In today’s daily current affairs briefing for UPSC aspirants, we explore the latest developments that hold relevance for the upcoming civil services examination. Our focus today includes a critical analysis of recent policy changes, international affairs, and national developments, all of which play a pivotal role in shaping the socio-political and economic landscape of India. Stay informed and stay ahead in your UPSC preparations with our daily current affairs updates, as we provide you with concise, well-researched insights to help you connect the dots between contemporary events and the broader canvas of the civil services syllabus.
Contents
- 1 India’s Supply Chain Opportunities
- 2 Reasons behind Morocco’s earthquake
- 3 Global Biofuel Alliance
- 4 National e-Vidhan Application
- 5 Nipah Virus
- 6 Araku Coffee
- 7 2nd Berlin Forum on Chemicals and Sustainability
- 8 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 8.1 Q: What are daily current affairs?
- 8.2 Q: Why is it important to stay updated with daily current affairs?
- 8.3 Q: Where can I access daily current affairs information?
- 8.4 Q: How can I effectively incorporate daily current affairs into my routine?
- 8.5 Q: What are some tips for critical analysis of daily current affairs?
India’s Supply Chain Opportunities
Tag: GS-2 Global Trade and International relations
In News:
Amidst the efforts to cut dependence on China-centric global supply chains, the G20 announcement on the India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC) has the potential to make India an Asian hub in global supply chains.
About India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC):
- The launch of IMEC was announced by the Indian PM at the G20 leader’s summit. The project includes India, UAE, Saudi Arabia, the European Union, France, Italy, Germany and the US.
- The rail and shipping corridor is part of the Partnership for Global Infrastructure Investment (PGII), a collaborative effort by G7 nations to fund infrastructure projects in developing nations. PGII is considered to be the bloc’s counter to China’s Belt and Road Initiative.
- The corridor will include a rail link as well as an electricity cable, a hydrogen pipeline, and a high-speed data cable to enable greater trade among the involved countries.
What are Supply Chains?
- Supply chains, also known as global production networks or global value chains, refer to the geographical location of various stages of production such as design, production, assembly, marketing, and service activities cost-effectively.
- The shift in industrial production from local and regional supply to global supply took place gradually over the last 100 years. Global supply chains have been the leading model of industrial production since the 1980s
Reasons for shifting of global supply chains moving away from China:
- Declining preference for China: Even before the Covid-19 pandemic, Western firms had begun to reduce their reliance on China, and its popularity as a sourcing market was diminishing.
- Shift to cost-effective locations: Some production stages in Chinese supply chains, particularly the labor-intensive ones, are moving to lower-cost locations due to rising wages and supply chain bottlenecks within China, and investor concerns about tighter regulation of foreign firms.
- Risks of concentration of Supply chains in China: The global risks of supply chains concentrated in mainland China and Hong Kong together account for 20% of world exports of intermediate goods.
- Geopolitical relations of China: Internal risks and the country’s trade war with the US, is forcing multinational companies to rethink their global sourcing strategies.
- Considerations of profitability are influencing a trend of relocating production either to friendly countries or back to the US despite the high costs of shifting a supply chain.
India as an attractive supply chain hub:
- Emerging Manufacturing Hubs: India can become a complementary Asian manufacturing hub to China by reaping gains from foreign technology transfers and creating value-adding jobs.
- Mature sectors: Manufacturing sectors in India such as automotives, pharmaceuticals, and electronics assembly are already mature sectors, and likely to emerge as winners in this race.
- Geopolitical and economic factors: WTO lists India as the fifth largest importer of intermediate goods in 2022 Q4, suggesting that geopolitical and economic stability will attract foreign investors.
- New Trade Policy: Trade policy has placed renewed emphasis on preferential trade through a flurry of bilateral deals with trading partners.
- India’s Free Trade Agreements (FTA) with several countries such as UAE-India CEPA, early harvest for the Australia-India FTA. These new deals reflect plans for deep economic integration.
Strategies to promote regional supply chains in South Asia:
- Up scaling the Make in India Programme into a Make in South Asia Programme: India can provide fiscal incentives to Indian manufacturers to expand into Bangladesh and Sri Lanka, which are in apparel supply chains.
- Conclusion of comprehensive bilateral FTA with Bangladesh and Sri Lanka to support regional rules-based trade and investment.
Way Forward:
- Promotion of export-oriented FDI: Maintaining an open-door policy toward FDI in manufacturing and facilitating investment at a high level, with competitive fiscal incentives and the creation of modern SEZs as public-private partnerships.
- Local companies need smart business strategies to join global supply chains as compared to big companies which have advantages due to the larger scale of production access to foreign technology, and ability to spend more on marketing.
- Cautious approach towards adopting China’s interventionist styles as there is a significant risk of government failure and cronyism
- Better targeting of multinationals in new industrial activities in which there may be a potential comparative advantage and better coordination between the central and state governments.
- Upstream investment in tertiary-level education in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics.
Reasons behind Morocco’s earthquake
Tags: GS – 1: Physical Geography (Earthquakes)
Why in News:
Recently, Morocco has been hit by a powerful earthquake with a magnitude of 6.8, causing a death toll exceeding 2,400 people. Its epicenter was located in the Al-Haouz province, in the Atlas Mountains of the historic city of Marrakech.
Reasons for the earthquake in Morocco:
- Morocco is situated in a region where the Eurasian and African tectonic plates converge.
- The Atlas Mountains, where the earthquake occurred, are actively rising due to the convergence of these two large tectonic plates.
- Although the region had not experienced major recorded earthquakes before, stress had been accumulating underground for an extended period due to the slow movement of tectonic plates.
- The Oblique-Reverse Fault is present in areas of compression along the convergent plate boundaries. The stress along these fault lines can induce earthquakes as rocks abruptly shift to release accumulated stress.
Reasons for heavy damage in Morocco:
- The epicenter of the earthquake is roughly 18.5 km below the Earth’s surface. So, it was a very shallow earthquake. Shallow earthquakes carry a much higher amount of energy when they hit the surface.
- The earthquake’s epicenter was in the High Atlas Mountains which is close to the city of Marrakesh, causing it to affect populated areas and infrastructure.
- Earthquakes are not very common in North Africa. Therefore, Morocco was not prepared for such a calamity.
- Many changes were introduced to construction rules after Morocco faced the earthquake in 1960, but buildings in rural areas and older cities were not built to withstand the earthquake. Many houses collapsed in Marrakech, a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
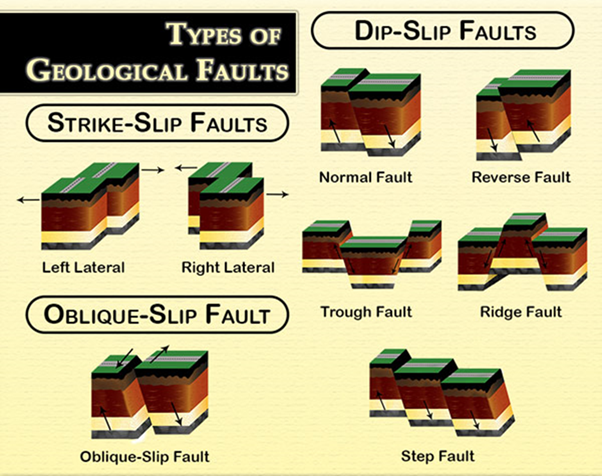
Types of Faults:
- Dip Slips:
- In these faults, the movement is along the direction of the dip plane.
- Vertical movement either up (reverse dip-slip) or down (normal dip-slip) along the fault plane.
- Strike-Slip Faults:
- In these faults, the movement is horizontal along the fault plane and is parallel to the strike of the fault.
- These faults are common where tectonic plates slide past each other horizontally.
- Oblique-Slip Faults:
- These faults show characteristics of both dip-slip and strike-slip faults.
- Movement occurs in two directions – horizontal (strike-slip) and vertical (dip-slip) along the fault plane.
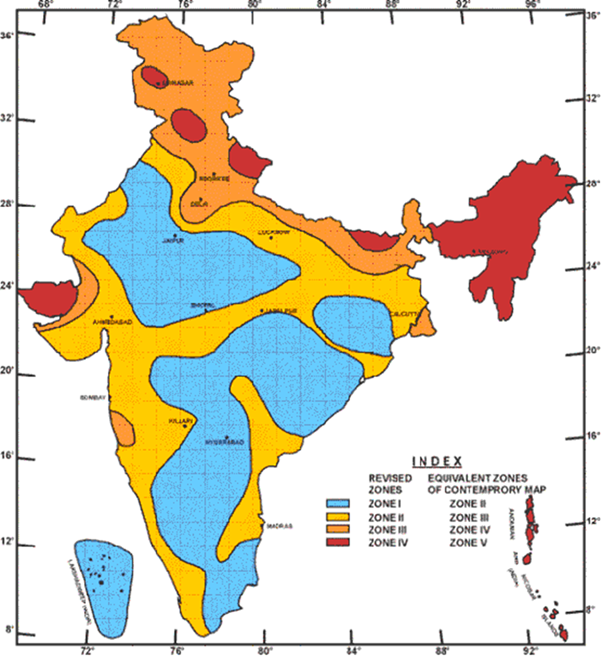
Earthquake prone areas in India:
- The Western Himalayas in India are considered one of the most dangerous seismic zones globally.
- The entire Himalayan region, spanning from the Hindu Kush mountains to Arunachal Pradesh, is at risk of a major earthquake with a magnitude exceeding 8 on the Richter scale.
- This is because of the substantial energy accumulation along fault lines due to the ongoing interaction of various tectonic plates.
Way Forward:
- Earthquakes cannot be accurately predicted because there is currently no equipment or method to detect precursory signals within the Earth that would indicate an impending major earthquake.
- However, we can mitigate their impact. Through integrated studies of the region’s geology, geophysics and geodesy we can find out where there are active earthquake faults.
- We can also estimate how powerful the earthquakes on these faults could be and how often they might happen again.
- The best way to minimise earthquake damage is to improve seismic building design codes to withstand the highest possible seismic activity.
- Traditional homes and rock constructions in mountain villages should be reinforced to prevent future disasters.
Global Biofuel Alliance
Tags: GS – 3: Environment & Ecology (Renewable Energy)
Why in News:
Recently, on the sidelines of the G20 Summit, India has launched the Global Biofuels Alliance, which aims to accelerate the transition to sustainable biofuels and reduce the world’s dependency on traditional fossil fuels.
Biofuels:
- Biofuels are renewable energy sources derived from biomass, such as crop stubble, plant waste, and municipal solid waste.
- Biofuels may be solid, liquid or gaseous.
- Solid: Wood, dried plant material, and manure
- Liquid: Bioethanol and Biodiesel
- Gaseous: Biogas
- Various Generations of Biofuels:
- First generation: It is produced from consumable food items containing starch (rice and wheat), sugar (beets and sugarcane) for bio-alcohols, or vegetable oils for biodiesel.
- Second generation: It is mainly obtained from non-food feedstocks such as forest/industry/agricultural wastes and waste or used vegetable oils.
- Third generation: It is known as ‘algae fuel’ and is derived from algae in the form of both biodiesel and bio-alcohols.
- Fourth generation: Like the third generation, 4G biofuels are made using non-arable land. However, unlike the third, they do not need the destruction of biomass.
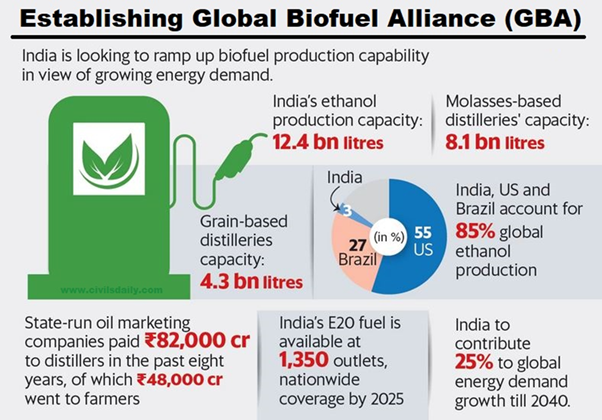
Global Biofuels Alliance:
- It is an India-led Initiative to develop an alliance of Governments, International organizations, and Industry to facilitate the adoption of biofuels.
- A total of 19 countries and 12 international organizations have so far agreed to join the alliance, including both G20 members and non-member countries.
- India, Brazil, and the US are the founding members of the alliance.
- India, the US, and Brazil account for a total of 85 percent of the global ethanol production with the US holding a 55 percent share followed by Brazil at 27 percent and India at 3 percent.
Significance of Global Biofuels Alliance:
- India sees this alliance as a means to advance energy transitions in developing countries and promote a circular economy.
- India, a major oil importer, is working on building its capacity to produce biofuels, particularly from sugarcane and agricultural waste.
- India aims to increase the blending of ethanol in petrol to 20% by 2025 and is establishing compressed biogas (CBG) plants.
- The initiative aligns with India’s goal of transitioning to alternative fuels and reducing its carbon emissions, with a target of achieving net-zero emissions by 2070.
AYUSHMAN BHAV CAMPAIGN
Tag: GS-3, Health Infrastructure
In News:
Recently, the President of India virtually launched the Ayushman Bhav Campaign.
About
Ayushman Bhava is an umbrella campaign that will ensure the optimum delivery of health schemes to every intended beneficiary, including those in the last mile.
Component of Ayushman Bhava Campaign
- Ayushman Apke Dwar 3.0: It aimed at the creation and distribution of Ayushman cards to all remaining eligible beneficiaries;
- Ayushman Mela: Weekly health melas will be held at the level of AB-HWCs and Community Health Centres (CHCs) and
- Ayushman Sabha: A village/ward level sabha to be held to enhance awareness about various health care schemes and services.
- Ayushman Gram Panchayat’: The campaign will eventually ensure gram/nagar panchayat to attain the status of ‘Ayushman Gram Panchayat’ or ‘Ayushman Ward’ with saturation of selected health indicators.

National e-Vidhan Application
Tag: GS-2 Governance
In News:
Recently, the President of India inaugurated the ‘National e-Vidhan Application (NeVA)
About
- The National e-Vidhan Application (NeVA) is a significant component of the “Digital India Programme” by the Government of India, encompassing 44 Mission Mode Projects (MMPs).
- Its primary objective is to facilitate the transition of all State Legislatures into a paperless environment, effectively converting them into ‘Digital Houses.’
- NeVA is designed as a versatile and member-centric application, agnostic to the type of device used. Its purpose is to empower legislators by providing comprehensive information at their fingertips.
- This information includes member contact details, procedural rules, notices, bills, starred/unstarred questions and answers, committee reports, and more, all accessible via handheld devices or tablets.
- As of the present status, 21 State legislatures have entered into Memorandums of Understanding for the implementation of NeVA, with the project receiving approval from 17 of these legislatures.
- The Nodal Ministry overseeing the NeVA initiative is the Ministry of Parliamentary Affairs.

Nipah Virus
Tag: GS-3, Science and Technology
In News:
Two deaths were reported in Kerala due to the Nipah Virus.
About
- Nipah virus (NiV) is a zoonotic virus (it is transmitted from animals to humans) and can also be transmitted through contaminated food or directly between people.
- In infected people, it causes a range of illnesses from asymptomatic (subclinical) infection to acute respiratory illness and fatal encephalitis.
- The virus can also cause severe disease in animals such as pigs, resulting in significant economic losses for farmers.

Araku Coffee
Tag: GS-1 Geography
In News:
Recently, Araku Coffee was gifted to G-20 delegates by the government of India
About
- Araku Valley Arabica coffee can be described as coffee from the Eastern Ghats hilly tracks of Visakhapatnam district of Andhra Pradesh and Odisha region grown at an elevation of 900-1100m Mean Sea Level (MSL).
- The coffee is grown in the hilly terrains of Ananthagiri, Paderu, Pedabayalu, G Madugula, Koraput, etc.
- These coffee beans bear the essence of the valley’s rich soil and temperate climate. Pure Arabica with a rare aromatic profile, Araku Coffee is known for its unique texture and symphony of flavors.
- Farmers grow coffee without the use of machines and chemicals.
- This variety is produced by the tribals, who follow an organic approach in which they emphasize management practices involving substantial use of organic manures, green manuring, and organic pest management practices.
- Araku Coffee is often referred to as “India’s answer to Blue Mountain coffee” due to its excellent flavor profile and premium quality.
2nd Berlin Forum on Chemicals and Sustainability
Tag: GS-3 Environment
In News:
Recently, the environment minister participated in ‘High-Level Dialogue on Human Health and Environment convened under the 2nd Berlin Forum on Chemicals and Sustainability
About
- The 2nd Berlin Forum on Chemicals and Sustainability is a prestigious event focused on offering strategic direction and impetus for addressing critical global concerns related to the responsible handling of chemicals and waste.
- Hosted by the German Federal Ministry for the Environment, Nature Conservation, Nuclear Safety, and Consumer Protection (BMU).
- This forum seeks to galvanize political support and enhance the level of ambition for the ‘ Strategic Approach to International Chemicals Management (SAICM) Beyond 2020 agenda during the forthcoming 5th meeting of the International Conference on Chemicals Management (ICCM5).
- The inaugural Berlin Forum on Chemicals and Sustainability underscored the imperative of establishing a science-policy interface (SPI) for the management of chemicals and waste.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are daily current affairs?
A: Daily current affairs refer to the most recent and relevant events, developments, and news stories that are happening around the world on a day-to-day basis. These can encompass a wide range of topics, including politics, economics, science, technology, sports, and more.
Q: Why is it important to stay updated with daily current affairs?
A: Staying updated with daily current affairs is crucial because it helps individuals make informed decisions in their personal and professional lives. It enables people to understand the world around them, stay aware of significant events, and engage in informed discussions about important issues.
Q: Where can I access daily current affairs information?
A: There are various sources for daily current affairs, including newspapers, news websites, television news broadcasts, radio programs, and dedicated apps or newsletters. Social media platforms are also widely used to share and access current affairs information.
Q: How can I effectively incorporate daily current affairs into my routine?
A: To incorporate daily current affairs into your routine, consider setting aside specific times each day to read or watch news updates. You can also subscribe to newsletters or follow news apps to receive curated content. Engaging in discussions with peers or participating in online forums can further enhance your understanding of current events.
Q: What are some tips for critical analysis of daily current affairs?
A: When analyzing daily current affairs, it’s essential to cross-reference information from multiple sources to ensure accuracy. Additionally, consider the source’s credibility and bias, if any. Develop the ability to identify the main points and implications of news stories, and critically evaluate the significance and impact of the events reported.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here
Visit our YouTube Channel – here


