Inter-state border disputes in India represent a complex web of historical, political, and socio-cultural issues that have persisted since the country’s independence in 1947. These disputes, often characterized by conflicting territorial claims between neighboring states, have been a source of tension, political friction, and even violence. From the northern regions of Jammu and Kashmir to the southern states of Karnataka and Tamil Nadu, these conflicts have manifested in various forms, ranging from legal battles to occasional outbreaks of violence. The intricate nature of India’s federal structure, compounded by diverse linguistic, cultural, and historical factors, further complicates the resolution of these disputes. This essay aims to critically examine the underlying problems fueling inter-State border disputes in India, shedding light on the historical context, political dynamics, legal complexities, and socio-economic ramifications that continue to impede their resolution.
Contents
Answer
Introduction:
Inter-state border disputes in India refer to conflicts between different states regarding territorial boundaries. These disputes often arise due to historical, cultural, economic, or administrative reasons.
Body
Causes of Inter-State Border Disputes:
- Historical Legacy: Many disputes trace back to the historical demarcation of regions, leading to disagreements between states.
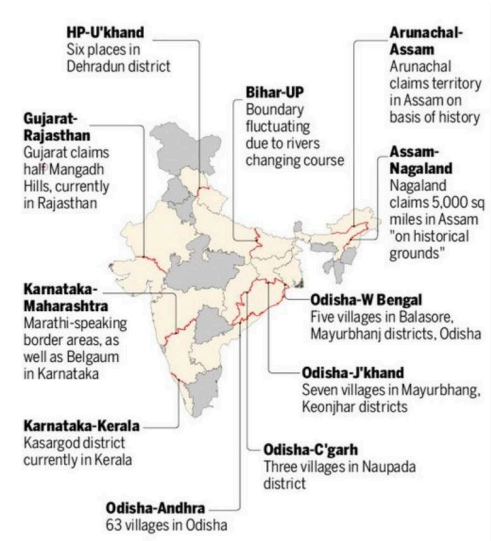
Example: Karnataka and Tamil Nadu over the Cauvery River water-sharing. - Resource Allocation: Competition for scarce resources like water or minerals can spark conflicts.
Example: Punjab and Haryana over water-sharing from the Bhakra-Nangal dam. - Cultural and Ethnic Differences: Divergent cultural identities may contribute to disputes.
as seen in the case of Assam and Nagaland. - Political Boundaries: Changes in political boundaries over time can lead to disagreements.
Example: Maharashtra and Karnataka over Belgaum. - Administrative Decisions: Administrative decisions regarding district reorganization may create tensions.
Example: Telangana and Andhra Pradesh after the bifurcation. - Population Migration: Migration patterns can alter demographic realities, leading to disputes.
Example: The Meghalaya-Assam border dispute involving demographic shifts. - Inadequate Legal Framework: Lack of clear legal frameworks for border delineation can lead to disputes.
Example: Border issues between Uttar Pradesh and Uttarakhand.
Results of Inter-State Border Disputes:
- Economic Disruption: Disputes can hinder economic development and cross-border trade, impacting the overall prosperity of the regions involved.
- Social Unrest: Border disputes often create social tensions and animosities among the affected communities, affecting the social fabric.
- Administrative Challenges: Governance becomes complicated, with overlapping jurisdictions causing administrative hurdles.
- Security Concerns: Unsettled borders can pose security challenges, leading to the deployment of security forces in sensitive areas.
- Deterioration of Relations: Prolonged disputes strain inter-state relations, hindering cooperation on various fronts.
- Environmental Impact: Disputes over natural resources may result in environmental degradation due to unsustainable resource exploitation.
- Legal Implications: Prolonged disputes may lead to legal battles, consuming resources and time in litigation.
Conclusion:
To address inter-state border disputes, a futuristic approach involves establishing clear legal frameworks, promoting dialogue, and encouraging states to collaborate on resource management. Additionally, involving neutral mediators and adopting a
cooperative federalism model can contribute to lasting solutions, fostering harmony and development among states in India.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here