The southwest monsoon system in India is a critical climatic phenomenon that significantly influences the country’s agricultural, economic, and social landscape. However, the unpredictability of this monsoon remains a formidable challenge for both policymakers and stakeholders. Various factors contribute to the complexity and variability of the southwest monsoon, making it a subject of extensive examination. In this context, a critical analysis of the factors affecting the unpredictability of the southwest monsoon system becomes imperative for understanding and addressing the challenges posed by its erratic behavior. This examination encompasses a multifaceted exploration of meteorological, geographical, and atmospheric elements that play pivotal roles in shaping the dynamics of the monsoon in the South-West region of India.
Contents
Answer
A study by the Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology found that the frequency of extreme rainfall events over India has increased by 20% since the 1950s, SWM in India is affected by many factors thus the unpredictability factor is very high.
- Several natural and climate change-induced anthropogenic factors affect the unpredictability of the SWM,
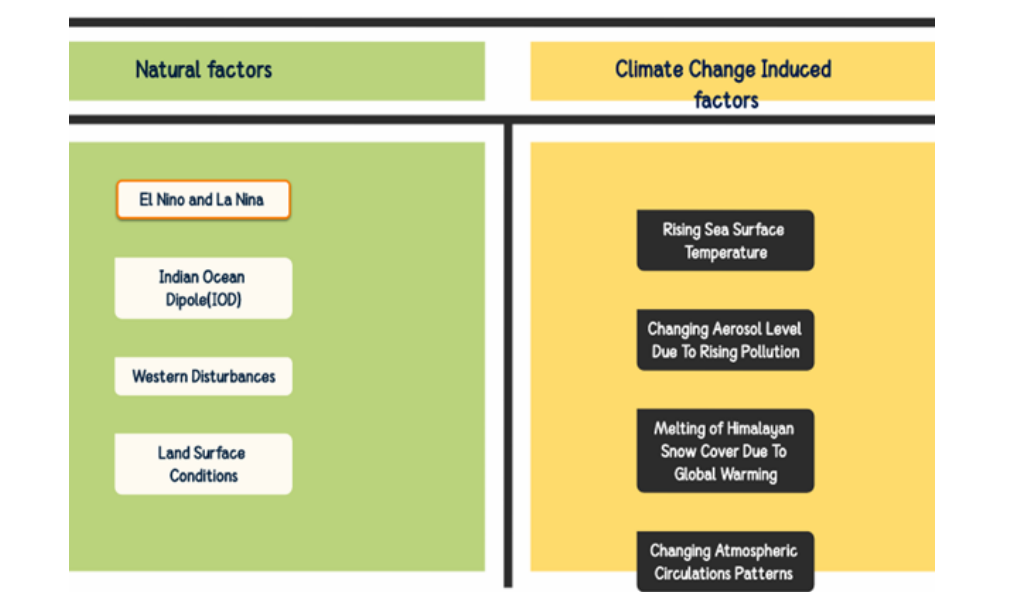
Natural Factors
- El Niño-La Nina
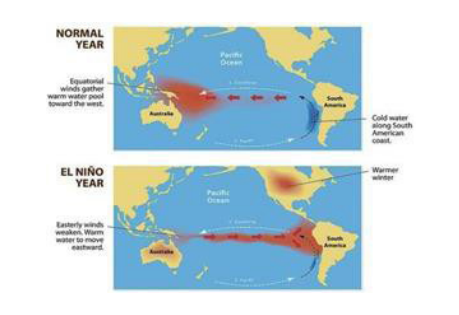
- A climate pattern that involves changes in the temperature of the tropical Pacific Ocean.
- El Niño years are associated with weaker SWM rainfall eg. During the 1997 El Niño event, India experienced a severe drought.
- La Niña years are associated with stronger SWM rainfall, rainfall over India is typically increased by 10-20% eg. During the 2007 La Niña event, India experienced widespread flooding.
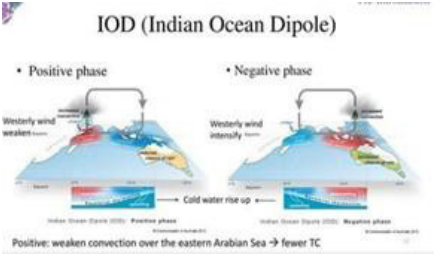
Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD)
A climate pattern that involves changes in the sea surface temperature of the Indian Ocean.
- Positive IOD events are associated with weaker SWM rainfall
- Negative IOD events are associated with stronger SWM rainfall
Western disturbances
- Western disturbances are extra-tropical cyclones that originate from the Mediterranean Sea and move towards India
- Bring winter rainfall to northern India, but they can also weaken the SWM
Land-surface conditions
- Such as soil moisture and snow cover can also influence the SWM
- For example, less snowfall at the Tibetan plateau can suppress the formation of a strong pressure gradient for effective wind circulation thus weakening the SWM.
Climate Change-Induced Anthropogenic Factors
Rising Sea Surface Temperature
- Warmer ocean temperatures can lead to more evaporation-more water vapor in the atmosphere and more intense rainfall events. However, it can also cause more prolonged dry spells, as the water vapor may not be evenly distributed throughout the region.
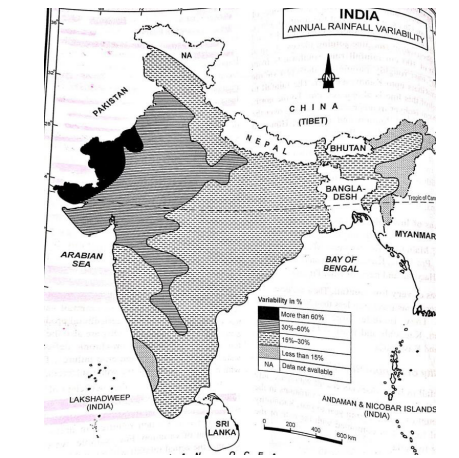
- Warmer SSTs can disrupt the atmospheric circulation patterns that drive the monsoon, and changes in the onset, duration, and intensity of the monsoon. For example- a warmer Arabian Sea can weaken the monsoon winds, leading to a delayed onset and reduced rainfall.
- Warmer SSTs can increase the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events, such as cyclones and floods. This can further disrupt the monsoon and make it more difficult to predict. Example-Cyclone Biparjoy made landfall in Gujarat on June 12, 2023, and brought heavy rainfall to the state and surrounding areas including semi-arid regions of Rajasthan.

Changing Aerosol Level Due to Rising Pollution
- Aerosols are tiny particles suspended in the atmosphere
- Can reduce the amount of solar radiation that reaches the Earth, which can weaken the SWM.
Melting of Himalayan Snow Cover Due to Rising Temperatures
- The snow cover reflects sunlight into space, which helps to cool the atmosphere and drive the monsoon winds.
- The Himalayan snow cover plays an important role in regulating the monsoon, When the snow cover melts, it absorbs sunlight and heats the atmosphere, changing the atmospheric circulation patterns that drive the monsoon.
- A study published in the journal Nature Climate Change found that the melting of the Himalayan snow cover is delaying the onset of the monsoon by an average of 5 days per decade.
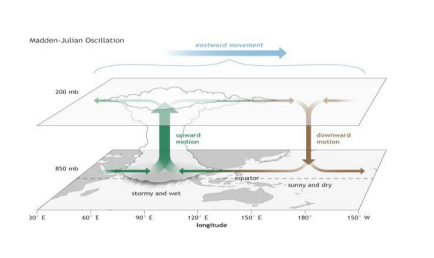
Changing Atmospheric Circulation Patterns
- Such as The Madden-Julian Oscillation (MJO) and the Tropical Easterly Jet (TEJ), can modulate the intensity and duration of the SWM
- Climate change is causing more frequent and unpredictable western disturbances in India by warming the Arctic faster than the rest of the planet, which is making the jet stream wavier and more unpredictable Western disturbances in June-July over India
- Global warming is causing more frequent and intense El Niño and La Niña events by warming the tropical Pacific Ocean, which provides more energy for the ENSO system. Eg El Nino 2023 SWM is a highly localized phenomenon that varies across India, making it difficult to forecast accurately for the entire country. Monsoon Mission, Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology (IITM) studies,
- The National Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasting (NCMRWF) provides some institutional and policy frameworks to predict monsoons better.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here