In today’s daily current affairs briefing for UPSC aspirants, we explore the latest developments that hold relevance for the upcoming civil services examination. Our focus today includes a critical analysis of recent policy changes, international affairs, and national developments, all of which play a pivotal role in shaping the socio-political and economic landscape of India. Stay informed and stay ahead in your UPSC preparations with our daily current affairs updates, as we provide you with concise, well-researched insights to help you connect the dots between contemporary events and the broader canvas of the civil services syllabus.
Contents
- 1 Mines and Minerals Amendment Bill
- 1.1 In News:
- 1.2 About the Critical and deep-seated minerals:
- 1.3 Critical and Deep-seated minerals Imported by India:
- 1.4 Need for private sector participation in exploration of critical and deep-seated minerals
- 1.5 Major Amendments proposed in Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation) Amendment Bill, 2023
- 1.6 How does the Mines and Minerals Bill 2023 aim to encourage private players
- 1.7 Concerns with the Bill:
- 2 Carbon Capture and Storage
- 3 Separation of Power and Jan Vishwas Act
- 4 Revised Good Manufacturing Practices Standards
- 5 WMO: 2022 State of the Climate in Asia Report
- 6 Genetic Diversity in the Indian Population
- 7 Deepor Beel
- 8 Tamil Palm manuscripts: Gnanamuyarchi
- 9 Adichanallur archaeological site (Tamil Nadu)
- 10 Amrit Bharat Station Scheme (ABSS)
- 11 Nuclear Medicine
- 12 FAQs
- 12.1 Q: What are daily current affairs?
- 12.2 Q: Why is it important to stay updated with daily current affairs?
- 12.3 Q: Where can I access daily current affairs information?
- 12.4 Q: How can I effectively incorporate daily current affairs into my routine?
- 12.5 Q: What are some tips for critical analysis of daily current affairs?
- 13 In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
Mines and Minerals Amendment Bill
Tag: GS-1 Distribution of key natural resources; GS-3 Issues related to Development; Energy and Mineral Resources
In News:
Parliament recently passed the Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation) Amendment Bill, 2023, to attract private sector investment in the exploration of critical and deep-seated minerals in the country.
About the Critical and deep-seated minerals:
- Critical minerals are those minerals which are essential for economic development and national security. Example lithium, beryllium, niobium etc.
- Deep seated minerals are those minerals which occur at a depth of more than 300 metres from the surface of land with poor surface manifestations. Example gold, silver, copper, zinc, lead, nickel, cobalt, platinum group of minerals, diamonds, etc. are high value minerals.
Critical and Deep-seated minerals Imported by India:
- India is 100% import-dependent on countries including China, Russia, Australia, South Africa, and the U.S. for the supply of critical minerals like lithium, cobalt, nickel, niobium, beryllium, and tantalum.
- India’s imports Lithium worth $22.15 million in 2021-2022
- For deep seated minerals, India imported 12 lakh tonnes of copper worth Rs. 27,000 crore in 2022-23. It imported 32,298.21 tonnes of Nickel worth Rs. 6,549.34 crore.
- Such high dependence on imports exposes the vulnerability of India to supply chain shocks as witnessed during the Ukraine-Russia war.
Need for private sector participation in exploration of critical and deep-seated minerals
- Immense Geological Potential: India has geological and tectonic settings conducive to hosting potential mineral resources, similar to mineral rich countries like Australia and Eastern Africa.
- Poor Investment in Mineral Explorations: India spends less than 1% of the global mineral exploration budget despite having huge potential for minerals.
- Limited exploration due to dominance of the public sector: India has explored just 10% of its Obvious Geological Potential (OGP), less than 2% of which is mined. This is because the majority of explorations are carried out by Geological Survey of India and PSUs like Mineral Exploration Corporation Limited (MECL).
- Mining policies restricting engagement of private sector: India’s mining policy had kept Greenfield exploration of minerals out of the purview of private-sector explorers.
- Low risk taking ability of PSU’s: Exploration activities are risky operation as less than 1% of explored projects becoming commercially viable mines
- Involvement of Complex techniques: Exploration requires techniques like aerial surveys, geological mapping, and geochemical analyses and is highly specialised, which private sectors can better deliver.
Major Amendments proposed in Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation) Amendment Bill, 2023
| Key Provisions | Existing MMDR Act 1957 | MMDR Amendment Bill |
| Allocation to Private sectors for Mining Atomic Minerals | Only State agencies allowed in the exploration of the atomic minerals. | Private sector allowed to mine six out of 12 atomic minerals such as lithium, beryllium, niobium, titanium, tantalum and zirconium. Centre will also have powers to auction mining lease and composite licence for critical minerals such as gold, silver, copper etc. |
| Auction for Exploration Licence | Exploration licenses limited to Government bodies and PSU’s. | The state government grants licences through competitive bidding, while the Central government prescribes auction details. |
| Maximum Area in which Activities are Permitted | Prospecting licence allows activities in an area up to 25 square kilometres. | Bill allows activities under a single exploration licence in an area up to 1,000 square kilometres. |
| Incentive for exploration Licence | No substantial incentives for exploration. | After exploration of resources, the state government must conduct an auction for mining lease within six months. The licensee will receive a share in the auction value of the mining lease for the mineral prospected by them. |
How does the Mines and Minerals Bill 2023 aim to encourage private players
- Exploration & commercial mining of 6 Atomic minerals: The Bill allows 6 atomic minerals to be commercially mined which was previously reserved for government entities.
- Enabling mining activities: The bill allows pitting, trenching, drilling, and sub-surface excavation as part of reconnaissance, which included mapping and surveys, which were earlier prohibited.
- New licence type: The Bill proposes a new type of licence i.e. exploration licence (EL), for a period of five years to encourage reconnaissance-level and or prospective stage exploration by the private sector.
- Expansion of maximum area for exploration: The bills expands the maximum area for exploration; activities in upto 1,000 sq kms will be allowed under a single exploration licence.
Concerns with the Bill:
- Revenue generation delays: Private companies’ revenue from exploration depends on premium shares after mine auctions, subject to government clearance timelines and potential delays due to deposit complexity and geography. This could impact exploration project viability.
- Lack of clarity in Revenue amount: Explorers would not be able to ascertain the revenue they would generate through auction premium.
- Auctioning of exploration licence: Auctioning of something which has value is feasible, however auctioning licences for exploration of potential minerals becomes difficult.
- Government control over auctioning of discovered resources limits the profits of private players, who only get a share of the premium at an unknown stage.
Source: The Hindu
Carbon Capture and Storage
Tag: GS-3 Environment
In News:
Recently, the UK government reaffirmed its support for projects to capture and store carbon dioxide emissions as part of its efforts to reach net zero goals.
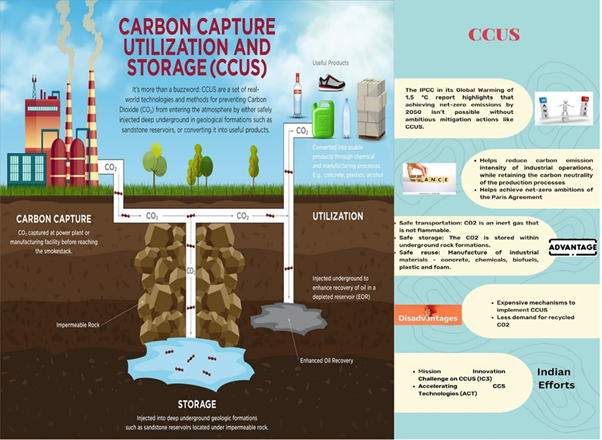
About CCS
- Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS), also known as Carbon Capture and Sequestration, is a technology and process designed to mitigate the release of carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions into the atmosphere, thereby helping to combat climate change.
- It involves capturing carbon dioxide emissions from industrial processes or power plants, transporting the captured CO2 to a suitable storage location, and securely storing it underground in geological formations.
- The primary goal of CCS is to reduce the concentration of CO2 in the atmosphere and limit its contribution to global warming.
The CCS process consists of three main steps:
Capture:
Carbon dioxide is captured from industrial sources such as power plants, cement factories, and other high-emission industries.
- Methods for capturing CO2,
- Post-combustion capture (removing CO2 from flue gases after combustion),
- Pre-combustion capture (removing CO2 before combustion occurs),
- Oxy-fuel combustion (burning fuels in an oxygen-rich environment to produce a concentrated stream of CO2).
Transport:
Captured CO2 is transported via pipelines, ships, or other means to a suitable storage site. Transport infrastructure must be established to ensure the safe and efficient movement of the captured CO2.
Storage:
The captured CO2 is then injected deep underground into geological formations, such as depleted oil and gas reservoirs, saline aquifers (porous rock formations that contain salty water), or other suitable geological structures.
Primary approaches of Carbon Capture and Storage:
- Point-source CCS: It involves capturing CO2 directly at the site of its production, such as industrial smokestacks.
- Direct air capture (DAC): It focuses on removing CO2 that has already been emitted into the atmosphere. The recent UK initiatives specifically target point-source CCS.
Applications of Carbon Capture and Storage:
- Power Generation: CCS can be applied to fossil fuel power plants, such as coal-fired and natural gas power plants. These plants are major sources of CO2 emissions. By capturing the CO2 emitted during combustion, CCS can help reduce the carbon footprint of electricity generation.
- Hydrogen Production: Hydrogen is considered a clean energy carrier, but its production often generates CO2 emissions. By capturing the CO2 during hydrogen production, CCS can enable “blue hydrogen,” which is hydrogen produced with CCS, to reduce the carbon impact.
- Industrial Processes: Industries like cement, steel, and chemicals produce substantial CO2 emissions. CCS can be integrated into these processes to capture and store CO2 emissions, helping to decarbonize these sectors.
- Mineralization: Captured carbon can be reacted with certain minerals to form stable carbonates, which can be stored safely underground or used in construction materials. This process, known as mineral carbonation, offers a long-term and secure method of carbon storage.
- Greenhouses and Indoor Agriculture: Captured carbon dioxide can be supplied to greenhouses and indoor farming facilities to enhance plant growth.
- Other applications of CCS: Enhanced Oil Recovery (EOR), Bioenergy, Direct Air Capture (DAC), Natural Gas Processing, Waste-to-Energy Facilities and Dry Ice Production

Challenges of CCS:
- Economic Cost: Building infrastructure for capture, transportation, and storage requires significant upfront capital expenditures for CCS. The overall viability of CCS projects can be impacted by the cost of CO2 capture from flue gases or industrial processes.
- Geological Storage Suitability: Finding and securing geological formations that are appropriate for long-term CO2 storage is difficult. Some geological formations are not suitable for storing CO2 because of the possibility of leaks or seismic activity.
- Fossil fuel companies’ operational viability may be unintentionally prolonged by CSS implementation, according to some environmental organisations that have expressed concerns about CSS’s effectiveness.
Source: Reuters
Separation of Power and Jan Vishwas Act
Tags: GS – 2: Indian Polity (Separation of Powers)
In News:
The recently enacted Jan Vishwas Act, 2022, aimed at easing business regulations, transfers the authority to impose penalties for offences from the judiciary to the bureaucracy. This has raised concerns about the separation of powers, as bureaucrats become both prosecutors and judges.
Principle of Separation of Power:
- Separation of Powers is a fundamental principle in governance where the powers of a government are divided among different branches to prevent any one branch from having unchecked authority.
- It ensures a system of checks and balances.
- The Indian Constitution does not explicitly prescribe a strict separation of powers between the judiciary and the executive.
- Article 50 instructs the state to work towards achieving this separation in due time. However, such a separation was not accomplished initially because the criminal magistracy was originally part of the executive at the time of Independence.
- It was only around 1970 that certain State legislatures, like West Bengal, enacted laws to separate the judicial and executive functions within the criminal magistracy under the Criminal Procedure Code, 1898.
Jan Vishwas Act, 2022:
- This Act aims to enhance Ease of Living and Ease of Doing Business and to decriminalize minor offences that don’t harm public interest or national security, replacing them with civil penalties.
- Decriminalizes 180 offences across 42 laws governing environment, agriculture, media, industry and trade, publication, etc.
- Replaces imprisonment clauses with monetary fines.
- Removes all offences and penalties under Indian Post Office Act, 1898 (considered obsolete in the present context).
- Introduces Adjudicating Officers for determining penalties.
- Periodic revision of fines with a 10% increase every 3 years.
- It allows compounding of some offences. (meaning offenders can settle their cases by paying a certain amount without going through a court trial.
- It replaces criminal imprisonment with monetary penalties but shifts the authority to impose penalties to the bureaucracy.
- Questions were raised about the technical competence of adjudicating officers under the Act, especially in environmental legal proceedings.
Interference of Bureaucracy in the Judicial power:
- Judicial Tribunals: Ministries create judicial tribunals to take over judicial functions, often appointing bureaucrats as “technical members”.
- Statutory Regulators: The Union government establishes regulators like SEBI and CCI with the authority to impose substantial fines on private sector entities.
- Adjudicatory Officers: The government introduces adjudicatory officers in legislation like the Prevention of Money Laundering Act, IT Act, and Food Safety Act. These officers, who are bureaucrats, possess powers to impose penalties or confirm property attachment orders.
Source: The Hindu
Revised Good Manufacturing Practices Standards
Tags: GS – 3: Indian Economy (Industrial Growth)
Why in News:
Recently, the government of India has directed all pharmaceutical companies to implement the Revised Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP), bringing their processes at par with Global Standards.
Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) standards:
- GMP standards are guidelines and regulations that ensure the quality, safety, and consistency of pharmaceutical products.
- It is designed to minimize the risks involved in any pharmaceutical production that cannot be eliminated through testing the final product.
- WHO (World Health Organization) has established detailed guidelines for GMP. Many countries have formulated their own requirements for GMP based on WHO GMP.
- GMP system was first incorporated in India in 1988 in Schedule M of Drugs and Cosmetics Rules, 1945. It was revised in 2018, bringing them on par with WHO standards.
- At present, only 2,000 of 10,500 manufacturing units in the country were found to be compliant with WHO-GMP standards.
Revised GMP Guidelines:
- The new guidelines introduce a pharmaceutical quality system, which emphasizes the establishment of a comprehensive quality management system throughout the manufacturing process.
- Companies are now required to implement quality risk management practices to identify potential risks to the quality of their products and take appropriate preventive measures.
- Companies are now required to conduct stability studies based on climate conditions.
- The new guidelines emphasize the use of computerized systems to manage GMP-related processes.
- Companies with over Rs 250 crore turnover must adopt the revised GMP within six months, while smaller enterprises having a turnover of less than 250 crore have a year.
- The new schedule also lists out the requirements for additional types of products, including biological products, agents with radioactive ingredients, or plant-derived products.
Significance of Revised GMP guidelines:
- Implementation of the new norms will bring the Indian industry on par with global standards.
- There has been a string of incidents where other countries have reported alleged contamination in India-manufactured syrups, eye-drops, and eye ointments.
- The improved standards will ensure that pharmaceutical companies follow standard processes, quality control measures, and do not cut corners, improving the quality of medicines available in India as well as sold in the global market.
- It will improve the quality of drugs in the domestic markets.
Source: Indian Express
WMO: 2022 State of the Climate in Asia Report
Tags: GS-II: Important reports
In News:
WMO report highlights Droughts, floods, and high temperatures as major disasters in Asia in 2022.
About WMO: 2022 State of the Climate in Asia Report
- The World Meteorological Organisation (WMO) has recently released the “2022 State of the Climate in Asia” report.
- It has been compiled by WMO in collaboration with National Meteorological and Hydrological Services (NMHSs), research institutions, and UN agencies.
- The report summarizes the climate conditions and extreme events experienced in Asia during 2022 with an objective to assess the socioeconomic impact of extreme climate events in the region.
- It provides a comprehensive overview of temperature trends, precipitation patterns, glacier changes, cyclones, floods, and more.
- Major findings:
- 2022 has been the second or third warmest year on record globally while the average surface temperature exceeded indicates a significant warming trend.
- There have been disparities in precipitation with regions like parts of Iraq, Hindu Kush, Ganges, and Brahmaputra Rivers experiencing deficits.
- An alarming reduction in glacier masses across the High Mountain Asia region with glaciers, such as Urumqi Glacier No. 1 in eastern Tien Shan, showed significant negative mass balances.
- Nearly 25 named tropical cyclones formed over the western North Pacific Ocean and the South China Sea with Nanmadol typhoon being the strongest tropical cyclone of the year.
- Economic losses from floods exceeded the 20-year average, notably affecting Pakistan, China, and India while drought-related economic damages were estimated to be around $7.6 billion in Asia.
- The report emphasized the significance of mitigating climate change to prevent further damage to the environment and societies in Asia.
- These findings will serve as a valuable resource for policymakers, researchers, and the public to better understand the ongoing climate crisis and its regional implications.
- Overall, the WMO report will help to raise awareness about the urgency of taking action to adapt to and mitigate the impacts of climate change in Asia.
Source: The Hindu
Genetic Diversity in the Indian Population
Tags: GS-III: Genetic studies
In News:
Study links Endogamy to persistence of harmful Genetic Variants in India
About Genetic Diversity in the Indian Population:
- Jeffrey Wall and colleagues from the University of California has recently conducted a study involving around 5,000 individuals from India, Pakistan, and Bangladesh.
- Whole-genome sequencing was performed to detect genetic changes, including deletions, insertions, and alterations.
- India is known for its remarkable cultural and linguistic diversity, and this diversity extends to its genetic makeup consisting of a multitude of ethnicities, languages, religions, and cultural practices.
- This diversity is reflected in the genetic composition of the population, with distinct genetic variations across different regions and communities.
- Major findings:
- Genetic differences exist between various regions of India due to historical and geographical factors as different ethnic groups within India have unique genetic traits and variations.
- These variations can influence susceptibility to diseases, responses to medications, and overall health profiles.
- Endogamy has led to genetic isolation in many Indian communities resulting in the preservation of specific genetic traits and the emergence of unique genetic variants within these communities.
- Endogamy and consanguineous marriages contribute to higher levels of inbreeding within some Indian communities.
- It has increased the likelihood of individuals carrying two identical genetic variants for a gene (homozygosity), which can lead to the expression of recessive genetic disorders.
- The unique genetic makeup of the Indian population influences the occurrence of disorders such as diabetes, heart diseases, and certain types of cancers.
- Many health traits and disorders are influenced by multiple genes and environmental factors, making their genetic analysis complex.
- Genetic studies provide insights into the genetic basis of diseases, leading to personalized medicine approaches and will help in tailoring healthcare interventions for different population groups.
- Genetic research can also contribute to disease prevention, early diagnosis, and more effective treatments.
- However, Studying the genetic diversity of India’s population requires comprehensive data collection from diverse communities.
- Other issues include ethical considerations, privacy concerns, and the need for informed consent which are critical aspects of genetic research.
- Overall, Genetic diversity studies in India will go a long way to contribute to the global understanding of human genetics and its implications for health and wellness.
Source: The Hindu
Deepor Beel
Tags: GS – 3 Conservation, Environmental Pollution & Degradation
Why in news?
Deepor Beel, a vital wetland in Guwahati, Assam, faces anthropogenic threats despite its protected status.
About:
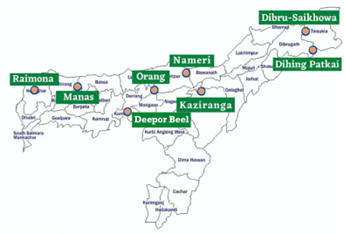
- Word ‘deepor’ comes from the Sanskrit word dipa, which means elephants and ‘beel’ means lake in Assamese.
- It is one of the largest freshwater lakes in Assam and an Important Bird Area by Birdlife International.
- Deepor Beel has been designated as a Ramsar Site in November 2002 and it is the only Ramsar site in Assam.
- It is located towards the southwest of Guwahati city, Assam and is the erstwhile water channel of River Brahmaputra.
- It constitutes a unique habitat for aquatic flora and avian fauna.
- Deepor Beel adjoins the Rani Reserve Forest from where herds of elephants come periodically to forage in the wetland.
- Some globally threatened birds are supported, including Spot-billed Pelican, Lesser Greater Adjutant Stork and Baer’s Pochard.
Source: Down to Earth
Tamil Palm manuscripts: Gnanamuyarchi
Tags: GS –1 Ancient History
Why in news?
Recently, Palm manuscripts from the 18th Century titled Gnanamuyarchi have been discovered in an Armenian monastery in Northern Itlay.
About:

- A manuscript is a handwritten or typewritten document, usually historical or literary in nature, before the age of printing. For example, ancient religious Sanskrit texts written on palm or birch leaf.
More in News (About Gnanamuyarchi)
- The manuscript could be a copy of the first Tamil translation of Spiritual Exercise, written by St. Ignatius of Loyola in the 16th century.
- The translation was mostly done by Michele Bertoldi, known in Tamil as Gnanaprakasasamy.
- The manuscript was initially misclassified as ‘Indian Papyrus Lamulic Language–XIII Century,’ unaware that they were written in Tamil.
- The monastery authorities think the manuscripts might have been brought to Italy by Armenians in Chennai.
Source: The Hindu
Adichanallur archaeological site (Tamil Nadu)
Tags: GS –1 Art & Culture
Why in news?
Recently, Union Finance Minister laid the foundation stone for the ‘Iconic Site Museum’ at the Adichanallur site.

About:
- Adichanallur is an ancient and historical Iron-age burial site located in Thoothukudi District Tamil Nadu, set along the banks of the Tamirabarani (Porunai) river.
- It holds significance in showcasing the megalithic culture.
- It is one of the five sites selected as ‘Iconic sites’ in the budget 2020-21 for development.
- Other sites are Rakhigarhi (Haryana), Hastinapur (UP), Dholavira (Gujarat), and Shivsagar (Assam).
Other significant initiatives are:
- Development of ‘Panchtheerth’ sites based on Babasaheb Ambedkar’s life.
- Construction of the National War Memorial and National Police Memorial in Delhi
- Establishment of ten new Tribal Freedom Fighter Museums
- Heritage sites like Somnath and Kashi Vishwanath Temple have been revitalized.
- Tourism circuits under the Swadesh Darshan Scheme, such as the Buddhist, Ramayana, Coastal, Desert, and Himalayan Circuits, are being established.
- Over 3 lakh manuscripts containing over 3 crore pages have been digitized for knowledge preservation.
- Plans for a new National Museum in Delhi with 950 rooms spread across the North and South Blocks have been announced.
- ‘Pradhanmantri Sangrahalaya’ has been established to honour every Prime Minister of India since Independence.
Source: PIB Gov.
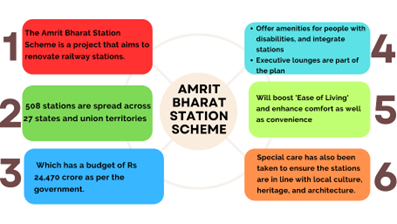
Amrit Bharat Station Scheme (ABSS)
Tags: GS –2 Government Policies & Interventions
Why in news?
Recently, PM Narendra Modi laid the foundation stone for the redevelopment works of 508 railway stations in the country through video conferencing under the Amrit Bharat Station Scheme.
About:
- The Amrit Bharat Station Scheme (ABSS) was launched by the Ministry of Railways in February 2023 with the aim of modernizing and enhancing railway stations across India.
- Amrit Bharat Station Scheme envisions a comprehensive transformation of railway stations, creating modern and passenger-friendly spaces while also supporting local businesses and promoting India’s heritage and culture.
- Objectives of the ABSS:
- The ABSS aims at enhancing the facilities beyond the Minimum Essential Amenities.
- It also aimed at construction of Roof Plazas and City Centres at the station.
- It caters for the introduction of new amenities as well as upgradation and replacement of existing amenities.
Proposed features of Amrit stations:
- All Amrit stations will adhere to green building standards, contributing to environmental sustainability.
- This will be in line with the government’s aims to make India’s railway network operate on net zero emissions by 2030.
- Each station will embody both modern aspirations and ancient heritage, showcasing the country’s rich cultural history.
- Stations will be designed based on specific themes, integrating local landmarks and cultural elements.
- E.g., Jaipur station’s design will include elements resembling the iconic Hawa Mahal and Amer Fort of Rajasthan.
More Information:
- The 508 stations that have been selected for redevelopment are located in 27 states and union territories of India, covering all regions and zones.
- Some of the states with the highest number of stations are Uttar Pradesh and Rajasthan with 55 each, Bihar with 49, Maharashtra with 44, etc.
- The scheme also envisages the participation of private sector, state governments and local bodies in the redevelopment process.
Source: PIB Gov.
Nuclear Medicine
Tags: GS –3 Health
Why in news?
Recently, India has expressed its support for South Africa’s Integrated Early Warning systems and Russia’s BRICS Collaboration in Nuclear Medicine.
About:
- Nuclear medicine uses radioactive material inside the body to see how organs or tissue are functioning (for diagnosis) or to target and destroy damaged or diseased organs or tissue (for treatment).
- It involves the use of small amounts of radioactive materials, known as radiopharmaceuticals, which are introduced into the body.
- These substances emit gamma rays that can be detected by specialized cameras to create images of organs and tissues.
- This imaging technique helps in diagnosing various conditions, such as cancer, heart disease, and bone disorders, by providing detailed information about the functioning and structure of internal organs.
- Nuclear medicine treatments involve using radioactive substances to target and destroy specific cells or tissues, such as cancer cells.
Source: PIB Gov.
FAQs
Q: What are daily current affairs?
A: Daily current affairs refer to the most recent and relevant events, developments, and news stories that are happening around the world on a day-to-day basis. These can encompass a wide range of topics, including politics, economics, science, technology, sports, and more.
Q: Why is it important to stay updated with daily current affairs?
A: Staying updated with daily current affairs is crucial because it helps individuals make informed decisions in their personal and professional lives. It enables people to understand the world around them, stay aware of significant events, and engage in informed discussions about important issues.
Q: Where can I access daily current affairs information?
A: There are various sources for daily current affairs, including newspapers, news websites, television news broadcasts, radio programs, and dedicated apps or newsletters. Social media platforms are also widely used to share and access current affairs information.
Q: How can I effectively incorporate daily current affairs into my routine?
A: To incorporate daily current affairs into your routine, consider setting aside specific times each day to read or watch news updates. You can also subscribe to newsletters or follow news apps to receive curated content. Engaging in discussions with peers or participating in online forums can further enhance your understanding of current events.
Q: What are some tips for critical analysis of daily current affairs?
A: When analyzing daily current affairs, it’s essential to cross-reference information from multiple sources to ensure accuracy. Additionally, consider the source’s credibility and bias, if any. Develop the ability to identify the main points and implications of news stories, and critically evaluate the significance and impact of the events reported.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here


