In today’s daily current affairs briefing for UPSC aspirants, we explore the latest developments that hold relevance for the upcoming civil services examination. Our focus today includes a critical analysis of recent policy changes, international affairs, and national developments, all of which play a pivotal role in shaping the socio-political and economic landscape of India. Stay informed and stay ahead in your UPSC preparations with our daily current affairs updates, as we provide you with concise, well-researched insights to help you connect the dots between contemporary events and the broader canvas of the civil services syllabus.
Contents
- 1 Monsoon, El Nino, And Their Impact on Agriculture
- 2 Lowering the Minimum Age for Contesting Election
- 3 Justice G. Rohini-led Commission
- 4 National Research Foundation (NRF) Bill
- 5 Water neutrality in Indian industries
- 6 5% of birds in India are endemic
- 7 Israeli Spike Non-Line of Sight (NLOS) anti-tank guided missiles
- 8 Fediverse
- 9 Devika: North India’s First River Rejuvenation Project
- 10 Digital Health Incentives Scheme (DHIS)
- 11 Bhu-Vision
- 12 Einstein cross
- 13 Assam’s Manas Tiger Reserve
- 14 FAQs
- 15 FAQs
- 15.1 Q: What are daily current affairs?
- 15.2 Q: Why is it important to stay updated with daily current affairs?
- 15.3 Q: Where can I access daily current affairs information?
- 15.4 Q: How can I effectively incorporate daily current affairs into my routine?
- 15.5 Q: What are some tips for critical analysis of daily current affairs?
- 16 In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
Monsoon, El Nino, And Their Impact on Agriculture
Tag: GS-1 Geography
In News:
The increase in rainfall during July has led to a positive upturn in kharif crop sowings, including rice but concern regarding the intensifying El Nino phenomenon, which might have consequences for the rabi crop.
About
Impact of Monsoon on Indian Agriculture
Positive Impacts:
- Enhanced Crop Production: Sufficient monsoon rainfall fosters optimal soil moisture levels, fostering robust crop growth and leading to amplified agricultural yields. This water availability supports the cultivation of diverse crops such as rice, wheat, millet, and pulses.
- Economic Upliftment: Successful monsoons contribute to rural prosperity by generating income for farmers and laborers. This infusion of income stimulates heightened demand for goods and services in rural economies, subsequently fostering a positive impact on the overall national economic growth.
- Groundwater Replenishment: The monsoon plays a pivotal role in recharging groundwater reserves, particularly in areas grappling with water scarcity. This recharge is vital for the sustainability of agricultural practices in regions where water resources are limited.
Negative Impacts
- Unpredictable Monsoon Behavior: The timing, intensity, and distribution of monsoons exhibit an erratic nature, creating uncertainties in the planning and management of agriculture and crops. Whether monsoons arrive late or early, they can disrupt planting schedules and influence crop yields.
- Droughts and Flooding: Monsoon failures or excessive rainfall can trigger droughts or floods, respectively. Both situations pose significant threats to agriculture. Droughts lead to water scarcity, crop losses, and diminished yields, while floods have the potential to harm crops, erode fertile topsoil, and result in losses of livestock.
- Crop Damage: Prolonged and excessive monsoon rains can bring about crop diseases, reducing both crop quality and yield. These conditions also impede farmers’ ability to effectively carry out agricultural activities.
- Soil Erosion: Intense rainfall can contribute to soil erosion, depleting soil fertility and impacting long-term agricultural productivity. Additionally, soil erosion affects water bodies and may lead to the accumulation of sediment in reservoirs, thereby reducing their capacity to store water.
- Rising Food Prices: Inconsistent monsoon patterns can influence crop production, leading to potential shortages and subsequent inflation of food prices. This can have negative repercussions on the economy, particularly for low-income households that allocate a significant portion of their income toward purchasing food.
El-nino Impacts
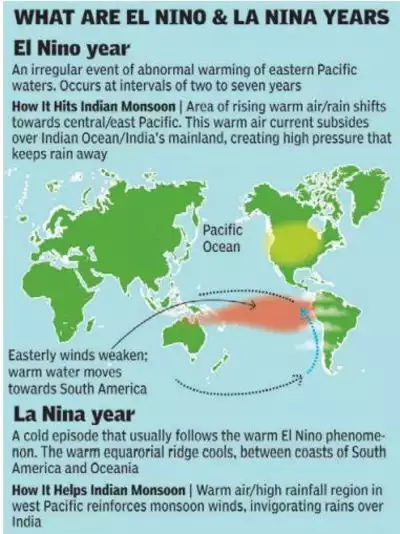
- Droughts and Water Scarcity: El Niño tends to bring drier conditions to some regions, leading to reduced rainfall and water scarcity. This can result in droughts that negatively impact crop growth and yield. Insufficient water availability can also lead to reduced irrigation capacity, affecting both rain-fed and irrigated agriculture.
- Crop Failures: The combination of higher temperatures and decreased rainfall during El Niño events can stress crops, leading to heat stress and water stress. This can result in lower crop yields, stunted growth, and even complete crop failures in some cases.
- Pest and Disease Outbreaks: El Niño’s altered climate conditions can create favorable environments for the proliferation of pests and diseases that can damage crops. Increased humidity and warmth can contribute to the rapid spread of certain pathogens and pests, leading to reduced crop quality and quantity.
- Shift in Growing Seasons: El Niño can disrupt the typical timing of growing seasons due to changes in rainfall patterns. Farmers may need to adjust their planting schedules to adapt to delayed or erratic rains, which can lead to mismatches between crop development stages and optimal conditions.
- Reduced Agricultural Productivity: The combined effects of drought, heat stress, and increased pest pressure can result in reduced agricultural productivity. This can impact food production, availability, and overall food security.
- Livestock and Pasture Concerns: El Niño’s impact isn’t limited to crops; it can also affect livestock and pastures. Reduced forage availability due to dry conditions can lead to inadequate nutrition for livestock, affecting their health and productivity.
- Economic Consequences: Agricultural losses during El Niño events can have economic repercussions for both farmers and the broader economy. Lower crop yields and livestock productivity can lead to decreased income for farmers and increased food prices for consumers.
- Global Trade Disruptions: Regions that are major producers of certain crops can experience reduced output due to El Niño, leading to disruptions in global trade and food supply chains.
Source: Indian Express
Lowering the Minimum Age for Contesting Election
Tags: GS – 2: Indian Polity (Election Process)
Why in News:
Recently, a Parliamentary panel has suggested lowering the minimum age for contesting in Assembly elections from 25 years to 18 years.
Benefits of Lowering the Minimum Age:
- It will allow young individuals to participate actively in the political process and bring fresh perspectives to policy discussions. Example – Canada has minimum age for candidacy in federal elections as 18.
- It will promote diversity in leadership by allowing representation from different age groups, backgrounds, and experiences.
- Young candidates may have insights into contemporary issues like technology, climate change, and social justice.
- It will encourage political awareness and involvement among youth, contributing to a more engaged and informed citizenry. Example, youth-led movements such as “March for Our Lives” in the USA.
Concerns with Lowering the Minimum Age:
- Young candidates might lack the experience and maturity required for effective decision-making and governance.
- Young candidates may have a limited understanding of the complexities of governance and public policy.
- Lowering the age might lead to unprepared candidates entering the political arena, resulting in ineffective representation.
- Young candidates might be more susceptible to external influence, as they may have less exposure to political dynamics.
Election Commission’s Response:
- The Election Commission (EC) has said that expecting 18-year-olds to have the required experience and maturity to serve as public representatives was unrealistic.
- It advised the panel not to change the constitutional provision for the age requirement to contest in the Lok Sabha, Rajya Sabha, Legislative Assemblies, and Legislative Councils, unless compelling reasons exist.
Other Proposals by the Committee:
- The committee discussed the concept of a common electoral roll for different types of elections but urged caution, emphasizing the importance of maintaining the principles of federalism.
- The committee expressed concerns about linking the Aadhaar and Voter IDs of non-citizens, suggesting the establishment of legal provisions to ensure non-citizens with Aadhaar are not included on electoral rolls.
- The committee invited comments from political parties on Election Commission’s proposal for remote voting for internal migrants.
Source: Indian Express
Justice G. Rohini-led Commission
Tags: GS – 2: Governance (Government Policies and Intervention)
Why in News:
Recently, the report of a Rohini Commission set up to examine the sub-categorisation of Other Backward Classes (OBCs) has been submitted to the President.
Justice G. Rohini Commission:
- The commission was set up on 2nd October, 2017 under Article 340 of the Constitution (President’s power to appoint a Commission to investigate the conditions of the backward classes).
- Terms of Reference:
- Examine the extent of inequitable distribution of benefits of reservation among the castes or communities included in the broad category of OBCs with reference to such classes included in the Central List.
- Work out the mechanism, criteria, norms and parameters in a scientific approach for sub-categorisation within such OBCs.
- Take up the exercise of identifying the respective castes or communities or sub-castes or synonyms in the Central List of OBCs and classifying them into their respective sub-categories.
- Study the entries in the Central List of OBCs and recommend corrections for repetitions, ambiguities, inconsistencies, and errors in spelling or transcription.
Historical Evolution of Reservation of OBCs in India:
- Kelkar Commission (1953): The first instance of recognizing backward classes beyond the Scheduled Castes (SCs) and Scheduled Tribes (STs) on a national level.
- Mandal Commission Report (1980): It estimated that the OBC population constituted 52% and identified 1,257 communities as backward.
- It suggested an increase in the existing quotas from 22.5% to 49.5%, extending the reservation to include OBCs.
- Following these recommendations, the central government implemented the reservation policy, reserving 27% of seats in union civil posts and services for OBCs under Article 16(4).
- It was also enforced in central government educational institutions under Article 15(4).
- In 2008, the Supreme Court directed he central government to exclude the “creamy layer” among the OBCs from benefiting from the reservation policy, ensuring that it reaches the most disadvantaged.
- 102nd Constitutional Amendment Act, 2018: It granted constitutional status to the National Commission for Backward Classes (NCBC).
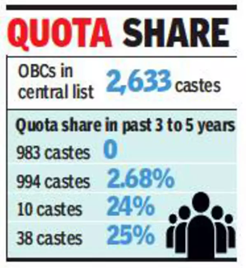
Need for sub-categorisation of OBCs:
- OBCs get 27% reservation in central government jobs and admission to educational institutions. There are more than 2,600 entries in the Central List of OBCs but over the years only a few affluent communities among them have benefited from the quota.
- In 2018, an analysis of data from 1.3 lakh central government jobs and OBC admissions to central higher education institutions revealed that 97% of benefits were availed by just 25% of OBC castes.
- Approximately 37% (983) of OBC communities had no representation in these opportunities, underscoring the necessity for sub-categorization.
- Therefore, there is an argument that a “sub-categorisation” of OBCs — quotas within the 27% quota — is needed in order to ensure “equitable distribution” of the benefits of reservation.
Source: The Hindu
National Research Foundation (NRF) Bill
Tags: GS-II: Government policies
In News:
National Research Foundation Bill introduced in Lok Sabha
About National Research Foundation (NRF) Bill
- Union Minister of Science and Technology has recently tabled The Anusandhan National Research Foundation Bill (NRF), 2023 in Lok Sabha of parliament.
- The NRF is established as an apex body to guide scientific research in line with the National Education Policy (NEP).
- It aims to promote research and development across Indian research institutions, colleges, and universities.
- Major highlights:
- Nearly ₹36,000 crore to be raised from industries and philanthropists while government will support funding worth ₹10,000 crore.
- Also, an additional ₹4,000 crore via subsuming the Science and Engineering Research Board (SERB) into NRF.
- Department of Science and Technology (DST) will be designated as the administrative department of NRF and its governing body will be led by the Prime Minister as ex-officio president.
- Its Executive council will be chaired by the Principal Scientific Advisor to government while Union Ministers of Science and Technology and Minister of Education will act as ex-officio vice-presidents.
- NRF will help to facilitate collaboration among industry, academia, government departments, and research institutions.
- It will create an interface mechanism for industry, state governments, scientific and line ministries and will impact all ministries.
- Previously, In June 2022, the Union Cabinet approved the NRF Bill with an allocation of ₹50,000 crore over five years.
- Overall, a focused policy framework and regulatory processes will go a long way to boost spending on research and development.
Source: Hindustan Times
Water neutrality in Indian industries
Tags: GS-II: Government Policies
In News:
NITI Aayog sets Water Neutrality Standards for Companies
About Water neutrality in Indian industries
- Government’s think-tank NITI Aayog has recently introduced water neutrality standards for industries.
- The approach aims to conserve water, enhance its efficient usage, and establish a means to assess and validate industry claims.
- NITI Aayog has outlined the definition and approach for water neutrality, aiming to save water and validate industry claims.
- Major highlights:
- Water neutrality is now defined as the total freshwater consumption, including direct and indirect/virtual water use within water-critical supply chains.
- The consumption should be less than or equal to quantifiable water savings achieved through strategies undertaken, with a focus on operational water use efficiencies and conservation efforts.
- It is estimated that adopting water neutrality standards can help save up to 38.23 BCM (billion cubic meters) of water over the next decade (till 2032).
- Water neutrality aims to reduce water demand without replacing existing regulatory tools as it doesn’t intend to replace regulatory measures but rather focuses on reducing water demand.
- NITI Aayog has also highlighted challenges in independently validating water claims made by industries as many industry claims of being “water positive” lack independent validation.
- The assessment of water impact by third parties raises concerns about validity as they lack comprehensive on-ground verification.
- Water neutrality/positive impact assessment requires matching extracted water with recharged/conserved water at the same location.
- Overall, there is a need to bring more accountability to assessment standards only then new standards will reach its intended goals in near future.
Source: Niti Gov.
5% of birds in India are endemic
Tag: GS-3 Biodiversity Conservation
In News:
The publication, titled “75 Endemic Birds of India”, was recently released on the 108th foundation day of the Zoological Survey of India (ZSI), which points out that about 5% of birds found in the country are endemic and are not reported in other parts of the world.
About the Report:
- The report is aimed at making information about endemic birds of the country available to everyone, and highlighting the efforts to conserve species that are found only in restricted areas
- The details of endemic bird species contained in the publication include etymology (meanings of scientific names) and their historical relevance along with vital facts such as subspecies’ differences, distinguishing traits, preferred habitats, breeding habits, and food preferences,
Key Highlights of the Report:
- India is home to 1,353 bird species, which represents approximately 12.40% of global bird diversity. Of these 1,353 bird species, 78 (5%) are endemic to the country.
- Among the 78 species, three species have not been recorded in the last few decades.
- The Report highlights the importance of endemic bird species, as endemic species are restrictive in nature and it is important that their habitats are conserved.
- The 75 bird species belong to 11 different orders, 31 families, and 55 genera, and exhibit remarkable distribution patterns across various regions in India.
- The highest number of endemic species have been recorded in the
- Western Ghats: 28 bird species.
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands: 25 bird species. Endemism in Andaman must have developed because of the geographical isolation of the region. Example must have developed because of the geographical isolation of the region
- Regarding the conservation status, the report points out that among 78 species (as per IUCN):
- Threatened species: 25
- Critically Endangered: 3
- Endangered: 5
- Vulnerable: 17
- Near Threatened: 11
Source: The Hindu
Israeli Spike Non-Line of Sight (NLOS) anti-tank guided missiles
Tag: GS-3 Defence and Security challenges; Defence Technology
In News:
The Indian Air Force recently received Israel’s Spike Non Line of Sight (NLOS) anti-tank guided missiles which can hit targets from distances up to 30 km away.
About the Spike Non Line of Sight (NLOS) Anti-tank Guided Missile (ATGM):
- It is a fire-and-forget anti-tank and anti-personnel missile with a tandem-charge high-explosive warhead.
- It is developed by Rafael Advanced Defense Systems, a defence technology company based in Israel.
- It is available in man-portable, vehicle-launched, and helicopter-launched variants.

- Spike missiles are being used by the defence forces of Israel and another 38 countries, including India, Netherlands, Germany, Italy, Peru, Spain, Belgium, Brazil, Canada, UK, Philippines, and Singapore.
- The NLOS missiles are now going to be integrated with the Russian-origin fleet of Mi-17V5 helicopters which would be able take out targets from long ranges and can prove to be very effective against enemy targets and assets hidden behind mountains or hills
Significance of SPIKE NLOS-ATGM for India:
- Presence of hostile neighbours at both the Eastern and Western flank makes it essential for India to boost its defence capabilities so that tank and infantry troops could be deterred from advancing.
- The IAF aims to bolster its arsenal through indigenous production and foreign acquisitions to address security threats, as demonstrated by this acquisition of long-range anti-tank missiles.
- The Chinese advance at the Line of Actual Control near Eastern Ladakh sector, made India realise the potential of such weapons in countering aggression.
Source: Ani News
Fediverse
Tags: GS – 3 Internal Security
Why in news?
Meta, the parent company for Facebook, Instagram, and WhatsApp, recently launched its Twitter, now X, rival Threads.

About:
- Threads will be the company’s first app to join the fediverse – a network of servers operated by third parties.
Fediverse
- The fediverse is a group of federated social networking services that work on decentralised networks operated using open-source standards.
- In this system, a network of servers, managed by third parties, facilitates communication between users of various social media platforms, enabling seamless cross-platform interaction.
- Meta, the parent company of Facebook, Instagram, and WhatsApp, is planning to include its new Threads app in the fediverse.
- This approach allows users to communicate across different social media platforms without creating separate accounts for each one.
- Platforms like Pixelfed, PeerTube, Lemmy, Diaspora, Movim, Prismo WriteFreely, and others already utilize the fediverse.
More Information:
- For example, if a user on Threads, once it enables use of the fediverse, is unable to use their profile for some reason, they can transport all their data to another platform.
- This data would include their follower list, profile information, and posts.
- This kind of cross-platform communication is not facilitated by traditional social media platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter.
- Additionally, if the servers for an existing platform go down, users of platforms on the fediverse can retain and shift their data to another platform that is part of it.
Source: The Hindu
Devika: North India’s First River Rejuvenation Project
Tags: GS – 3 Infrastructure
Why in news?
India’s first River Rejuvenation Project, named Devika, is almost finished and was inaugurated by PM Modi.
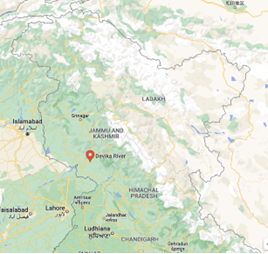
About:
- Project Devika is North India’s first river rejuvenation project.
- This project modeled after the ‘Namami Ganga‘initiative, is aimed at restoring the health of the Devika River (in Udhampur, Jammu & Kashmir).
- Under the project, bathing “ghats” (places) on the banks of the Devika River will be developed, encroachments will be removed, natural water bodies will be restored, and catchment areas will be developed along with cremation ground.
- The primary goal is to ensure the efficient disposal of liquid waste, preventing pollution and maintaining the river’s sanctity.
- In addition to liquid waste, the project also encompasses the crucial aspect of Solid Waste Management.
- The Liquid Waste Management Project involves creating a network of pipes and manholes connecting households under the Devika Rejuvenation Project.
- Additionally, a Solid Waste Management Project is planned to further enhance the river’s restoration.
- Financial Allocation is shared between Central and Union Territory (UT) at a 90:10 ratio.
- Panchayati Raj Institutions (PRIs) play a crucial role in ensuring the success of the project at the grassroots level.
| Devika river |
| Devika river originates from the hilly Suddha Mahadev temple in the Udhampur district of Jammu and Kashmir and flows down towards western Punjab (now in Pakistan) where it merges with the Ravi River. The river holds religious significance as it is revered by Hindus as the sister of river Ganga. |
Source: PIB Gov.
Digital Health Incentives Scheme (DHIS)
Tags: GS –2 Government Policies & Interventions, GS –2 Central Sector Schemes, Health
Why in news?
Recently, National Health Authority (NHA) has announced an extension of its Digital Health Incentives Scheme (DHIS) under the Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM).
About:
- The DHIS was launched with effect from 1st January 2023 as part of the Ayushman Bharat Health Account (ABHA).
- The Digital Health Incentives Scheme (DHIS) offers financial incentives to hospitals, diagnostic labs, and digital health solution providers for adopting and enabling digital health technologies and practices.
- Aim:
- The scheme aims to promote the creation and linkage of digital health records to Ayushman Bharat Health Account (ABHA) numbers of patients.
- Eligibility:
- Health facilities (hospitals, diagnostic labs) and registered Digital Solution Companies (DSCs) under ABDM’s Health Facility Registry (HFR) are eligible to participate in the scheme.
- Amount:
- They can earn financial incentives of up to Rs 4 crores based on the number of digital health records created and linked to ABHA (Ayushman Bharat Health Account) numbers of patients.
Additional Information:
- National Health Authority:
- NHA (founded in 2018) is an attached office of the Ministry of Health & Family Welfare.
- It is responsible for implementing India’s flagship public health insurance/assurance scheme Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana.
| Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission |
| The Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM) is a national initiative that aims to develop the digital health infrastructure of the country. It was launched in September 2021. Ayushman Bharat is a flagship scheme of India which was launched as recommended by the National Health Policy 2017, to achieve the vision of Universal Health Coverage (UHC). It aims to provide digital health IDs for all Indian citizens to help hospitals, insurance firms, and citizens access health records electronically when required. The National Health Authority (NHA) under the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare is the implementing Agency. |
Source: PIB Gov.
Bhu-Vision
Tags: GS – 3 Economy
Why in news?
Recently, a revolutionary IoT-based automated soil testing and agronomy advisory platform, Bhu-Vision (also known as KRISHI-RASTAA Soil Testing System), has been officially launched at AICRP (ICAR-IIRR), Hyderabad.

About:
- Developed by ICAR-Indian Institute of Rice Research (ICAR-IIRR), Hyderabad.
- This system seamlessly conducts 12 key soil parameter tests in just 30 minutes, providing quick, accurate results directly to farmers and stakeholders through a soil health card on their mobile devices.
- These parameters include pH, electrical conductivity, organic carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium, sulfur, iron, zinc, and boron.
- It signifies a promising future for agricultural technology in India, contributing to a more comprehensive understanding of the nation’s soil health and agricultural landscape.
- This platform will play a vital role in completing the nation’s soil health map.
Source: Time Tech
Einstein cross
Tags: GS – 3 Science and Technology, Space Technology
Why in news?
Recently, Astronomers have discovered a stunning, rare example of an “Einstein cross” splitting and magnifying light from the far depths of the universe.
About:
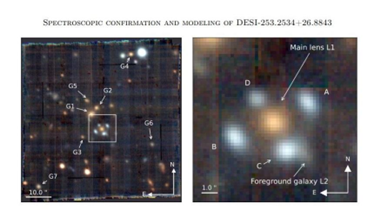
- Einstein predicted the existence of these crosses back in 1915.
- In this case, a foreground elliptical galaxy, located around 6 billion light-years from Earth, has distorted and split a beam of light from a background galaxy about 11 billion light-years away.
- The result is a pattern of four blue smudges around the orange glow of the foreground galaxy.
- The background light likely originates from a quasar, a young galaxy with a supermassive black hole at its core emitting intense radiation.
Einstein’s theory of general relativity
- Einstein’s theory of general relativity describes the way massive objects warp the fabric of the universe, called space-time.
- Gravity, Einstein discovered, isn’t produced by an unseen force; rather, it’s simply our experience of space-time curving and distorting in the presence of matter and energy.
- It explains how massive objects warp space-time, and the strong gravity of the foreground galaxy curved the light from the quasar, creating the Einstein cross pattern.
Source: Livescience
Assam’s Manas Tiger Reserve
Tags: GS – 3 Environment, Conservation
Why in news?
Recently, Assam’s Manas Tiger Reserve is facing significant staffing challenges, with nearly 63% of required positions vacant.
About:
- The All-India Tiger Estimation 2022 has indicated that Assam’s Manas National Park and Tiger Reserve is moving from a low to a high-tiger-density area.
Manas Tiger Reserve
- Manas Tiger Reserve spans across the districts of Kokrajhar, Chirang, Buxa, and Udalguri in
- north-west Assam.
- Manas is located at the foothills of the Eastern Himalayas.
- To the north, it is separated from the Royal Manas National Park of Bhutan by the River Manas and its tributaries- Beki and Hakua; while to the west, it is separated from the Buxa Tiger Reserve of West Bengal by the River Sankosh.
- The Manas River is a major tributary of the Brahmaputra River, which passes through the heart of the national park.
- Vegetation:
- The primary forest types include semi-evergreen forests, mixed moist and dry deciduous forests, alluvial grasslands, creeper swamp forests, Eastern seasonal Swamp forests, and Cane and bamboo breaks.
- Flora:
- Endemic plant species like the Catechu tree, Sissoo, and White siris thrive here.
- Fauna:
- Endemic fauna includes the Pygmy hog, Golden langur, and Assam roofed turtle.
- The area has a unique distinction of being a Natural World Heritage Site, a Tiger Reserve, an Elephant Reserve, a Biosphere Reserve and an Important Bird Area.
- It forms part of a large tiger conservation landscape which includes Buxa-Nameri-Pakke-Namdapha tiger reserves and protected areas of Bhutan and Myanmar.
Source: The Hindu
FAQs
FAQs
Q: What are daily current affairs?
A: Daily current affairs refer to the most recent and relevant events, developments, and news stories that are happening around the world on a day-to-day basis. These can encompass a wide range of topics, including politics, economics, science, technology, sports, and more.
Q: Why is it important to stay updated with daily current affairs?
A: Staying updated with daily current affairs is crucial because it helps individuals make informed decisions in their personal and professional lives. It enables people to understand the world around them, stay aware of significant events, and engage in informed discussions about important issues.
Q: Where can I access daily current affairs information?
A: There are various sources for daily current affairs, including newspapers, news websites, television news broadcasts, radio programs, and dedicated apps or newsletters. Social media platforms are also widely used to share and access current affairs information.
Q: How can I effectively incorporate daily current affairs into my routine?
A: To incorporate daily current affairs into your routine, consider setting aside specific times each day to read or watch news updates. You can also subscribe to newsletters or follow news apps to receive curated content. Engaging in discussions with peers or participating in online forums can further enhance your understanding of current events.
Q: What are some tips for critical analysis of daily current affairs?
A: When analyzing daily current affairs, it’s essential to cross-reference information from multiple sources to ensure accuracy. Additionally, consider the source’s credibility and bias, if any. Develop the ability to identify the main points and implications of news stories, and critically evaluate the significance and impact of the events reported.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here


