likely to continue.
- Growing Elderly Population: While still a small segment, the population above 65 years is gradually increasing. In 2022, it stood at 6.9%, and this number is expected to rise in the coming decades
- Urban Migration: Rapid urbanization has led to a shift in age demographics, with more young people migrating to urban areas in search of better opportunities.
- Regional Variations: Age distribution varies across regions, with southern states having lower birth rates and higher life expectancy compared to northern states.
- Gender Disparities: There are gender disparities in age distribution, with certain regions and communities experiencing skewed sex ratios, which can impact the age structure.
Present Status of Workforce:

- Growing Workforce: India boasts a large and growing workforce, with over 60% of the population actively engaged in the labor force.
- Youthful Workforce: The workforce is predominantly youthful, with a significant portion below the age of 35, which presents both opportunities and challenges for economic growth.
- Informal Sector Dominance: A substantial portion of the workforce is engaged in the informal sector, lacking job security, social protection, and access to formal employment benefits.
- Skill Mismatch: Despite the large workforce, there’s a significant skill mismatch, with many individuals lacking the necessary skills required for modern industries.
- Rural-Urban Divide: There’s a notable rural-urban divide in the workforce, with urban areas offering more opportunities for formal employment and higher wages compared to rural areas.
- Gender Disparities: Gender disparities persist in the workforce, with women being underrepresented, particularly in formal employment sectors, due to socio-cultural factors and lack of opportunities.
Conclusion:
To address the present age structure and workforce dynamics, India needs comprehensive policies that promote inclusive growth, invest in education and skill development, address gender disparities, and encourage innovation and entrepreneurship. Focusing on these areas will not only harness the demographic dividend but also ensure sustainable and equitable development in the future.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here