
In an increasingly interconnected world, the need for South-South learning has never been more evident. This global era calls for a paradigm shift in how nations, particularly those in the Global South, engage with one another. As we navigate the complex challenges of the 21st century, it is imperative to recognize that solutions often lie not only in traditional North-South cooperation but also in the exchange of knowledge and experiences among countries facing similar socio-economic and developmental contexts. South-South learning offers a unique opportunity for nations to share successful strategies, innovative approaches, and best practices, ultimately fostering a sense of collective empowerment and self-reliance. This collaborative approach can lead to the emergence of creative solutions tailored to the unique circumstances of countries in the Global South, thus paving the way for sustainable development and resilience in an ever-changing global landscape.
Tag: GS-2 Important International institutions, Bilateral, Regional and Global groupings
Exam View: Achievements of India as G20 president; Challenges in front of G21; Global South steer the world towards food and nutritional security amidst climate change
Contents
- 1 Context:
- 2 Achievements of India as G20 president:
- 3 Challenges in front of G21:
- 4 How can the Global South steer the world towards food and nutritional security amidst climate change?
- 5 Invest in women’s education and empowerment:
- 6 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 6.1 1. What is South-South Learning, and how does it differ from traditional North-South cooperation?
- 6.2 2. Why is South-South Learning important in today’s global context?
- 6.3 3. How can South-South Learning benefit countries in the Global South?
- 6.4 4. What are some examples of successful South-South Learning initiatives?
- 6.5 5. How can countries promote and facilitate South-South Learning?
- 7 In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
Context:
India’s G20 presidency has been lauded for creating a global consensus amidst the growing global divergence and collectively bringing out the G20 New Delhi Leaders’ Declaration.
Achievements of India as G20 president:
- Reshaping the global mindset: India’s G20 presidency will be remembered as a catalyst in reshaping the mindset of developed nations and integrating the aspirations of Africa, into the mainstream.
- Inclusion of the African Union in the G20, now known as the G21: India’s masterstroke with inclusion of the African Union in G20, acknowledges the significance and potential of Africa as a vital partner in global development and stability. The new G21 will now comprise 84% of the world’s population.
- Fostering South-South learning and collaboration: India has proposed initiating a comparative analysis cross-learnings and innovative solutions to address the challenges faced by both regions.
- Raising awareness of the challenges faced by developing countries: India has used its G20 presidency to highlight the issues of food and nutritional security, climate change, and poverty.
- Sharing India’s best practices: India has shared its experiences in areas such as sanitation, bio-fortification and digital public infrastructure with other countries.
Challenges in front of G21:
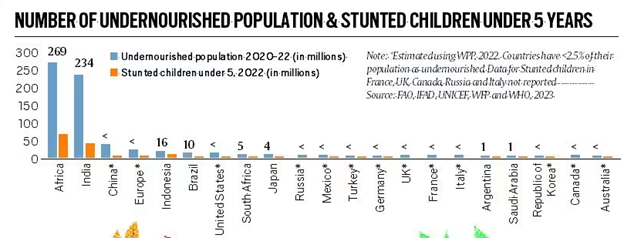
- Population growth, persistent poverty, and widespread undernourishment amidst climate change:
- High concentration of undernourished population: India and Africa, constituting 36% of the global population and are home to 69.4% (503 million) of the world’s undernourished people in 2020-22.
- Child Malnutrition: India and Africa together account for 67% and 75.8% of the world’s children under five afflicted with the malnutrition problems of stunting and wasting.
- Ensuring that Africa has a meaningful voice in the G21 and that its priorities are reflected in the group’s agenda.
- Building the capacity of African countries to implement the G21’s decisions and recommendations: This includes providing financial and technical assistance, as well as helping African countries to develop their own national and regional development plans.
- Consensus building: G21 can become too large and unwieldy, and that adding more members has made it more difficult to reach consensus on important issues.
How can the Global South steer the world towards food and nutritional security amidst climate change?
- International Agricultural Trade: International borders need to stay open for agricultural trade. India exported 85 million tonnes of cereals to the world, contributing to global food security.
- Climate financing:
- Developed countries: Developed countries must commit to providing $100 billion for the loss and damage caused by climate change. This commitment will pave the way for large-scale climate mitigation and adaptation efforts in developing economies.
- Role of World Bank: It could play a catalytic role in mobilising funds even from the private sector to address the global challenges of poverty reduction, ensuring food and nutritional security and combating climate change through adaptation and mitigation policies
- Private capital investments are essential to complement the current sources of financing. This could unlock more than $6-7 billion in lending for poorer nations to fight climate change.
- Promote South-South cooperation for nutritional security: India and Africa could foster learning and collaboration in the pursuit of sustainable agriculture and food systems.
- Nutrition-sensitive agriculture: Scaling up bio-fortification of staple crops, an innovative and cost effective technique, can ensure availability of nutritious diets in areas affected by chronic malnutrition.
- New varieties of nutrient-rich staple food crops like iron and zinc biofortified pearl millet, zinc-bio fortified rice and wheat, and iron biofortified beans have been developed.
Invest in women’s education and empowerment:
- Reduction in under nutrition: Empirical analysis at ICRIER using NFHS (2019-21) data highlights that mothers’ education and BMI index have a strong association with reducing undernutrition among children.
- Increase in the female labour force participation and fostering long-term economic growth could be ensured through investment in women’s education.
- Investments in WASH(Water, Sanitation and Hygiene) initiatives: This could bring a multiplier effect on nutritional outcomes. Swachh Bharat Abhiyan, which aims to eliminate open defecation and eradicate manual scavenging has multiplier effects in terms of nutrition and poverty reduction.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is South-South Learning, and how does it differ from traditional North-South cooperation?
A: South-South Learning involves the exchange of knowledge, experiences, and best practices among countries in the Global South, which face similar socio-economic and developmental challenges. Unlike traditional North-South cooperation, it focuses on collaboration among countries with similar contexts, promoting self-reliance and tailored solutions.
2. Why is South-South Learning important in today’s global context?
A: South-South Learning is essential because it recognizes the shared challenges and opportunities faced by countries in the Global South. It empowers nations to leverage their collective knowledge and experiences, fostering innovative and context-specific solutions for sustainable development in a rapidly changing world.
3. How can South-South Learning benefit countries in the Global South?
A: South-South Learning allows countries to learn from one another’s successes and failures. It can accelerate development, promote self-sufficiency, and reduce dependency on external aid. Additionally, it can lead to cost-effective and culturally relevant solutions, driving progress in critical sectors.
4. What are some examples of successful South-South Learning initiatives?
A: Examples include India’s experience in eradicating polio, which was shared with other countries in the Global South to combat the disease effectively. Similarly, Bhutan’s Gross National Happiness Index has inspired discussions on holistic well-being and development in other nations.
5. How can countries promote and facilitate South-South Learning?
A: Countries can encourage South-South Learning by establishing platforms for dialogue and knowledge exchange, facilitating partnerships, and providing resources for collaborative projects. Regional organizations and international agencies can also play a vital role in supporting and funding initiatives that promote this approach to development and cooperation.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here

