
In today’s daily current affairs briefing for UPSC aspirants, we explore the latest developments that hold relevance for the upcoming civil services examination. Our focus today includes a critical analysis of recent policy changes, international affairs, and national developments, all of which play a pivotal role in shaping the socio-political and economic landscape of India. Stay informed and stay ahead in your UPSC preparations with our daily current affairs updates, as we provide you with concise, well-researched insights to help you connect the dots between contemporary events and the broader canvas of the civil services syllabus.
Contents
- 1 Intellectual property protection in agriculture
- 2 X-class solar flare
- 3 LIGO India
- 4 UAE and Space
- 5 India signs the US-led Artemis Accords
- 6 Marine Heatwave
- 7 Variable Rate Reverse Repo Auctions (VARRRs)
- 8 2,200 earthquakes in Iceland in 24 hours
- 9 World Investment Report
- 10 Peste des petits ruminants (PPR)
- 11 Ex SALVEX
- 12 Churachandpur’ in Manipur
- 13 Indonesia
- 14 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 14.1 Q: What are daily current affairs?
- 14.2 Q: Why is it important to stay updated with daily current affairs?
- 14.3 Q: Where can I access daily current affairs information?
- 14.4 Q: How can I effectively incorporate daily current affairs into my routine?
- 14.5 Q: What are some tips for critical analysis of daily current affairs?
- 15 In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
Intellectual property protection in agriculture
Tag: GS-3 Intellectual property right
In News:
The Delhi High Court upheld a decision by the Plant Variety Protection and Farmers’ Rights Authority (PPVFRA) to cancel the intellectual property rights previously awarded to PepsiCo India for a potato variety it had developed.
About the case
- The potato variety known as FL 2027, which has characteristics such as high dry matter and low sugar content, making it ideal for chip production, was developed in 1996 by a breeder working for a division of PepsiCo Inc.
- PepsiCo India obtained a certificate of registration from the Plant Variety Protection and Farmers’ Rights Authority (PPVFRA) in 2016, granting them exclusive rights to commercially produce, sell, market, distribute, import, or export FL 2027 for a period of six years.
- Through contract cultivation and buy-back agreements at predetermined prices, approximately 14,000 farmers in India grew FL 2027.
Revocation of registration:
- PPVFRA revoked the registration for FL 2027 in 2021 and rejected PepsiCo India’s application for renewal of its registration, for lack of novelty.
- PepsiCo challenged both orders before the Delhi HC. The court upheld the PPVFRA’s decision.
- The HC has faulted PepsiCo for wrongly applying for registration of FL 2027 under the category of “new variety” and giving an incorrect date for its first commercialisation.
Plant Variety Protection and Farmers’ Rights Act 2001:
The Plant Variety Protection and Farmers’ Rights Act of 2001 aims to achieve the following objectives:
- Establishing an effective system for safeguarding plant varieties and protecting the rights of both farmers and plant breeders.
- Encouraging the advancement and creation of new plant varieties.
- Recognizing and safeguarding the rights of farmers in preserving, enhancing, and providing access to plant genetic resources for the development of new plant varieties.
- Promoting agricultural development by protecting the rights of plant breeders and encouraging investment in research and development for the creation of new plant varieties.
- Supporting the growth of the seed industry in the country, thereby ensuring the availability of high-quality seeds and planting material for farmers.
Rights granted under the Act include:
- Breeders’ Rights: Breeders are granted exclusive privileges to produce, sell, market, distribute, import, or export the protected plant variety.
- Researchers’ Rights: Researchers are permitted to utilize any of the registered varieties for conducting experiments or research purposes.
- Farmers’ Rights: Farmers who have developed or evolved a new plant variety are entitled to registration and protection under the same provisions as breeders. Additionally, farmers’ varieties can also be registered as extant varieties, meeting the criteria of distinctiveness, uniformity, and stability, even if they lack novelty.
Implementation of the Act: Ministry of agriculture and farmers welfare established the PPVFRA in 2005 for the implementation of the provisions of the Act.
Source: Indian Express
X-class solar flare
Tag: GS-1 Physical Geography; Important Geophysical Phenomena
In News:
A powerful X-class flare flashed at Earth, causing radio blackout for about one hour on the day side of Earth, in parts of southeast Asia, Australia, and New Zealand.
About Solar Flares:
- Solar flares are giant explosions on the sun that send energy, light and high speed particles into space which are often associated with solar magnetic storms known as coronal mass ejections (CME).
- CMEs are huge bubbles of radiation and particles from the Sun which explode into space at very high speed when the Sun’s magnetic field lines suddenly reorganise.
- They are seen as bright areas on the sun and they can last from minutes to hours.
- In a matter of just a few minutes, solar flares can heat the material to many millions of degrees and produce a burst of radiation across the electromagnetic spectrum, including from radio waves to x-rays and gamma rays.
Impact of Solar flares:
- They can affect radio communications, power grids and navigation signals, because the extreme solar radiation ionizes the parts of the planet’s upper atmosphere, degrading high-frequency radio waves that travel there.
- Solar activity triggers energetic displays of Northern Lights, or aurora borealis, sometimes pushing them further south than their normal Arctic occurrence.
- Solar flares can disorient GPS, knock satellites out of orbit and affect the spacecraft and astronauts in the space centres.
Trends of Solar flares:
- More solar flares and eruptions are predicted with increase in frequency, as the sun reaches its peak of 11-year solar cycle in 2025.
- The Sun has already produced three moderate “M-class” flares in the past day, and there is a forecast for more M-class flares in the coming days, with a slight chance of another X-class flare occurring.
Source: Science Expert
LIGO India
Tag: GS 3-Scientific Innovations & Discoveries
In News:
An advanced gravitational wave detector called the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-wave Observatory (LIGO) is being planned to be built in Hingoli district of Maharashtra. It will be the world’s third facility after two LIGO setups in the US.
About LIGO- India Project:
- LIGO is an international network of laboratories that detect the ripples in spacetime produced by the movement of large celestial objects like stars and planets.
- LIGO-India is a collaboration between the LIGO Laboratory (operated by Caltech and MIT in the US) and three Institutes in India.
- It will be built by the Department of Atomic Energy (DAE) and DST, with a memorandum of understanding with the National Science Foundation, the US, along with several national and international research and academic institutions.
Gravitational Waves:
- General theory of Relativity predicted that moving objects would generate gravitational waves in spacetime which can cause a temporary deformation in a body when it comes in contact.
- When a gravitational wave passes the Earth, the Earth gets squeezed in one direction, and bulges in the perpendicular direction.
- But as gravity is the weakest of all natural forces, the deforming effect of gravitational waves is extremely tiny.
Significance of LIGO India:
- Brings India as an active collaborator in a number of international science projects such as Large Hadron Collider experiments, and ITER, creation of a thermonuclear reactor etc.
- The project promises huge spin-off benefits for its science and technology sector since India has not yet built a cutting-edge scientific facility on this scale on its own soil.
- It gives a more precise measurement and understanding of how fast the universe is expanding.
Source: The Hindu
UAE and Space
Tags: GS-3: Space
In News:
UAE makes an ambitious foray in the field of space exploration and is emerging as a major player in the global space industry.
About UAE and Space:
- The UAE has recently established a National Space Fund worth AED 3 billion (₹6,600 crore) to strengthen its position in the space sector.
- The fund aims to consolidate the UAE’s role in space exploration and diversify the national economy besides nurturing young talents in emerging space technologies.
- Major projects:
- The first project funded by the National Space Fund is the development of a constellation of advanced remote sensing satellites.
- The country’s flagship project, the Emirates Mars Mission, launched the Hope Probe in 2020, marking the first-ever Arab mission to study the Martian atmosphere and climate.
- In addition to Mars exploration, the UAE is actively involved in lunar missions, with plans for the Emirates Lunar Mission 2024 and the development of a new lunar rover named Rashid 2.
- The UAE has also long-term plans to establish the first human settlement on Mars by 2117 in collaboration with international space institutions.
- It has also trained its astronaut Sultan Al Neyadi for a mission to the International Space Station for sharing insights about life in space.
- The UAE’s space program has not only contributed to scientific advancements but also created job opportunities, with over 3,200 jobs generated in the sector.
- The UAE’s space ambitions are not limited to its border as other Gulf countries, such as Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, and Saudi Arabia, are also collectively driving the growth of the space industry.
- The UAE, Bahrain, and Saudi Arabia are also signatories of the Artemis Accords, which aim to facilitate crewed exploration of the Moon by 2024.
- Overall, the UAE’s space program is driven by the vision to transition to a post-oil economy, promote science and technology and firmly establishing itself as a key player in the global space sector.
Source: The Hindu
India signs the US-led Artemis Accords
Tags: GS-3:International Agreements
In News:
India signs Artemis Accords reflecting its interest in participating in global efforts and collaborations in space exploration.
About India and Artemis Accord:
- India recently became the 27th signatory of the Artemis Accords, a US-led international partnership for planetary exploration and research.
- The Artemis Accords were created in 2020 as a set of principles and guidelines for the civil exploration and use of the Moon, Mars, comets, and asteroids.
- The Accords are closely linked to the Artemis Program, which aims to return astronauts to the lunar surface, establish a space camp, and conduct deep space exploration.
- The Artemis Accords have been signed by 26 other countries, including Japan, Australia, the UK, France, and Canada.
- Major highlights:
- The Accords provide a framework for international cooperation in advancing the governance of space exploration, including the extraction of space resources.
- It offers potential benefits for India, such as fast-tracking its human spaceflight capabilities and ambitions through collaborations with other signatory countries.
- Collaboration with NASA and other Accords signatories can enhance India’s contributions to future lunar missions and the establishment of the Gateway, a lunar orbital station.
- Signing the Accords can also provide India with opportunities to shape the governance of resource extraction on the Moon and contribute to future crewed missions.
- However, to fully leverage the benefits of the Accords, India needs to increase its space budget to support space science missions and technology development.
- Overall, India’s signing of the Accords demonstrates its commitment to international cooperation and its willingness to contribute to the advancement of space exploration on a global scale.
Source: Indian Express
Marine Heatwave
Tags: GS – 1: Geography (Climate), GS – 3: Environment (Environmental pollution and degradation)
Why in News:
Recently experts are reporting that an ongoing heatwave in India’s eastern sea is causing extreme rain in its northwest.
Reasons for heavy rainfall in Northwest India:
- During the monsoon, the northern Bay of Bengal tends to be warm as it enables the monsoon winds blowing from the southwest to cross over into the Bay of Bengal and bring moisture into the Indian subcontinent.
- However, the northern Bay of Bengal currently has been experiencing an intense marine heatwave. Due to this, it is warmer than usual and may be contributing to the extreme rainfall in northwest India.
Marine Heatwaves:
- A marine heat wave is a coherent area of extreme warm sea surface temperature that persists for days to months.
- The most common cause of marine heat waves are ocean currents which can build up areas of warm water and air-sea heat flux, or warming through the ocean surface from the atmosphere.
- Sunlight passes through the atmosphere and heats the surface of the ocean. If there are weak winds this warm water doesn’t mix with the cooler waters below. It sits on top and continues to heat leading to marine heat waves
Source: Down to Earth
Variable Rate Reverse Repo Auctions (VARRRs)
Tags: GS – 3: Indian Economy (Monetary Policy)
Why in News:
Recently, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has said that it will conduct a three-day variable rate reverse repo (VRRR) auction for Rs 2 lakh crore.
Variable rate reverse repo Auction (VRRR):
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) uses various ways to increase or decrease liquidity in the banking system. Repo rate is the rate at which the central bank gives loans to commercial banks against government securities.
- Reverse repo rate is the interest that RBI pays to banks for the funds. Variable rate reverse repo (VRRR) is a sub-type of reverse repo.
- VRRR is usually undertaken to reduce surplus liquidity by withdrawing existing cash in the system.
- RBI has been conducting VRRR every day since June 30 to ensure that the overnight call money rate remains close to the target rate of 6.50 per cent.
Reasons for RBI conducting auctions:
- Typically, governments (Central and State) pay contractors and disburse salaries towards the end of a month or the first week of next month. So, Banks have inflows.
- Return of ₹2,000 bank notes by the public is adding to the systemic liquidity. The RBI recently said that ₹2.72-lakh crore, or 76 per cent of the ₹2,000 banknotes in circulation as on May 19, have returned to the banking system as of June-end.
- So, the RBI could continue intervening via reverse repo auctions to keep liquidity close to neutral.
Source: The Hindu Business Line
2,200 earthquakes in Iceland in 24 hours
Tag: GS-1 Geography
Why in news?
Almost 2,200 earthquakes were recorded in the area around Iceland’s capital Reykjavik in the past 24 hours.
About
- Iceland is Europe’s biggest and most active volcanic region. The North Atlantic island straddles the Mid-Atlantic Ridge- separating the Eurasian and North American tectonic plates.
- Iceland experiences frequent volcanic activity, due to its location both on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, a divergent tectonic plate boundary, and over a hot spot.
- The Mid-Atlantic Ridge is a mid-ocean ridge (a divergent or constructive plate boundary) located along the floor of the Atlantic Ocean and part of the longest mountain range in the world. In the
- North Atlantic, the ridge separates the North American from the Eurasian Plate and the African Plate, north and south of the Azores Triple Junction.
Mount Fagradalsfjall
- Fagradalsfjall is a tuya volcano formed in the Last Glacial Period on the Reykjanes Peninsula, around 40 kilometres from Reykjavík, Iceland.
- Fagradalsfjall is also the name for the wider volcanic system covering an area 5 kilometres wide and 16 kilometres long between the Svartsengi and Krýsuvík systems.
Source: Hindustan Times
World Investment Report
Tag: GS-3 Economy
Why in news?
Recently, United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD) released World Investment Report 2023.
About
- According to UNCTAD FDI in developing countries in Asia remained flat year-on-year at $662 billion during 2022 despite clocking about half of global inflows.
- Despite maintaining a flat growth rate India and ASEAN highlighted as the most buoyant regions for the FDI.
- The report also highlighted a global decline in FDI, with a 12% drop to $1.3 trillion in 2022.
- According to the report annual investment required to support clean energy transitions amounts to $1.7 trillion, while developing countries attracted only $544 billion in FDI for clean energy in 2022.
- The report further reveals a substantial investment gap across all sectors of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), which has increased to over $4 trillion per year from $2.5 trillion in 2015.
Source: Economic Times
Peste des petits ruminants (PPR)
Tag: GS-3 Science, Animal disease
Why in news?
About 60 sheep and goats died and more than 200 fell sick due to the outbreak of a highly contagious disease at Hadsar pasture near Tindi of Lahaul-Spiti.
About
- Peste des petits ruminants (PPR), also known as sheep and goat plague, is a highly contagious viral disease of small ruminants (goats and sheep).
- The virus is closely related to the rinderpest virus, which was eradicated in 2011.
- PPR is characterized by fever, respiratory and digestive symptoms, and high mortality rates. There is no specific treatment for PPR, but vaccination is effective in preventing the disease.
- PPR is widespread in Africa, Asia, and the Middle East. The disease has also been reported in Europe and South America. PPR is a major threat to small ruminant production in these regions. The disease can cause significant economic losses, as well as social and environmental impacts.
- The World Organisation for Animal Health (WOAH) and the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) have launched a global campaign to eradicate PPR by 2030. The campaign is focused on vaccination, surveillance, and risk management.
Key facts about PPR:
- The virus is spread through direct contact with infected animals, as well as through indirect contact with contaminated materials.
- The incubation period for PPR is typically 3-7 days.
- Clinical signs of PPR can include fever, respiratory symptoms (such as coughing and sneezing), diarrhea, and neurological signs (such as staggering and seizures).
- The mortality rate for PPR can be high, ranging from 30% to 70%.
- There is no specific treatment for PPR, but supportive care can help to improve the survival rate of infected animals.
- Vaccination is the most effective way to prevent PPR.
Source: Hindustan Times
Ex SALVEX
Tag: GS-3 Science Defence
Why in news?
Recently, Indian Navy and the US Navy joined forces for the highly anticipated seventh edition of the IN-USN Salvage and Explosive Ordnance Disposal (EOD) exercise.
About
- SALVEX is an exercise aimed to strengthen US and Indian divers’ capability in diving and salvage techniques. It was started in 2005 between USA and India.
- In 2011, US and Indian Navy divers began the joint Salvage and Explosive Ordnance Disposal (EOD) exercise, SALVEX series of exercises off Port Blair in the Andaman Sea, India.
- The exercise saw participation from both the navies which included the ships – INS Nireekshak and USNS Salvor in addition to Specialist Diving and EOD teams.
Source: Financial Expresss
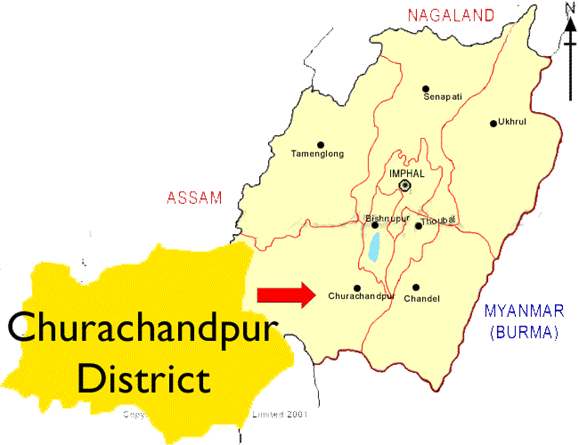
Churachandpur’ in Manipur
Tag: GS-1 Geography
Why in news?
Cross over to Manipur’s Churachandpur district — where the violence first began — from its boundary with Bishnupur district, and the efforts to erase that name are evident at every turn.
About
- Churachandpur district in the Indian state of Manipur is a land of diverse cultures and traditions. It is home to a number of tribal groups, the majority of which belong to the Chin-Kuki-Mizo-Zomi (CKMZ) group.
- The district is also home to a number of historical sites, including the Lamka Fort, which was built in the 18th century by the Kuki chieftain Thangal General.
- Churachandpur district is named after the Meitei King Churachand Singh, who was the Maharaja of Manipur Kingdom. The district was previously known as Manipur South District, and it came into existence in 1969 along with the district reorganization of Manipur.
- The district is located in the southwestern part of Manipur, and it is bordered by Mizoram to the south, Nagaland to the east, Assam to the west, and the Churachandpur district itself to the north. The district is home to a number of rivers, including the Khuga River, the Tuivai River, and the Barak River.
- The name Churachandpur — which was first introduced in the area in 1921 — draws from Churachand Singh, the king of the Manipur Kingdom from 1891 to 1941.
- After the end of the Anglo-Kuki War in 1919, which the Kukis lost, the administration of the hills surrounding the Manipur kingdom was re-organised and brought under regular administrative control by the British, who divided it into three sub-divisions.

Source: Indian Express
Indonesia
Tag: GS-1 Geography
Why in news?
The IEA expects Indonesia, the world’s largest nickel producer, to meet two thirds of the world’s needs for the metal. According to data from the Indonesian government, about 50 nickel mining companies currently operate in North Konawe Regency, across the water from Labengki Island.
About
- Indonesia, country located off the coast of mainland Southeast Asia in the Indian and Pacific oceans. It is an archipelago that lies across the Equator and spans a distance equivalent to one-eighth of Earth’s circumference.
- Indonesia is the World’s largest Island Country with more than 17,000 islands. It has the 4th largest population in the world. It is the country having the highest Muslim population.
- India and Indonesia have shared two millennia of close cultural and commercial contacts. The Hindu, Buddhist and later Muslim faith travelled to Indonesia from the shores of India. The Indonesian folk art and dramas are based on stories from the great epics of Ramayana and Mahabharata. T
The Major Active Volcanoes
- Mount Merapi (Java)
- Mount Semeru (Java)
- Mount Krakatoa (Sunda Strait)
- Mount Tambora (Sumbawa)
- Mount Agung (Bali)
The Major Mountains:
- Mount Kerinci (Sumatra)
- Mount Rinjani (Lombok)
- Mount Semeru (Java)
- Mount Lawu (Java)
- Mount Merbabu (Java)
Source: BBC News
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are daily current affairs?
A: Daily current affairs refer to the most recent and relevant events, developments, and news stories that are happening around the world on a day-to-day basis. These can encompass a wide range of topics, including politics, economics, science, technology, sports, and more.
Q: Why is it important to stay updated with daily current affairs?
A: Staying updated with daily current affairs is crucial because it helps individuals make informed decisions in their personal and professional lives. It enables people to understand the world around them, stay aware of significant events, and engage in informed discussions about important issues.
Q: Where can I access daily current affairs information?
A: There are various sources for daily current affairs, including newspapers, news websites, television news broadcasts, radio programs, and dedicated apps or newsletters. Social media platforms are also widely used to share and access current affairs information.
Q: How can I effectively incorporate daily current affairs into my routine?
A: To incorporate daily current affairs into your routine, consider setting aside specific times each day to read or watch news updates. You can also subscribe to newsletters or follow news apps to receive curated content. Engaging in discussions with peers or participating in online forums can further enhance your understanding of current events.
Q: What are some tips for critical analysis of daily current affairs?
A: When analyzing daily current affairs, it’s essential to cross-reference information from multiple sources to ensure accuracy. Additionally, consider the source’s credibility and bias, if any. Develop the ability to identify the main points and implications of news stories, and critically evaluate the significance and impact of the events reported.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here

