
Explore the assertion that growth varies across different locations, examining its validity within the framework of the growth pole theory. This theory posits that economic development is unevenly distributed, with certain regions acting as catalysts for growth while others lag behind. Growth poles are areas characterized by high levels of investment, innovation, and infrastructure development, which stimulate economic activity and attract resources from surrounding areas. However, critics argue that this approach exacerbates regional disparities, concentrating wealth and opportunities in select locations while neglecting peripheral regions. By critically analyzing the growth pole theory, we can gain insights into the complexities of regional development dynamics and explore alternative strategies for promoting balanced growth and equitable development across diverse geographical areas.
Contents
Answer:
Introduction:
The Growth Pole Theory, proposed by Francois Perroux in the 1950s, suggests that economic development is not evenly distributed but rather concentrates in specific areas known as “growth poles.” These growth poles act as magnets, attracting resources, investment, and development, leading to economic expansion within their vicinity.
Body:
Growth Pole theory:
- Growth pole theory highlights the uneven distribution of economic growth, emphasizing the concentration of development in certain areas while others lag behind.
- It identifies growth poles as dynamic centers of economic activity, typically characterized by infrastructure, human capital, and favorable business environments.
- These growth poles serve as catalysts for regional development, creating spillover effects that benefit surrounding areas through increased employment, investment, and infrastructure development.
“Growth is not uniform in different places”
- In line with the growth pole theory, growth is indeed uneven, with certain regions experiencing rapid economic development while others stagnate or experience decline.
- Growth poles tend to exacerbate regional disparities by concentrating resources and opportunities in specific areas, leading to the neglect or marginalization of other regions.
- While growth poles stimulate development within their vicinity, they often create peripheral regions that remain underdeveloped, leading to spatial inequality and uneven distribution of wealth.
- The concentration of economic activity in growth poles may result in overpopulation, congestion, and environmental degradation, further exacerbating disparities between regions.
- Additionally, the success of growth poles relies on external factors such as government policies, market conditions, and global economic trends, which can further widen regional disparities.
- Furthermore, the concept of growth poles may overlook the potential of smaller towns or rural areas to contribute to economic growth, leading to neglect of their development potential.
- Moreover, growth poles can create dependency among peripheral regions, relying on the growth pole for resources and opportunities, which can hinder their long-term sustainability and autonomy.
Case Study:
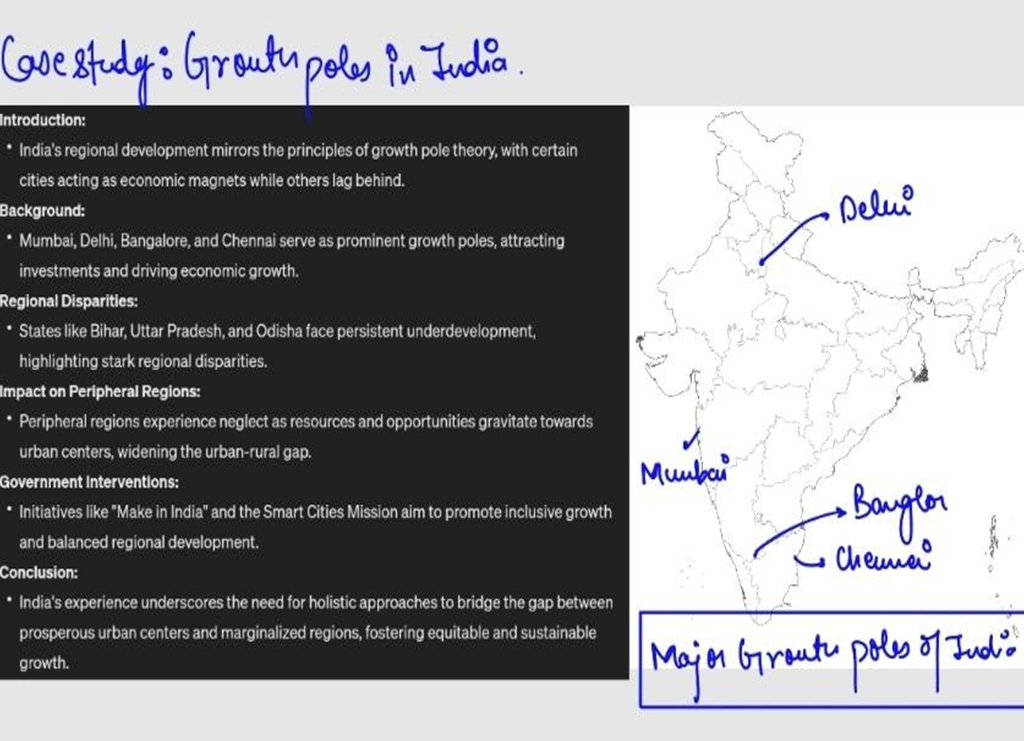
Conclusion:
By adopting a more holistic approach to regional development, societies can mitigate the adverse effects of uneven growth and promote prosperity for all regions.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here

