


Contents
- 1 The barrier to Women’s Labor Force Participation
- 2 Self-Reliant India Fund for MSMEs
- 3 The Multi-State Cooperative Societies (Amendment) Bill 2023
- 4 Post-quantum Cryptography
- 5 Heat Waves
- 6 About the measures taken by IMD to tackle heat waves:
- 7 Akhil Bharatiya Shiksha Samagam and ULLAS Initiative
- 8 SAGE PORTAL
- 9 MSME CARD
- 10 Mahila Samman Savings Certificate Scheme (MSSC)
- 11 Justice Rohini Commission
- 12 Hepatitis
- 13 RBI’s Digital Payments Index
- 14 Scrub Typhus
- 15 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 15.1 Q: What are daily current affairs?
- 15.2 Q: Why is it important to stay updated with daily current affairs?
- 15.3 Q: Where can I access daily current affairs information?
- 15.4 Q: How can I effectively incorporate daily current affairs into my routine?
- 15.5 Q: What are some tips for critical analysis of daily current affairs?
The barrier to Women’s Labor Force Participation
Tag: GS-3 Economy
In News:
Recently, the Tamil Nadu government launched camps to facilitate the registration of applicants for the Kalaignar Magalir Urimai Thogai Thittam, or women’s basic income scheme.
About
The scheme Aimed to “recognize women’s unpaid labor”, The scheme will provide ₹1,000 per month to women in eligible households. In Marriages, the wife bears and rears children and minds the home, and therefore bears the brunt of unpaid care and domestic work, hindering their Participation in the Labour Force.
Factors contributing to lower women’s participation in the labor force:
- Patriarchal Social Norms: Deep-rooted societal norms and traditional gender roles often restrict women’s access to education and employment opportunities. Cultural expectations may prioritize women’s roles as caregivers and homemakers, discouraging their active involvement in the workforce.
- Gender Wage Gap: Women frequently encounter wage disparities compared to men, even when performing similar work. This wage gap can demotivate women from seeking formal employment due to the unfair compensation they may receive.
- As per the World Inequality Report, 2022, women in India just capture 18% of labor income, while men earn 82%.
- Unpaid Care Work: The unequal distribution of unpaid care and domestic responsibilities falls disproportionately on women, leaving them with limited time and energy for paid employment. This imbalance, where women bear the majority of household duties, acts as a significant barrier to their participation in the labor force.
- Social and Cultural Stigma: In certain societies, there may be negative attitudes or societal resistance towards women working outside the home, leading to lower labor force participation rates among women.
Statistics Regarding Unpaid Care of Women
- Female Labour Force Participation Rate: India’s female labor force participation rate (LFPR) has been declining for more than 20 years, despite the share of educated women surging in this period. In the last two decades, female LFPR has fallen from 30% to 24%, despite the Class 10 enrolment rate among girls increasing from over 46% to 87%.
- Labour Force Participation rate in other countries: India’s female LFPR (24%) was the lowest among all these countries. India had the second-highest female population in the group. In contrast, China, which has the highest female population, had the highest female LFPR of 61%.
- Time Spending in domestic work by women is more than men: Women who are not in the labour force spend the highest amount of time on unpaid domestic/care work, averaging 457 minutes or 7.5 hours a day. But employed women were not far behind, spending 348 minutes or 5.8 hours a day. Unemployed men spend 3.5 hours per day on such chores, over two hours less than employed women. Employed men spend 2.7 hours a day on such chores, over three hours less than employed women.
- Married women spend the most amount of time engaged in unpaid work (nearly 8 hours) compared to women who are widowed/divorced/separated (5.7 hours) or have never married (4.3 hours). In contrast, married men spend the least amount of time on unpaid work (2.8 hours) compared to men who are widowed/divorced/separated (4.2 hours) or have never married (3.1 hours).
Self-Reliant India Fund for MSMEs
Tags: GS – 3: Indian Economy (Growth and Development)
Why in News:
Recently, the Government of India announced a Rs 50,000 crore Equity infusion for Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) as a part of the Aatmanirbhar Bharat package through the Fund of Funds.
Self-Reliant India (SRI) Fund:
- The SRI Fund operates through a mother-fund and daughter-fund structure for equity or quasi-equity investments.
- The National Small Industries Corporation (NSIC) Venture Capital Fund Limited (NVCFL) is registered as the Mother Fund under the SRI Fund implementation.
- It has been registered as a Category-II Alternative Investment Fund (AIF) with SEBI.
- The objective of the SRI Fund is to provide equity funding to viable and high-potential MSMEs, fostering their growth and transformation into larger enterprises.
- Rs. 10,000 crores contributed by the Government of India and Rs. 40,000 crores from Private Equity and Venture Capital funds.
Other Initiatives for MSMEs:
- MSME Champions Scheme: This scheme provides financial assistance to MSMEs to enhance their competitiveness and innovation capabilities.
- Infusion in Credit Guarantee Fund: As part of the Budget 2023-24, the government announced an infusion of Rs. 9,000 crores in the corpus of Credit Guarantee Fund Trust for Micro & Small Enterprises.
- Raising and Accelerating MSME Performance (RAMP): This initiative focuses on strengthening institutions and governance of MSME programs at both the central and state levels.
- Amendment in Income Tax Act: The Finance Act 2023 brought about an amendment in Section 43B of the Income Tax Act, 1961, to offer more favorable tax provisions for MSMEs.
The Multi-State Cooperative Societies (Amendment) Bill 2023
Tags: GS – 2: Governance (Government policies and interventions for Development in various sectors)
Why in News:
Recently, the Lok Sabha has passed the Multi-State Cooperative Societies (Amendment) Bill 2023.
Cooperatives in India:
- Co-operatives are voluntary, democratic, and autonomous organizations controlled by their members who actively participate in their policies and decision-making.
- After independence, the first five-year plan (1951-56), emphasized the adoption of co-operatives to cover various aspects of community development.
- According to Article 43B (DPSP) of the Indian Constitution inserted by the 97th Amendment (2011), states shall endeavor to promote voluntary formation, autonomous functioning, democratic control, and professional management of cooperative societies.
Multi-state Co-operative Societies:
- These are societies that have operations in more than one state. For example, a farmer-producers organization (FPO) which procures grains from farmers from multiple states.
- The Multi-State Co-operative Societies Act 2002 provides for the formation and functioning of multi-state co-operatives.
- According to the Supreme Court of India, Part IXB – The Co-operative Societies (also inserted by the 97th Amendment), will only be applicable to multi-state co-operative societies, as states have the jurisdiction to legislate over state co-operative societies.
Key provisions of the Multi-State Cooperative Societies (Amendment) Bill 2023:
- It seeks to amend the Multi-State Co-operative Societies Act 2002.
- Co-operative Election Authority: The central government will establish the Authority to conduct such elections. It will consist of a chairperson, VC, and up to 3 members appointed by the central government on the recommendations of a selection committee.
- Amalgamation of co-operative societies: Allows state co-operative societies to merge into an existing multi-state co-operative society, subject to the respective state laws.
- Co-operative Rehabilitation, Reconstruction, and Development Fund: Multi-state co-operative societies that are in profit for the preceding three financial years shall finance the Fund.
- Any shares held by the central and state governments cannot be redeemed without their prior approval.
- Co-operative Ombudsman: The central government will appoint one or more such Ombudsman with territorial jurisdiction. They shall complete the process of inquiry and adjudication within 3 months from the receipt of the complaint.
Significance of the Bill:
- It will strengthen cooperatives by making them transparent and introducing a system of regular elections.
- The Bill aims to address issues with the operation and governance of cooperative societies as well as match its provisions with those in Part IXB of the Constitution.
- Imposes a cost on well-functioning societies: Sick multi-state co-operative societies will be revived by a Fund that will be financed through contributions by profitable multi-state co-operative societies.
- Against the co-operative principles of autonomy and independence: By restricting the redemption of its shareholding in multi-state co-operative societies.
Post-quantum Cryptography
Tag: GS Paper-3: IT & Computers; Indigenisation of Technology; Achievements of Indians in Science and Technology.
In News:
There has been a lot of worry about quantum computing and its potential impact on computer security. Post-quantum cryptography involves exploring alternative techniques to counter vulnerabilities against quantum attacks.
About quantum computing:
Modern digital computers are all based on the idea of making electricity do certain things using clever circuitry and pretending that logical operations are occurring.
When these circuits or gates are built using lasers, all new kinds of gates can be built in addition to the basic ones.
The principles of quantum mechanics enabled a set of gates that were utterly impossible to build using electronics.
In other words, using quantum states to represent logic (instead of high and low voltages) allows us to compute very differently.
For example, one common classical gate is a “not” gate: this simply outputs the opposite of the input. On a quantum computer, one could have a “square root of not” gate.
This new, different kind of computation is very powerful.
Many things that were complex and cumbersome when run on electronic logic become incredibly simple on a quantum system.
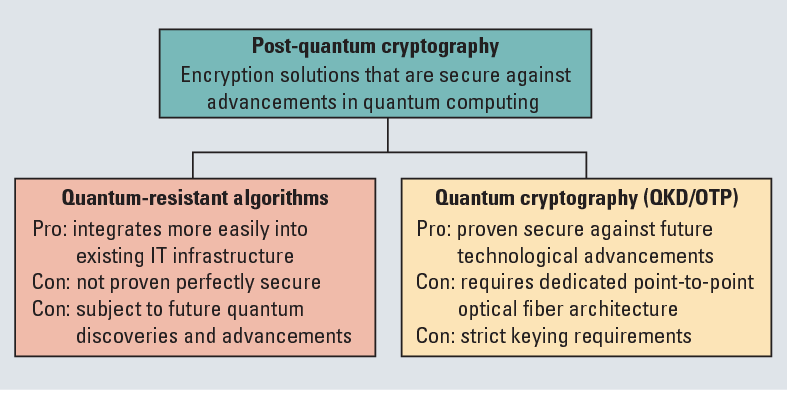
What is the need for post-quantum cryptography?
- Governments and organizations across the world are rushing to develop quantum computing platforms and advanced security algorithms to defend against such machines.
- One prominent example of the latter is the U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology’s Post-Quantum Cryptography Standardisation project.
- India has recently announced collaborations with the U.S. in quantum computing and launched the National Quantum Mission.
- Much of our current security is based on techniques such as RSA, elliptic curves, and Diffie-Hellman key exchange.
- Unfortunately, in 1994, Peter Shor developed a quantum algorithm that (with certain modifications) can break all of these with ease.
- Quantum computing is a fast-changing field. One promising technique, supersingular isogeny Diffie-Hellman key exchange, was considered secure by many until it was utterly broken by Wouter Castryck and Thomas Decru last year.
- We are probably decades away from a quantum computer powerful enough to do anything meaningful or dangerous.
- However, it is important that we quickly and carefully transition to technologies secure against quantum attacks.
Heat Waves
GS Paper-1: Important Geophysical Phenomena;
GS Paper-2: Government policies and interventions;
GS Paper-3: Climate change.
In News:
In recent years deaths due to heat waves have decreased significantly.

About the measures taken by IMD to tackle heat waves:
- IMD issues forecasts and warnings related to severe weather events including heat waves in different spatial and temporal scales and shares the same with the public as well as disaster management authorities so as to initiate required mitigation measures.
- In the country, appreciable rises in maximum temperatures as well as heat waves are found to be more in the months of April, May & June.
- As an initiative, IMD is issuing a Seasonal Outlook for temperatures for the months of April, May & June in the last week of March for planning purposes.
- This outlook brings out the expected scenario of heat waves during the period.
- The seasonal outlook is followed by the Extended Range Outlook issued every Thursday for the next two weeks.
- In addition to this, the forecast and the colour-coded warnings for severe weather including heat wave warnings are issued on a daily basis for the next five days with an outlook for another two days.
- As an adaptive measure, IMD in collaboration with NDMA and local health departments has started heat action plans in many parts of the country to forewarn about the heat waves and also to advise the actions to be taken during such occasions.
- Recently IMD has launched the Heat Index, which provides information about the impact of humidity on high temperatures and thus provides a feel-like temperature for human beings which can be used as an indication for human discomfort.
- It provides guidance towards additional care to be taken by people to reduce discomfort.
- There is no specific fund allocation for the purpose of heat wave-related services.
Akhil Bharatiya Shiksha Samagam and ULLAS Initiative
Tags: GS-III: Education
In News:
Union government launches multiple initiatives on 3rd Anniversary of New Education Policy 2020 at Bharat Mandapam, New Delhi.
Akhil Bharatiya Shiksha Samagam and ULLAS Initiative
- Ministry of Education has recently launched the mobile application of ULLAS: Nav Bharat Saksharta Karyakram at the Akhil Bharatiya Shiksha Samagam 2023.
- Important features:
- ULLAS initiative aims to revolutionize education and literacy in India by creating a learning ecosystem that reaches every individual and bridges the gaps in basic literacy and critical life skills.
- The program imparts basic education, digital and financial literacy, and critical life skills to citizens aged 15 and above who missed the opportunity to attend school.
- The mobile application of ULLAS is user-friendly and interactive, available on both Android and iOS platforms.
- It will serve as a digital gateway for learners to access diverse learning resources through the DIKSHA portal of NCERT.
- It allows learners and volunteers to register through self-registration or by surveyors and aims to create a culture of continuous learning and knowledge-sharing in communities across India.
- The initiative focuses on promoting functional literacy, vocational skills, financial literacy, legal literacy, and digital literacy, and empowering citizens to participate in nation-building.
- The scheme also encourages volunteers to participate in the ULLAS initiative as a duty towards nation-building.
- Student volunteers will receive incentives such as credits in school/university and appreciation through certificates, letters, and felicitation.
- Overall, the launch of ULLAS will help spread knowledge across the nation, empowering citizens with education by using technology and community-driven efforts.
SAGE PORTAL
Tags: GS-II: Government Policies
In News:
Union government deliberates on the outcome of SAGE portal for elderly people
About SAGE Portal:
- SAGE or Senior-care Ageing Growth Engine is an initiative under the Umbrella Scheme of Atal Vayo Abhyuday Yojana (AVYAY), run by the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment.
- It aims to promote innovative ideas for elderly care and encourage youth to focus on addressing the problems faced by the elderly.
- Major highlights:
- SAGE portal acts as a platform for connecting entrepreneurs and start-ups with a focus on the “silver economy,” catering to the needs of senior citizens.
- It facilitates the entry of start-ups into the eldercare sector and promotes business innovation in this domain.
- It provides “one-stop access” to credible start-ups offering various elderly care products and services.
- The scheme identifies, evaluates, verifies, and aggregates products, solutions, and services directly to the stakeholders.
- Selected start-ups or start-up ideas will receive equity support of up to Rs. 1 crore per project through the Industrial Finance Corporation of India (IFCI).
- As per mandates, the government’s equity in any start-up should not exceed 49% to ensure private sector participation.
- Through SAGE, the government acts as a facilitator, enabling elderly citizens to access products and services offered by the identified start-ups.
- Overall, the initiative will go a long way to help harness the potential of entrepreneurship to enhance the quality of life and well-being of senior citizens in India.
MSME CARD
Tags: General Studies –3 Economy
Why in the news?
Recently, the Ministry of Micro Small and Medium Enterprises, (MSME) in association with the National Payment Corporation of India (NPCI) had launched the MSME RuPay Credit Card on a pilot basis, pan-India for Udyam registered MSMEs.
About:
- The MSME RuPay Credit Card provides a simplified payment mechanism for MSMEs to meet their business-related operational expenses like digital payments, utility bills payments, tax/statutory payments, etc.
- MSME borrowers also benefit of an interest-free credit period on their business spending as per the bank’s policy.
National Payment Corporation of India (NPCI)
- NPCI is an umbrella organization for operating retail payments and settlement systems in India.
- It is an initiative of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and the Indian Banks’ Association (IBA) under the provisions of the Payment and Settlement Systems Act, 2007, to create a robust Payment & Settlement Infrastructure in India.
Mahila Samman Savings Certificate Scheme (MSSC)
Tags: General Studies –2 Government Policies & Interventions
Why in the news?
Total deposits under the newly launched Mahila Samman Savings Certificate (MSSC) scheme have jumped over Rs 8600 crore and more than 14 lakh accounts have been opened across states.
About:
- MSSC is the newly launched small savings scheme of the Government to commemorate the Azadi ka Amrit Mahotsav.
- It is exclusively for women and girls in India.
Some of the features of the scheme include:
- MSSC account can be opened by women of any age group including the girl child with a minimum deposit of Rs 1000 and maximum deposit of Rs 2 Lakhs for a period of two years.
- The interest rate for MSSC is 7.5% p.a. which is compounded quarterly.
- The facility of partial withdrawal and premature closure on compassionate grounds are also available under this Scheme.
- The Government of India has authorized the Department of Posts, all Public Sector Banks, and four Private Sector Banks to operate MSSC.
- MSSC has been made available for a two-year period up to March 2025.
Data Points
- The highest number of MSSC scheme accounts has been opened in Maharashtra (2,96,771), followed by Tamil Nadu (2,55,125), Andhra Pradesh (1,21,734) and Karnataka (1,05,134).
- Among all states, the lowest number of MSSC accounts have been opened in Arunachal Pradesh (318), Bihar (7482), Goa (2786), Haryana (9247), Jharkhand (8391), Manipur (39), Meghalaya (530), Mizoram (1172), Nagaland (151), Sikkim (305), Tripura (4358).
Justice Rohini Commission
Tags: General Studies – 2 Polity & Governance
Why in the news?
Recently, A Commission for Other Backward Classes appointed to examine sub-categorization of Other Backward Classes has submitted its report to President Droupadi Murmu. About:
- Rohini Commission was constituted in 2017 under Article 340 of the Constitution with the approval of the President of India.
- Article 340 empowers the President of India to appoint a commission to investigate issues concerning OBCs and make recommendations to improve their situation.
- Prior to constituting the Rohini Commission, the Centre had granted the National Commission for Backward Classes (NCBC) constitutional status by the 102nd Amendment Act, 2018.
Functions of the Rohini Commission
- To study the various entries in the Central List of OBCs and recommend the correction of any repetitions, ambiguities, inconsistencies, and errors of spelling or transcription.
- To examine the extent of inequitable distribution of benefits of reservation among the OBCs.
- To develop the mechanism, criteria, norms, and parameters for sub-categorization within such OBCs using a scientific approach.
- To begin the process of identifying and classifying the respective castes, communities, and sub-castes in the Central List of OBCs.
Hepatitis
Tags: General Studies –2 Health
Why in the news?
World Hepatitis Day has been observed recently.
About:
- The day is an opportunity to step up national and international efforts on hepatitis, encourage individual actions and engagement, and highlight the need for a greater global response.
- 2023 Theme: ‘We’re not waiting’ — a call to people around the world to take action because Hepatitis Can’t Wait.
Hepatitis:
- Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver.
- Problem-causing agents: Heavy alcohol use, toxins, some medications, and certain medical conditions can cause hepatitis.
- However, hepatitis is often caused by a virus.
- There are five main strains of the hepatitis virus, referred to as types A, B, C, D, and E.
- While they all cause liver disease, they differ in important ways including modes of transmission, severity of the illness, geographical distribution, and prevention methods.
- In particular, types B and C lead to chronic disease in hundreds of millions of people and together are the most common cause of liver cirrhosis, liver cancer, and viral hepatitis-related deaths.
Some common risk factors associated with hepatitis infection, include:
- Poor sanitation and hygiene practices
- Consumption of contaminated food or water
- Being in contact with the infected person
- Having unprotected sex with an infected partner
- Sharing needles or other drug injection equipment with an infected person
- Pregnant women and babies born to mothers with Hepatitis B
- Symptoms: Fatigue, Jaundice, Loss of appetite, Nausea and vomiting, Abdominal pain, Dark urine, Clay-coloured stools, Joint pain, Fever, Unexplained Weight Loss and Flu-Like Symptoms
Treatment:
- Hepatitis A: Hepatitis A is a short-term illness and may not require treatment.
- Hepatitis B: There is no specific treatment program for acute hepatitis B.
- Hepatitis C: Antiviral medications can treat both acute and chronic forms of hepatitis C.
- Hepatitis D: The WHO trusted Source lists pegylated interferon alpha as a treatment for hepatitis D. However, this medication can have severe side effects.
- Hepatitis E: Currently, no specific medical therapies are available to treat hepatitis E. However, pregnant women who develop this infection require close monitoring and care.
- Autoimmune hepatitis: Corticosteroids, like prednisone or budesonide, are extremely important in the early treatment of autoimmune hepatitis. They’re effective in about 80 percent of people with this condition.
RBI’s Digital Payments Index
Tags: General Studies – 3 Economy
Why in the news?
As per the Reserve Bank of India’s Digital Payments Index (RBI-DPI), Digital payments across the country registered a growth of 13.24% in a year through March 2023.
About:
- The Digital Payments Index has been constructed by the RBI to measure the extent of digitization of payments across the country.
- It is based on multiple parameters and reflects the expansion of various digital payment modes accurately.
- It is a first-of-its-kind index to measure the spread of digital payments across the country.
- It is released semi-annually and consists of five main parameters with varying weights:
- Payment Enablers (weight 25%)
- Payment Infrastructure – Demand-side factors (10%)
- Payment Infrastructure – Supply-side factors (15%)
- Payment Performance (45%)
- Consumer Centricity (5%)
Scrub Typhus
Tags: General Studies – 3 Health
Why in the news?
Recently, the Health department has issued an alert against scrub typhus in Alappuzha.
About:
- Scrub Typhus is a life-threatening infection caused by Orientia tsutsugamushi bacteria which is a major public health threat in South and Southeast Asia.

- Spread: Through bites of Larval Mites of family trombiculid, also called Chiggers.
- It will not spread from person to person.
- Symptoms: fever, chills, headache, body aches, muscle pain, a dark scab-like region at the site of the chigger bite, enlarged lymph nodes, dry cough, skin rashes, red eyes, and in some cases mental changes, ranging from confusion to coma.
- Treatment: Scrub typhus should be treated with the antibiotic doxycycline. Doxycycline can be used in persons of any age.
- There is no vaccine available for this disease.
- India is one of the hotspots with at least 25% of the disease burden.
| Typhus |
| Typhus is a group of bacterial infectious diseases that include epidemic typhus, scrub typhus, and murine typhus. Epidemic typhus is due to Rickettsia prowazekii spread by body lice. Scrub typhus is due to Orientia tsutsugamushi spread by chiggers. Murine typhus is due to Rickettsia typhi spread by fleas. |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are daily current affairs?
A: Daily current affairs refer to the most recent and relevant events, developments, and news stories that are happening around the world on a day-to-day basis. These can encompass a wide range of topics, including politics, economics, science, technology, sports, and more.
Q: Why is it important to stay updated with daily current affairs?
A: Staying updated with daily current affairs is crucial because it helps individuals make informed decisions in their personal and professional lives. It enables people to understand the world around them, stay aware of significant events, and engage in informed discussions about important issues.
Q: Where can I access daily current affairs information?
A: There are various sources for daily current affairs, including newspapers, news websites, television news broadcasts, radio programs, and dedicated apps or newsletters. Social media platforms are also widely used to share and access current affairs information.
Q: How can I effectively incorporate daily current affairs into my routine?
A: To incorporate daily current affairs into your routine, consider setting aside specific times each day to read or watch news updates. You can also subscribe to newsletters or follow news apps to receive curated content. Engaging in discussions with peers or participating in online forums can further enhance your understanding of current events.
Q: What are some tips for critical analysis of daily current affairs?
A: When analyzing daily current affairs, it’s essential to cross-reference information from multiple sources to ensure accuracy. Additionally, consider the source’s credibility and bias, if any. Develop the ability to identify the main points and implications of news stories, and critically evaluate the significance and impact of the events reported.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here
Visit our YouTube Channel – here

