
India’s Arctic imperative is emblematic of its growing global engagement and strategic foresight. Despite being geographically distant from the Arctic region, India recognizes the profound impact of Arctic developments on its climate, economy, and security. As climate change accelerates the melting of polar ice, opening up new maritime routes and access to untapped resources, India is compelled to navigate this evolving geopolitical landscape. With an eye on harnessing economic opportunities, ensuring environmental sustainability, and safeguarding its strategic interests, India is increasingly asserting its presence and interests in the Arctic, shaping its foreign policy in unprecedented ways. This essay delves into India’s evolving role in the Arctic and examines the drivers behind its engagement in this rapidly changing region.
Tags: GS Paper – 3, Environmental Pollution & Degradation- Conservation
For Prelims: Arctic Region, Climate Change, Himadri Research Base, Greenland, National Centre for Polar and Ocean Research (NCPOR), Arctic Amplification, Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), IndARC, Albedo, Polar Jet Streams.
For Mains: Significance of the Arctic Region for India, Recent Challenges Related to the Arctic Region, India’s Arctic Policy.
Contents
Context:
- In March 2024, India’s inaugural winter expedition in the Arctic concluded triumphantly and India’s National Centre for Polar and Ocean Research regarding a winter mission to the Arctic, recent developments have led to a shift in perspective.
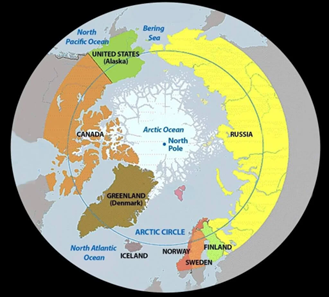
About the Arctic Region:
- Location and Geography:
- Situated at the northernmost part of Earth, the Arctic region is centred around the North Pole. Encompassing the Arctic Ocean and territories of several nations such as Canada, Russia, the United States, Norway, and Greenland, it spans a vast expanse.
- With its extreme cold temperatures, much of the region is cloaked in ice, particularly during the winter months.
- Climate and Environment:
- Defined by its frigid climate, the Arctic experiences temperatures frequently plummeting below freezing.
- The area is predominantly covered by ice, including sea ice and ice caps, which serve a pivotal role in regulating global climate patterns by reflecting sunlight.
- Despite its harsh conditions, the Arctic sustains a unique ecosystem, hosting iconic species like polar bears, seals, whales, and a diverse array of bird species.
The Significance of the Arctic Region:
- Economic Significance:
- The Arctic region boasts abundant natural resources, including coal, gypsum, diamonds, and substantial reserves of zinc, lead, placer gold, and quartz.
- The Arctic harbours significant untapped hydrocarbon resources, comprising about 30% of the world’s undiscovered natural gas.
- With increasing ice melt, these resources become more accessible, potentially addressing India’s energy security needs and scarcity of strategic and rare earth minerals.
- Geographical Significance:
- The Arctic plays a crucial role in global ocean circulation by facilitating the movement of cold and warm water around the planet.
- Furthermore, Arctic sea ice acts as a massive reflective surface, bouncing sunlight back into space and contributing to the Earth’s temperature regulation.
- Geopolitical Significance:
- China has dubbed trans-Arctic shipping routes as the “Polar Silk Road” as part of its Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), and alongside Russia, is constructing nuclear icebreakers.
- This has prompted a need to counter China’s influence in the Arctic, leading India to take a keen interest in the region through its Arctic policy.
- Environmental Significance:
- The Arctic’s melting ice provides valuable insights into the glacial melt in the Himalayas, often referred to as the “third pole,” which holds the world’s third-largest freshwater reserves after the North and South poles.
- This makes the study of the Arctic critical for Indian scientists, leading India to launch its first scientific expedition to the Arctic Ocean in 2007 and establish the Himadri research base in the Svalbard archipelago (Norway), actively engaging in research in the region ever since
The Reasons Behind India’s Growing Interest in the Arctic Region:
- Arctic Warming: The accelerated warming of the Arctic, surpassing earlier estimates, and its consequential effects on global climate patterns have prompted a reassessment of strategic needs and priorities.
- Trade Routes: India recognizes the potential of Arctic sea routes, particularly the Northern Sea Route, as a means to facilitate more efficient and cost-effective shipping for Indian trade. The utilisation of these routes could significantly reduce shipping costs and enhance trade opportunities.
- Geopolitical Dynamics: The increasing presence and investment of China in the Arctic, coupled with Russia’s decision to grant China expanded access to the Northern Sea Route, have heightened India’s geopolitical attention towards the region.
The Different Challenges Facing the Arctic Region:
- Policy Divide in India: Indian engagement in the Arctic sparks division among academic and policy circles due to differing views on the region’s impact on India’s economy, particularly concerning fossil fuel mining. Advocates urge a pragmatic approach, while sceptics raise environmental concerns.
- Arctic Amplification: Arctic warming outpaces global trends, accelerating the thawing of permafrost and releasing potent greenhouse gases, exacerbating ice melt and Arctic amplification.
- Rising Sea Level Concern: Melting Arctic ice contributes to rising sea levels, heightening coastal erosion and storm surges, posing significant threats to India’s extensive coastline and port cities, as noted by the World Meteorological Organization.
- Emerging Race Course: The opening of Arctic shipping routes fuels a resource extraction race among global powers, including the US, China, and Russia, vying for dominance in the region.
- Threat to Biodiversity: Diminishing Arctic ice and rising temperatures jeopardise Arctic wildlife survival, particularly polar bears, while shifting fish populations disrupt the Arctic food web. Extreme weather and wildfires further threaten Arctic ecosystems, including tundra areas.
Potential for Collaboration & step to be taken :
- Norway, as the current chair of the Arctic Council, maintains close relations with India. Collaboration between the two nations extends to studying changing conditions in the Arctic and Antarctic and their implications for South Asia.
- Denmark and Finland have engaged in collaborative efforts with India, focusing on waste management, pollution control, renewable energy, and green technology initiatives.
- Participation in the Arctic Council’s working groups presents India with opportunities to contribute significantly to addressing issues like the blue economy, infrastructure development, and responsible resource utilisation.
- India’s reputation as a ‘responsible stakeholder’ enhances its potential for collaboration, offering broader scope and opportunities for engagement in various areas of mutual interest.
- Establishing a single nodal body is crucial to streamline Arctic Research and Development efforts currently managed by the National Centre for Polar and Ocean Research (NCPOR) and the Ministry of External Affairs. This body would coordinate all government activities related to the Arctic.
- Adopting a Global Ocean Treaty: Global ocean governance, particularly in polar regions, warrants attention. Progressing towards a collaborative global ocean treaty, addressing challenges like rising sea levels, is imperative.
Conclusion:
Therefore, the Arctic, a vital ecosystem, faces unprecedented environmental challenges from climate change, including rapid ice melt and rising temperatures. These changes have profound implications for wildlife, indigenous communities, and global climate. International cooperation and sustainable practices are vital for its preservation and long-term viability.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q:1 Which of the following statements is/are correct about the deposits of ‘methane hydrate’? (2019)
- Global warming might trigger the release of methane gas from these deposits.
- Large deposits of ‘methane hydrate’ are found in Arctic Tundra and under the sea floor.
- Methane in the atmosphere oxidised to carbon dioxide after a decade or two.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
Mains
Q:1 How do the melting of the Arctic ice and glaciers of the Antarctic differently affect the weather patterns and human activities on the Earth? Explain. (2021)
Q:2 What is the economic significance of the discovery of oil in the Arctic Sea and its possible environmental consequences? (2015)
Source: (TH)
FAQs
Q: What is India’s interest in the Arctic region?
A: India sees the Arctic region as strategically important due to its geopolitical significance, natural resources, and the impact of climate change. The melting of Arctic ice opens up new shipping routes, resource extraction opportunities, and scientific research possibilities.
Q: How is India involved in Arctic affairs?
A: India became an observer in the Arctic Council in 2013, reflecting its growing interest in the region. It has since engaged in scientific research expeditions, collaborated with Arctic nations on climate change initiatives, and explored economic opportunities such as energy exploration and shipping routes.
Q: What are the challenges India faces in its Arctic pursuits?
A: India faces challenges such as limited infrastructure, lack of direct geographical proximity, and competition from other Arctic nations with more established presence and resources. Additionally, the environmental impacts of increased human activity in the Arctic pose concerns for India’s sustainable development goals.
Q: What are India’s priorities in the Arctic?
A: India’s priorities in the Arctic include scientific research, environmental conservation, and sustainable development. It aims to leverage its expertise in climate science and renewable energy to contribute to global efforts to mitigate climate change while ensuring the equitable utilization of Arctic resources.
Q: How does India balance its Arctic interests with global partnerships?
A: India seeks to balance its Arctic interests by engaging in multilateral forums like the Arctic Council while also strengthening bilateral partnerships with Arctic nations. It emphasizes cooperation, mutual respect, and adherence to international law in its Arctic engagements, aiming for a peaceful and sustainable Arctic future.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here

