
In today’s daily current affairs briefing for UPSC aspirants, we explore the latest developments that hold relevance for the upcoming civil services examination. Our focus today includes a critical analysis of recent policy changes, international affairs, and national developments, all of which play a pivotal role in shaping the socio-political and economic landscape of India. Stay informed and stay ahead in your UPSC preparations with our daily current affairs updates, as we provide you with concise, well-researched insights to help you connect the dots between contemporary events and the broader canvas of the civil services syllabus.
Contents
- 1 Arrest Warrants for Hamas Leaders and Israeli Prime Minister
- 2 Utilizing Biomass Cultivation on Degraded Land
- 3 Self Help Groups (SHGs)
- 4 Inter-Services Organisations Act
- 5 Bharal and Himalayan Ibex
- 6 Section 436A
- 7 Emblica chakrabartyi
- 8 International Booker Prize
- 9 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 9.1 Q: What are daily current affairs?
- 9.2 Q: Why is it important to stay updated with daily current affairs?
- 9.3 Q: Where can I access daily current affairs information?
- 9.4 Q: How can I effectively incorporate daily current affairs into my routine?
- 9.5 Q: What are some tips for critical analysis of daily current affairs?
- 10 In case you still have doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
Arrest Warrants for Hamas Leaders and Israeli Prime Minister
Tag: GS-2 IR
In News:
The Prosecutor of the International Criminal Court (ICC) requested arrest warrants against leaders of Hamas and Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu of Israel regarding the October 7, 2023 attacks on Israel and the subsequent war in Palestine.

What is the International Criminal Court (ICC)?
- Background
- The ICC is a permanent court established to prosecute serious international crimes committed by individuals, including genocide, war crimes, crimes against humanity, and aggression.
- It aims to combat global impunity and ensure accountability under international law, regardless of the perpetrator’s rank or status.
- HQ
- The ICC is headquartered in The Hague, The Netherlands.
- Statute
- Before becoming functional in 2002, the ICC’s founding treaty, the Rome Statute, was adopted by the UN General Assembly in 1998 in Rome, Italy.
- Membership
- To become a member of the ICC, countries must sign and ratify the Rome Statute under their respective legislatures.
- Currently, 124 countries are members of the ICC, with African countries comprising the largest bloc. Armenia joined the ICC in February 2024.
- Some notable countries, such as India, China, Iraq, North Korea, and Turkey, have never signed the Rome Statute, while others, including the US, Russia, Israel, and Syria, signed but never ratified it.
Functioning of the ICC
- Judges & Prosecutors
- The ICC conducts investigations through the Office of the Prosecutor and has 18 judges, each serving non-renewable nine-year terms.
- Process
- The ICC operates through pre-trial, trial, and appellate benches.
- The prosecutor conducts preliminary examinations before seeking permission from pre-trial judges to open a full investigation, ensuring the crimes meet a certain gravity threshold.
- Ways to Open Investigations
- Investigations can be initiated when a case is referred by a member country, by the UN Security Council, or by the prosecutor proprio motu.
- Non-member states can also be investigated under certain conditions, such as alleged crimes committed on member states’ territory or with their consent
- Jurisdiction over Israel
- Despite not being a party to the Rome Statute, the ICC has jurisdiction over crimes committed by nationals of both State Parties and non-state Parties, such as Israel, on the territory of a State Party, such as Palestine.
- Palestine’s membership in the Rome Treaty and the ICC’s decision in February 2021 extended its jurisdiction over Palestine, including Gaza and the West Bank, thereby extending to Israel.
Demand of Arrest Warrants by the Office of the Prosecutor
- The Office of the Prosecutor has sought arrest warrants for senior leaders of Hamas and Israeli officials, charging them with crimes against humanity and war crimes.
Accusations on These Leaders
- The charges include crimes such as murder, extermination, torture, rape, persecution, and other inhumane acts as crimes against humanity, and serious violations of the Geneva Conventions as war crimes.
Next Steps
- ICC decisions are binding, but the court relies on state cooperation for enforcement, including making arrests, transferring individuals to the ICC, freezing assets, and enforcing sentences.
- If arrest warrants are issued, all 124 State Parties are obligated to cooperate with the court, making international travel difficult for the accused leaders.
Source: IE
Utilizing Biomass Cultivation on Degraded Land
Tag: GS – 3 Conservation, Environmental Pollution & Degradation GS – 2 Government Policies & Interventions
In News:
Recently, the Principal Scientific Adviser (PSA) to the Government of India convened the inaugural meeting to explore biomass cultivation on degraded land, focusing on green biohydrogen production and bioenergy generation.
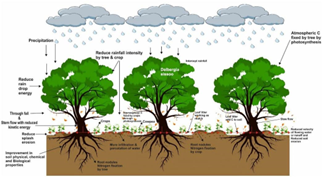
Key Highlights of the Meeting
- Biomass Cultivation Prospects
- Seaweed Cultivation: Discussion on the potential of seaweed cultivation for biomass as a source of bioenergy and the promotion of marine biomanufacturing start-ups.
- Plant-Based Biomass: Deliberation on biomass production using various plants, including algae, molasses, and sugarcane.
- Government Programs and Data Utilization
- National Green Hydrogen Mission Objective: Highlighted the aim to initiate focused pilots for biomass-based green biohydrogen production.
- Ministry of New & Renewable Energy (MNRE) Programs: Overview of various MNRE programs for Bioenergy and the National Biomass Atlas for agri-residue surplus data.
- Economic and Strategic Frameworks
- Data on Biomass: Presentation of the Bhuvan portal by the National Remote Sensing Centre (NRSC) and Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) for biomass availability from agri-residue and degraded Land Mapping, stressing the importance of biomass characterization data.
Biomass Cultivation on Degraded Land
- About Biomass Cultivation on Degraded Land
- Definition: Biomass cultivation on degraded land involves growing organic matter, such as crops or trees, on land rendered unsuitable for conventional agriculture due to factors like soil erosion or deforestation.
- Benefits: Soil restoration, erosion prevention, carbon sequestration, sustainable biohydrogen production, bioenergy generation, and enhanced food security.
- Challenges in Biomass Cultivation on Degraded Land
- Soil Quality: Rehabilitating soil quality is crucial for successful biomass cultivation on degraded land.
- Species Selection and Adaptation: Identifying resilient biomass crops adapted to harsh conditions is challenging.
- Water Availability and Management: Efficient irrigation methods are essential due to water scarcity on degraded land.
- Economic Viability and Market Demand: Initial investments and market demand alignment pose economic challenges.
- Biodiversity and Ecological Impact: Biomass cultivation may impact local ecosystems and biodiversity.
Way Forward
- Cultivation Techniques: Implement strategies to improve soil fertility, such as incorporating organic matter and employing biofloculation techniques.
- Biomass Cultivation with Agroforestry: Integrate fast-growing tree species with native grasses and legumes for multi-tiered cropping systems on degraded land.
- Drones for Degraded Land Diagnostics: Utilize drones with multispectral sensors for quick assessment of degraded land, soil mapping, and biodiversity evaluation.
- Market Development: Develop biomass markets and value chains to ensure economic viability and support rural livelihoods.
UPSC Previous Year Questions
Prelims (2013)
Q. With reference to the usefulness of the by-products of sugar industry, which of the following statements is/are correct?
- Bagasse can be used as biomass fuel for the generation of energy.
- Molasses can be used as one of the feedstocks for the production of synthetic chemical fertilizers.
- Molasses can be used for the production of ethanol.
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)
Source: PIB
Self Help Groups (SHGs)
Tag: GS – 2 GS – 1 Social Empowerment, Welfare Schemes, Government Policies & Interventions, Self Help Groups (SHGs)
In News:
The 26th anniversary of the Kudumbashree mission, which is an SHG, was recently celebrated in Kerala.
What are Self Help Groups (SHGs)?
- Definition and Composition: SHGs are self-governed groups comprising individuals with similar socio-economic backgrounds and objectives. Typically, each SHG consists of five to twenty members sharing common economic outlooks and social statuses.
- Origins of SHGs in India
- Early Efforts: Informal SHGs, particularly among women, existed for mutual support and collective action before the 1970s.
- SEWA (1972): The establishment of SEWA by Ela Bhatt marked a significant milestone, organizing poor and self-employed women workers.
- MYRADA and Pilot Programs (Mid-1980s): MYRADA pioneered SHGs as a microfinance strategy, focusing on providing credit to rural women.
- NABARD and SHG-Bank Linkage (1992): NABARD launched the SHG-Bank Linkage Programme, connecting SHGs with formal banking institutions.
- Government Initiatives and Policies Supporting SHGs
- Deen Dayal Antyodaya Yojana – National Rural Livelihoods Mission (DAY-NRLM)
- SHG-Bank Linkage Programme (SBLP)
- Mission for Financial Inclusion (MFI)
Impact of SHGs on Women
- Economic Empowerment
- Improved access to microfinance and credit.
- Facilitated income generation activities and entrepreneurship.
- Contributed to poverty alleviation and financial inclusion.
- Women’s Agency and Empowerment
- Provided leadership and assertiveness training.
- Enabled women to challenge traditional gender norms and assume leadership roles.
- Impact on Family and Society
- Fostered more equitable family relationships.
- Increased women’s representation in local governance.
- Mitigated social issues like domestic violence.
Challenges and Limitations Faced by SHGs
- Sustainability: Dependence on external support and effective internal management.
- Dependency: Overreliance on external aid hindering self-sustainability.
- Intersectional Challenges: Caste, class, and regional disparities impacting inclusivity.
- Agricultural Focus: Limited engagement in non-agricultural businesses.
- Lack of Technology: Rudimentary or no technology adoption.
- Market Access: Limited access to larger marketplaces.
- Poor Infrastructure: Located in areas with poor connectivity and infrastructure.
- Politicisation: Political interference leading to conflicts.
Way Forward
- Technology Integration: Utilize technology for efficiency and scalability, aiding in record-keeping and communication.
- Linkages with Financial Institutions: Strengthen connections with formal financial institutions to enhance sustainability.
- Environmental Sustainability: Integrate environmental concerns for resilience and sustainable development.
- Inclusivity Awareness: Encourage an inclusive approach to address socio-economic disparities within SHGs.
UPSC Previous Year Questions
Mains (2013)
Q. The legitimacy and accountability of Self Help Groups (SHGs) and their patrons, the micro-finance outfits, need systematic assessment and scrutiny for the sustained success of the concept. Discuss.
Source: TH
Inter-Services Organisations Act
Tag: GS – 2 GS – 3 Parliament, Various Security Forces & Agencies & Their Mandate
In News:
The recent enactment of the Inter-Services Organisations (ISOs) (Command, Control, and Discipline) Act empowers commanders in charge of ISOs to oversee personnel from all military branches, aiming to streamline operations and enhance collaboration.

Key Features of the Inter-Services Organisations (ISOs) Act
- Background
- The Armed Forces currently operate under separate Service Acts, leading to challenges in maintaining uniform discipline and coordination across inter-service establishments.
- The ISO Act doesn’t propose changes to existing service acts but aims to address coordination issues.
- Features of the Act
- Empowering ISO Leadership
- Commanders-in-Chief and Officers-in-Command of ISOs gain authority over service personnel under their command, irrespective of branch.
- This simplifies command structure and enhances decision-making efficiency.
- Empowering ISO Leadership
- Constituting and Classifying ISOs
- Existing ISOs like the Andaman and Nicobar Command will be formally recognized.
- New ISOs may be constituted, requiring personnel from at least two of the three services.
- A Joint Services Command (tri-service) can be formed, led by a Commander-in-Chief.
- Applicability and Qualifications
- The Act may extend to other centrally controlled forces beyond the Army, Navy, and Air Force.
- Eligibility criteria for Commanders-in-Chief and Officers-in-Command are specified.
- Control and Commanding Officer
- The central government retains authority over ISOs and can issue directives related to national security.
- The Commanding Officer position is established within ISOs, responsible for specific units and personnel.
Significance of Integration of Armed Forces
- Enhanced Operational Effectiveness: Joint planning and training improve coordination crucial for modern warfare.
- Faster Decision-Making: Streamlined command structures enable quicker decisions on the battlefield.
- Optimum Resource Utilization: Integration reduces duplication and optimizes resource allocation.
Conclusion
The integration of Indian armed forces, as facilitated by the ISO Act, enhances operational efficiency and decision-making. It’s a step toward modernizing defense capabilities to match contemporary warfare requirements, aligning with long-term strategic goals.
UPSC Previous Year Questions
Prelims (2014)
Q. In the Constitution of India, the promotion of international peace and security is included in the
(a) Preamble to the Constitution
(b) Directive Principles of State Policy
(c) Fundamental Duties
(d) Ninth Schedule
Ans: (b)
Mains (2014)
Q. “The diverse nature of India as a multi-religious and multi-ethnic society is not immune to the impact of radicalism which is seen in her neighbourhood.” Discuss along with strategies to be adopted to counter this environment.
Source: TH
Rangelands
Tag: GS-3 Environment
In News:
The United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification’s recently released report, titled “Global Land Outlook Thematic Report on Rangelands and Pastoralists,” underscores that rangelands are experiencing a ‘silent demise’.

Understanding Rangelands: Importance, Degradation, and Significance
- About Rangelands
- Rangelands, a significant category of Earth’s land cover, primarily comprise natural grasslands utilized by both livestock and wild animals for grazing and foraging purposes.
- The vegetation on rangelands varies, encompassing tallgrass prairies, steppes, desert shrublands, shrub woodlands, savannas, chaparrals, and tundras.
- Covering roughly half of the Earth’s land surface, rangelands are prominent features, particularly in western North America.
- Reasons for Degradation
- Degradation of rangelands is largely attributed to land use changes driven by factors like population growth, urban expansion, and conversion of pastures to cropland.
- Additional pressures include rapidly increasing demands for food, fiber, and fuel, excessive grazing, abandonment of land, and policies that encourage overexploitation.
- Significance of Rangelands
- Rangelands serve multiple purposes, including livestock forage, wildlife habitat, water and mineral resources, wood products, wildland recreation, and open space preservation.
- Economically vital, rangelands contribute significantly to many countries’ economies and are integral to various cultures worldwide.
- These regions, home to a quarter of the world’s languages and numerous World Heritage Sites, have shaped the traditions, customs, and identities of pastoralist communities for millennia.
- Approximately two billion people, including small-scale herders, ranchers, and farmers, rely on healthy rangelands for their livelihoods, highlighting their global importance.
Source: DTE
Bharal and Himalayan Ibex
Tag: GS-3
In News:
Wildlife authorities in the high-altitude, cold desert district of Lahaul & Spiti in Himachal Pradesh have initiated surveys as part of a census aimed at estimating the population of blue sheep or bharal and the Himalayan ibex. These species serve as the primary prey for the iconic snow leopard.

Overview of Bharal and Himalayan Ibex
Bharal
- The bharal, also known as the blue sheep, is a caprine species native to the high Himalayas.
- Scientifically known as Pseudois nayaur, it is the sole member of the genus Pseudois.
- Distribution includes India, Bhutan, China (specifically in Gansu, Ningxia, Sichuan, Tibet, and Inner Mongolia), Myanmar, Nepal, and Pakistan.
- Features include medium size (115 to 165 cm long along the head and body, with a tail of 10 to 20 cm), standing 69 to 91 cm high at the shoulder. Males are slightly larger than females.
- Their short, dense coat is slate grey with a bluish shine, with white underparts and backs of legs, and black chests and fronts of legs.
- Active throughout the day, they alternate between feeding and resting on grassy mountain slopes.
- Conservation Status: Least Concern on the IUCN Red List, and listed under Schedule 1 of the Wildlife Protection Act 1972.
Himalayan Ibex
- A subspecies of the Siberian ibex, native to the Himalayan region spanning India, Pakistan, Tibet, and Nepal.
- Scientifically named Capra sibirica hemalayanus.
- Inhabit high-altitude regions of the Himalayas, with elevations ranging from 3,000 to 5,800 meters.
- Found in parts of India, predominantly in Jammu and Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, and Uttarakhand.
- Features include an adult weight of about 90 kgs, standing around 40 inches tall, with huge curved horns. Males are larger than females.
- Coat color varies from light brown to reddish-brown, with a white belly and black and white markings on legs. Their coat is thick and woolly in winter, shedding in early summer.
- Usually found in small herds, running at speeds of up to 50 km/h.
- Conservation Status: Near Threatened on the IUCN Red List.
Source: DTE
Section 436A
Tag: GS-2
In News:
The Supreme Court (SC) has reaffirmed that the provisions of Section 436A of the Code of Criminal Procedure (CrPC) extend to individuals accused of money laundering as well.
Overview of Section 436A of the Criminal Procedure Code (CrPC)
- Introduction
- Section 436A was incorporated into the CrPC in 2005 through an amendment.
- It was added to address concerns regarding the prolonged detention of undertrials.
- Bail Provision
- According to Section 436A CrPC, an individual who has spent half of the maximum period of the prescribed sentence as an undertrial is eligible for release on bail.
- This provision applies to offenses where the death penalty is not specified as one of the punishments.
- Release Conditions
- The court is mandated to release the individual on their personal bond, with or without sureties, if they have undergone detention for up to half of the maximum imprisonment period specified for the offense.
- However, the court, after hearing the Public Prosecutor, may extend the detention beyond the half period or release the individual on bail, based on recorded reasons.
- Maximum Detention Period
- An individual cannot be detained during investigation, inquiry, or trial for more than the maximum period of imprisonment provided for the offense under the law.
- Exclusion of Delay Period
- The calculation of detention period under Section 436A for bail excludes any delay caused by the accused in the proceedings.
- Applicability to Special Acts
- The Supreme Court clarified that Section 436A applies to Special Acts as well, even in the absence of specific provisions to that effect.
Source: IE
Emblica chakrabartyi
Tag: GS-3
In News:
Recently, researchers announced the identification of a novel plant species, Emblica chakrabartyi, found in Adichilthotti within the Edamalayar forest range of Kerala.

Introducing Emblica chakrabartyi: A New Species of Gooseberry
- Emblica chakrabartyi, a newly discovered species within the gooseberry (Phyllanthaceae) family, is named after Tapas Chakrabarty, a former scientist at the Botanical Survey of India, in recognition of his contributions to the study of Phyllanthaceae.
- This plant typically grows to a height of about 2 meters and features large, shiny, elongated oval leaves measuring up to 13 cm in length.
- Flowering and fruiting of Emblica chakrabartyi occur from December to June, with male flowers arranged in inflorescence and female flowers solitary in the leaf axils.
- Each flower of this species has six yellowish-green petals, while its fruits turn brown to black upon ripening, with black seeds measuring about 8-9 mm in diameter.
- Emblica chakrabartyi is primarily found growing as shrubs in tropical rainforests, with a total of 55 species of the genus Emblica recorded worldwide, and it marks the eleventh species discovered in India.
Source: TH
International Booker Prize
Tag: GS-1
In News:
Recently, “Kairos” by Jenny Erpenbeck, translated by Michael Hofmann, was announced as the winner of the International Booker Prize 2024.
Overview of the International Booker Prize
- The International Booker Prize is an annual award presented for the finest single work of fiction from any part of the world, provided it has been translated into English.
- Initially established in 2005 as the Man Booker International Prize, it was originally awarded biennially for a body of work without a requirement for works to be in a language other than English.
- The prize aims to promote the reading of high-quality fiction from diverse global sources and has already influenced reading trends in the UK.
- Eligibility criteria dictate that the work must be long-form fiction, originally written in English by an author of any nationality, and published in the UK and/or Ireland.
- Prize money totaling £50,000 is split equally between the author and the translator, recognizing the crucial role of translation in bringing international literature to English-speaking audiences.
- Additionally, shortlisted authors and translators each receive £2,500 in recognition of their contribution to literature and translation.
Source: TH
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are daily current affairs?
A: Daily current affairs refer to the most recent and relevant events, developments, and news stories that are happening around the world on a day-to-day basis. These can encompass a wide range of topics, including politics, economics, science, technology, sports, and more.
Q: Why is it important to stay updated with daily current affairs?
A: Staying updated with daily current affairs is crucial because it helps individuals make informed decisions in their personal and professional lives. It enables people to understand the world around them, stay aware of significant events, and engage in informed discussions about important issues.
Q: Where can I access daily current affairs information?
A: There are various sources for daily current affairs, including newspapers, news websites, television news broadcasts, radio programs, and dedicated apps or newsletters. Social media platforms are also widely used to share and access current affairs information.
Q: How can I effectively incorporate daily current affairs into my routine?
A: To incorporate daily current affairs into your routine, consider setting aside specific times each day to read or watch news updates. You can also subscribe to newsletters or follow news apps to receive curated content. Engaging in discussions with peers or participating in online forums can further enhance your understanding of current events.
Q: What are some tips for critical analysis of daily current affairs?
A: When analyzing daily current affairs, it’s essential to cross-reference information from multiple sources to ensure accuracy. Additionally, consider the source’s credibility and bias, if any. Develop the ability to identify the main points and implications of news stories, and critically evaluate the significance and impact of the events reported.
In case you still have doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here

