Fiscal prudence and strategic investments are crucial for a country’s economic health and growth. Fiscal prudence means managing the government’s money wisely, ensuring spending doesn’t exceed income, and keeping debt under control. Strategic investments involve putting money into projects that promise long-term benefits, such as infrastructure, education, and technology. Together, these practices help create a stable economy, reduce financial risks, and promote sustainable development. By balancing careful financial management with thoughtful investments, a country can build a strong foundation for future prosperity and resilience.

Tags: GS- 3, Economy- Government Policies & Interventions– Planning– Employment– Inclusive Growth
For Prelims: Union Budget, fiscal consolidation,Public debt/ Gross Domestic Product(GDP)), customs duties Mudra loan,agri-tech innovations.
For Mains: Significance of Fiscal Prudence and Government Policies & Interventions for Indian Economy.
Contents
- 1 Context:
- 1.1 What are the Key Highlights of the Budget 2024 for the Indian Economy?
- 1.2 What is Fiscal Prudence?
- 1.3 Significance of Fiscal Prudence in Budget 2024:
- 1.4 Government Strategies for Fiscal Prudence and Economic Growth in Budget 2024
- 1.5 Current Economic Challenges in the Indian Economy
- 1.6 Reforms Needed to Revamp the Indian Economy
- 2 UPSC Civil Services, Previous Year Questions (PYQ)
- 3 FAQs
- 4 To get free counseling/support on UPSC preparation from expert mentors please call 9773890604
Context:
- In the face of global economic uncertainty and domestic fiscal issues, the 2024 budget showcases fiscal prudence and strategic vision, targeting economic stabilisation for India.
- It aims for a fiscal deficit of 4.9% of GDP, lower than expected, while adopting cautious revenue forecasts despite economic growth.
- With public debt rising relative to GDP, careful fiscal management is essential, constraining expansive policies.
- As public sector investment hits limits, the private sector must drive growth, supported by strong corporate balance sheets but needing clearer demand signals.

What are the Key Highlights of the Budget 2024 for the Indian Economy?
- Inflation Management: Inflation in India remains low and stable, trending towards the 4% target, reflecting overall macroeconomic stability.
- Export Competitiveness: The budget reduces customs duties across various sectors to boost export competitiveness. This aligns with trade theory, as lowering import tariffs can effectively act as a strategy to promote exports.
- Agriculture and Rural Development: The budget introduces 109 high-yielding and climate-resilient crop varieties, alongside a ₹1.52 lakh crore allocation for agriculture and allied sectors this year.
- Employment and Skilling: A package from the Prime Minister, comprising 5 schemes with a ₹2 lakh crore outlay, aims to facilitate employment, skill development, and opportunities for 4.1 crore youth over the next 5 years.
- Human Resource Development: The budget emphasises investment in education, skill development, and healthcare to strengthen the workforce.
- Urban Development Initiatives: The launch of PM Awas Yojana Urban 2.0 with a ₹10 lakh crore investment is intended to meet the housing needs of both urban poor and middle-class families.
- Ensuring Energy Security: New policies focus on energy conservation, renewable sources, and sustainable energy practices.
- Women Empowerment: More than ₹3 lakh crore is allocated for schemes specifically benefiting women and girls.

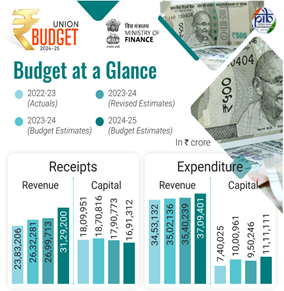
What is Fiscal Prudence?
Fiscal prudence is the disciplined management of government finances, emphasising the need for responsible fiscal policies and practices. It involves:
- Controlled Public Spending: Ensuring that government expenditures are within sustainable limits and prioritising spending to achieve economic objectives.
- Revenue Generation: Implementing effective strategies to increase government revenues while ensuring tax policies are fair and efficient.
- Borrowing and Debt Management: Managing public debt carefully to avoid excessive borrowing and ensure that debt levels remain sustainable.
- Macroeconomic Stability: Adopting policies that support overall economic stability and growth, including maintaining balanced budgets and avoiding excessive deficits.
Significance of Fiscal Prudence in Budget 2024:
- Macro-Level Impact:
- Debt Sustainability: The fiscal deficit target of 4.9% of GDP for FY 2023-24 aims to improve debt sustainability through measures like refinancing and extending maturities.
- Investor Confidence: Prudent fiscal policies enhance investor confidence by demonstrating a commitment to financial stability and growth.
- Credit Rating: A lower deficit and disciplined fiscal approach could improve credit ratings, reducing borrowing costs for the government and private sector.
- Economic Stability:
- Inflation Control: Managing deficits helps control inflationary pressures and stabilises prices.
- Stimulus Effectiveness: Prudent fiscal policies ensure that stimulus measures are effective and prevent long-term imbalances.
- Balanced Budgets: Balancing revenues and expenditures over economic cycles involves running deficits during downturns and surpluses during expansions.
- Transparency and Accountability: Ensuring transparency and regular audits builds trust and ensures efficient use of public funds.
Government Strategies for Fiscal Prudence and Economic Growth in Budget 2024
- Revenue Assumptions and Expenditure Management:
- Revenue Projections: A tax revenue growth of 10.8% against a GDP growth rate of 10.5% ensures realistic targets.
- Quality of Spending: Increasing capital expenditure to enhance productivity and stimulate key infrastructure sectors.
- Structural Reforms and Sectoral Focus:
- Sectoral Investments: Strategic investments in infrastructure, healthcare, education, and technology to boost growth.
- Export Promotion: Lowering customs duties to enhance export competitiveness.
- Financial Prudence and Market Stability:
- Financial Sector Reforms: Strengthening regulatory frameworks and enhancing transparency.
- Market-Oriented Policies: Rationalizing tariffs and improving ease of business to encourage private investment.
- Long-Term Economic Strategy:
- Competitiveness and Equity: Reforms in land, labour, and capital markets to boost competitiveness and reduce regional disparities.
- Land Reforms: Includes land acquisition laws, titling, registration, and leasing laws.
- Labour Reforms: Codification of labour laws and improvements in social security nets.
- Capital Reforms: Financial sector reforms, tax reforms, and easing the investment climate.
Current Economic Challenges in the Indian Economy
- Global Economic Uncertainty:
- Trade Impact: Global trade tensions, such as the US-China trade conflict and the Russia-Ukraine war, disrupt global supply chains and affect India’s export-driven sectors.
- Investment Flows: Foreign direct investment (FDI) inflows are influenced by global economic conditions, with uncertainties causing volatility in FDI, impacting sectors reliant on foreign capital.
- Commodity Prices: Fluctuations in global commodity prices, especially for crude oil and metals, affect India’s import bills and inflation, impacting domestic consumption and stability.
- Domestic Growth Slowdown:
- Structural Bottlenecks: Infrastructure constraints, bureaucratic inefficiencies, and regulatory complexities hinder growth, with delays in project implementation affecting manufacturing and export competitiveness. Agriculture remains vulnerable due to weather and infrastructure issues.
- Unemployment and Employment Quality: Youth unemployment is high, with a significant proportion of educated youth jobless due to skill mismatches. The informal sector dominates, leaving workers without job security and benefits.
- Fiscal Constraints:
- Fiscal Deficit: The projected fiscal deficit for FY 2023-24 is 6.8% of GDP, reflecting expenditure management challenges amidst revenue constraints.
- Public Debt Levels: Increased public debt-to-GDP ratio (81% in 2022) limits fiscal space for investments and social spending, posing risks to stability.
- Revenue Mobilisation: Enhancing tax collections and broadening the tax base are crucial to reduce deficits and support development priorities.
Reforms Needed to Revamp the Indian Economy
- Diversification of Trade Partnerships and Hedging Strategies:
- Expand Export Horizons: Target diverse markets such as Africa and Southeast Asia and strengthen ties with Brazil and Vietnam.
- Attract Long-Term FDI: Focus on sectors like renewable energy and digital infrastructure with stable policies.
- Commodity Price Stabilisation: Use strategic reserves and forward contracts to manage price fluctuations and secure energy needs.
- Fiscal Reforms and Fiscal Discipline:
- Maintain Fiscal Discipline: Target a fiscal deficit of 4.9% of GDP to ensure sustainable finances.
- Enhance Tax Compliance: Broaden the tax base through digital taxation and GST reforms to boost revenue.
- Infrastructure Development:
- Increase Investments: Allocate funds for transport, energy, and digital infrastructure, with significant investments under PM GatiShakti.
- Focus on Urban Development: Improve smart cities, urban mobility, and affordable housing to support rapid urbanisation.
- Manufacturing and Industrial Growth:
- Strengthen Manufacturing: Implement production-linked incentives (PLI) and make-in-India initiatives across key sectors.
- Ease of Doing Business: Simplify regulations and support MSMEs to foster entrepreneurship and job creation.
- Agricultural Reforms and Rural Development:
- Implement Market Reforms: Enhance agricultural infrastructure and expand irrigation with initiatives like PM-KISAN and the Agriculture Infrastructure Fund (AIF).
- Develop Rural Areas: Improve rural roads, electrification, and connectivity under PM Gram Sadak Yojana (PMGSY) to boost rural economies.
- Implement Market Reforms: Enhance agricultural infrastructure and expand irrigation with initiatives like PM-KISAN and the Agriculture Infrastructure Fund (AIF).
- Employment-Linked Incentives:
- Implement Employment Schemes: Announced schemes in Budget 2024,allocate Rs 2 lakh crore for job creation over the next five years.
- Scheme A: Provides a Direct Benefit Transfer of up to ₹15,000 in three instalments for first-time employees registered with EPFO.
- Scheme B: Offers job creation incentives for the manufacturing sector, benefiting both employees and employers based on their EPFO registrations.
- Scheme C: Supports employers by reimbursing up to ₹3,000 per month for two years for EPFO contributions for each additional employee hired.
UPSC Civil Services, Previous Year Questions (PYQ)
Prelims
Q1. In the context of governance, consider the following: (2010)
- Encouraging Foreign Direct Investment inflows
- Privatisation of higher educational Institutions
- Down-sizing of bureaucracy
- Selling/offloading the shares of Public Sector Undertakings
Which of the above can be used as measures to control the fiscal deficit in India?
- 1, 2 and 3
- 2, 3 and 4
- 1, 2 and 4
- 3 and 4 only
Ans: D
Mains
Q. Distinguish between Capital Budget and Revenue Budget. Explain the components of both these Budgets. (2021)
Q. Do you agree with the view that steady GDP growth and low inflation have left the Indian economy in good shape? Give reasons in support of your arguments. (2019)
Source: FE
FAQs
Q: What is fiscal prudence?
- Answer: Fiscal prudence means managing government finances responsibly. It involves controlling spending, reducing debt, and making sure that public money is used efficiently to benefit the economy and society.
Q: What are strategic investments?
- Answer: Strategic investments are planned and deliberate investments made by the government or businesses in key areas that can drive long-term growth and development. These include infrastructure, education, healthcare, and technology.
Q: Why is fiscal prudence important?
- Answer: Fiscal prudence is important because it ensures that a country does not spend more than it earns, which helps maintain economic stability. It prevents excessive debt, reduces the risk of financial crises, and ensures that resources are available for essential services.
Q: How do strategic investments benefit the economy?
- Answer: Strategic investments benefit the economy by promoting growth, creating jobs, and improving productivity. For example, investing in infrastructure like roads and bridges can enhance trade, while investing in education can produce a more skilled workforce.
Q: How can a government balance fiscal prudence with strategic investments?
- Answer: A government can balance fiscal prudence with strategic investments by carefully prioritizing spending, focusing on high-impact areas, and ensuring transparency and efficiency in the use of funds. This approach ensures that while the government manages its finances responsibly, it also invests in areas that will bring long-term benefits to the economy and society.
To get free counseling/support on UPSC preparation from expert mentors please call 9773890604
- Join our Main Telegram Channel and access PYQs, Current Affairs and UPSC Guidance for free – Edukemy for IAS
- Learn Economy for free- Economy for UPSC
- Mains Answer Writing Practice-Mains Answer Writing
- For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here

