
Explore the formation of ocean waves and distinguish between two fundamental types: waves of oscillation and waves of translation. Ocean waves originate from the transfer of energy from wind to water surface, generating undulations that propagate across vast expanses of ocean. Waves of oscillation involve circular motion of water particles confined to a specific area, commonly observed in shallow water near shorelines. In contrast, waves of translation involve the progressive movement of water masses, transmitting energy over long distances with minimal particle displacement. Understanding the mechanisms behind wave formation and the distinction between these two wave types offers insights into ocean dynamics and coastal processes. Delve into the complexities of ocean wave behavior, unraveling their diverse manifestations and implications for marine environments.
Contents
Answer:
Introduction:
Ocean waves are disturbances that propagate through the water surface. They are primarily caused by the transfer of energy from the wind to the water surface. These waves play a crucial role in shaping coastal landscapes, influencing marine ecosystems, and impacting human activities such as surfing, shipping, and coastal engineering.
Body:
Formation of Ocean Waves:
- Wind Interaction: Ocean waves are primarily formed by the transfer of energy from the wind to the water’s surface. As wind blows across the ocean, it creates friction, which generates ripples that eventually evolve into waves.
- Wave Development: These ripples develop into larger waves as wind energy transfers to the water, causing the water particles to move in circular or elliptical paths.
- Factors Affecting Wave Formation: Factors such as wind speed, duration, and fetch (the distance over which the wind blows) influence the size and shape of ocean waves.
- Wave Characteristics: Ocean waves vary in size, speed, and wavelength, depending on the prevailing wind conditions and geographical factors.
- Propagation: Once formed, waves propagate across the ocean surface, carrying energy over vast distances until they encounter land or other obstacles.
- Transformation: As waves approach shallow water or coastal areas, they may undergo changes in speed, height, and direction, leading to the formation of breaking waves or other wave phenomena.
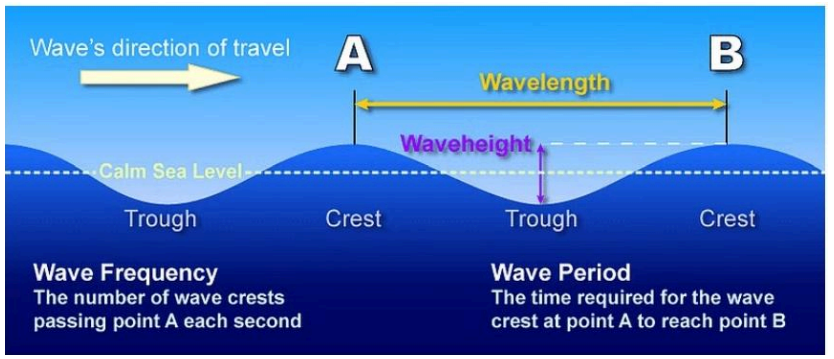
Distinguish between a wave of oscillation and a wave of translation of Ocean waves:

Conclusion:
Understanding the formation and characteristics of ocean waves is crucial for predicting and mitigating the impact of natural disasters such as tsunamis. Future research should focus on developing advanced warning systems and improving coastal infrastructure to minimize the loss of life and property caused by these phenomena.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here

