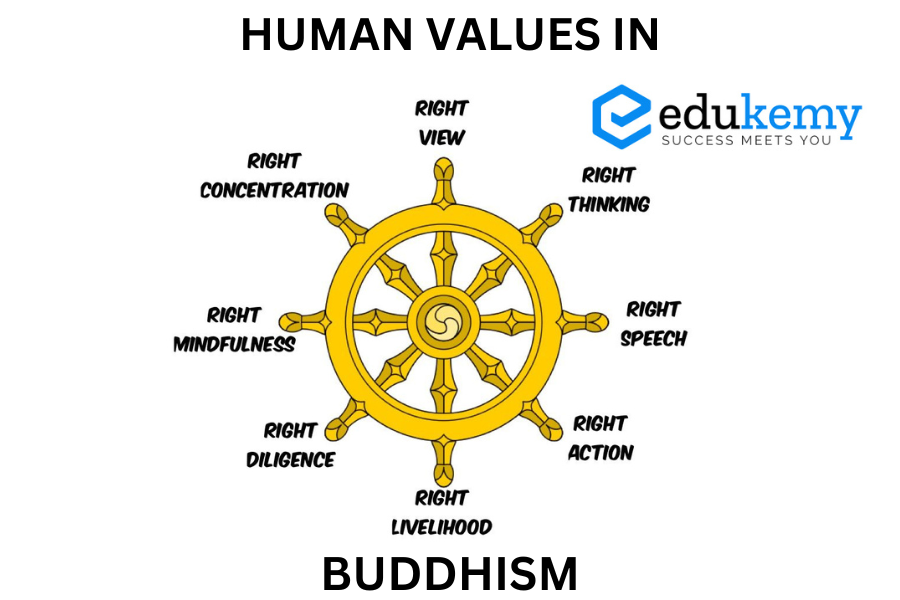
Human values in Buddhism are deeply intertwined with its ethical teachings, encapsulated in the Five Precepts, which serve as guidelines for moral conduct. These precepts advocate for abstaining from harming living beings, stealing, engaging in sexual misconduct, speaking falsely, and consuming intoxicants. By adhering to these principles, individuals cultivate compassion, integrity, and mindfulness in their actions, fostering harmony within themselves and their communities.
Buddhism, stemming from the teachings of Siddhartha Gautama, commonly known as the Buddha, is a spiritual tradition that emphasizes a profound understanding of human values. At its core, Buddhism offers a comprehensive framework for navigating the complexities of human existence and cultivating inner peace and wisdom. Central to Buddhist philosophy are the Four Noble Truths, which identify the inherent suffering in life and prescribe a path to liberation from it.
Furthermore, Buddhism places great importance on the cultivation of virtues such as loving-kindness, compassion, empathetic joy, and equanimity, collectively known as the Four Immeasurables or Brahmaviharas. These qualities form the foundation of a compassionate and altruistic way of life, promoting empathy and interconnectedness with all beings.
In essence, Buddhism offers a holistic approach to human values, emphasizing the interconnectedness of all life and the importance of ethical conduct, mindfulness, and compassion in fostering personal well-being and social harmony.
Buddhism is a religion and philosophy that originated in India over 2,500 years ago. It has spread across
the world and has influenced many cultures and societies. Buddhism emphasizes the importance of ethical
conduct, which is based on a set of human values that are central to Buddhist teachings. In this response, I
will provide a detailed account of human values in Buddhism.
Contents
Compassion (karuna):
Compassion is the most fundamental human value in Buddhism. It is the ability to
empathize with others and to feel their pain and suffering. Compassion is not just a feeling but also an
action, as it motivates us to help others who are suffering. The Buddha taught that all beings are equal and
that we should treat them with kindness and compassion, regardless of their status or position.
Loving-kindness (metta):
Loving-kindness is another central human value in Buddhism. It is the ability to
cultivate unconditional love and goodwill towards all beings. The Buddha taught that we should practice
loving-kindness towards ourselves and others, including our friends, enemies, and even those who harm
us.
Equanimity (upekkha):
Equanimity is the ability to maintain a balanced and peaceful state of mind, even in
the face of difficulties and challenges. It is the ability to remain calm and composed and to avoid becoming
attached or aversive to any particular situation or outcome. The Buddha taught that we should cultivate
equanimity as a means of achieving inner peace and happiness.
Wisdom (panna):
Wisdom is the ability to understand the true nature of reality and to see things as they
really are. It is the ability to discern between what is beneficial and what is harmful, and to act accordingly.
The Buddha taught that wisdom is the key to liberation from suffering, and that it can be developed through
meditation and contemplation.
Generosity (dana):
Generosity is the act of giving freely and without expectation of reward or recognition. It
is an expression of compassion and loving-kindness, and it helps to cultivate a sense of interconnectedness
and community. The Buddha taught that generosity is a virtuous act that can lead to happiness and inner
peace.
Ethical conduct (sila):
Ethical conduct is the practice of living in accordance with moral principles and
values. It involves refraining from harmful actions and cultivating positive habits and behaviors. The
Buddha taught that ethical conduct is essential for spiritual development, as it helps to purify the mind
and cultivate wholesome states of consciousness.
Mindfulness (sati):
Mindfulness is the ability to be present and fully engaged in the present moment,
without being distracted by thoughts or emotions. It is the ability to observe one’s thoughts and feelings
without becoming attached or identified with them. The Buddha taught that mindfulness is a powerful
tool for developing wisdom and compassion, and that it can be cultivated through meditation and daily
practice.
FAQs
Q: What are the core human values in Buddhism?
Buddhism emphasizes several core human values, including compassion, wisdom, mindfulness, ethics, and inner peace. These values form the basis for leading a virtuous and fulfilling life, as outlined in the teachings of the Buddha.
Q: How does Buddhism promote ethical conduct?
Buddhism promotes ethical conduct through the observance of the Five Precepts, which are guidelines for moral behavior. These precepts include refraining from harming living beings, stealing, engaging in sexual misconduct, speaking falsely, and consuming intoxicants. By adhering to these principles, individuals cultivate integrity, compassion, and respect for all life.
Q: What role does mindfulness play in Buddhism?
Mindfulness is a central practice in Buddhism, involving the cultivation of present-moment awareness and non-judgmental observation of one’s thoughts, feelings, and sensations. Through mindfulness meditation and daily mindfulness practices, individuals develop clarity of mind, emotional resilience, and a deeper understanding of the nature of reality.
Q: How does Buddhism address the suffering inherent in human existence?
Buddhism acknowledges the inevitability of suffering in human life, as encapsulated in the Four Noble Truths. These truths teach that suffering (dukkha) is a universal experience, caused by craving and attachment, but can be overcome through the cessation of craving and the realization of nirvana, a state of liberation and ultimate peace.
Q: What is the significance of compassion in Buddhism?
Compassion (karuna) is regarded as one of the highest virtues in Buddhism, reflecting the empathetic understanding and desire to alleviate the suffering of others. The cultivation of compassion is central to the Bodhisattva ideal, in which individuals aspire to attain enlightenment not only for themselves but also for the benefit of all sentient beings. Through acts of kindness, generosity, and loving-kindness meditation, practitioners cultivate compassion as a guiding principle in their lives.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here