
In today’s daily current affairs briefing for UPSC aspirants, we explore the latest developments that hold relevance for the upcoming civil services examination. Our focus today includes a critical analysis of recent policy changes, international affairs, and national developments, all of which play a pivotal role in shaping the socio-political and economic landscape of India. Stay informed and stay ahead in your UPSC preparations with our daily current affairs updates, as we provide you with concise, well-researched insights to help you connect the dots between contemporary events and the broader canvas of the civil services syllabus.
Contents
- 1 Welfare Schemes for the Minority Communities
- 2 The Cinematograph (Amendment) Bill 2023
- 3 The Offshore Areas Mineral (Development and Regulation) Amendment Bill, 2023
- 4 Jharkhand issues PESA draft rules for consultations
- 5 Registration of Births and Deaths (RBD) Amendment Bill, 2023
- 6 Cooling Solutions
- 7 India’s Rice Export Ban
- 8 Intelligent Traffic Management System
- 9 Bharat Mandapam
- 10 World Cities Culture Forum (WCCF)
- 11 Byculla railway station (Mumbai)
- 12 Persons with Disabilities
- 13 INDIAai
- 14 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 14.1 Q: What are daily current affairs?
- 14.2 Q: Why is it important to stay updated with daily current affairs?
- 14.3 Q: Where can I access daily current affairs information?
- 14.4 Q: How can I effectively incorporate daily current affairs into my routine?
- 14.5 Q: What are some tips for critical analysis of daily current affairs?
- 15 In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
Welfare Schemes for the Minority Communities
Tag: GS-2 Social Justice
In News:
The Government already implements various Schemes for the welfare and upliftment of every stratum, including minorities, especially the economically weaker and lesser privileged sections of society.
About
Different Schemes for the Welfare of Minority Communities in India
Educational Empowerment Schemes:
Pre-Matric Scholarship Scheme:
- This centrally funded scholarship is accessible to students in all states each year.
- It targets minority students studying in classes 1 to 10, assisting them in covering educational expenses and promoting their pursuit of education.
Post-Matric Scholarship Scheme:
- Implemented through State Governments and UT administrations, this scholarship scheme is designed for minority students studying in classes 11 and 12, as well as those pursuing undergraduate and postgraduate courses.
- The program aims to support students in their higher education endeavors, thus enhancing their future career prospects.
National Means Cum-Merit Scholarship Scheme (NMMSS):
- Launched in 2008 as a Centrally Sponsored Scheme (CSS), the NMMSS focuses on providing financial assistance to meritorious minority students facing economic constraints. By encouraging academic excellence, this initiative ensures equal opportunities for deserving students from minority backgrounds.
Education Loan Scheme by National Minorities Development & Finance Corporation (NMDFC):
- The NMDFC offers an Education Loan Scheme to students belonging to minority communities, including the Jain community.
- These loans provide concessional credit for pursuing technical and professional courses, with a maximum course duration of 5 years.
- Students can avail educational loans up to ₹20.00 lakh for 5-year courses within India and ₹30.00 lakh for 5-year courses abroad.
Employment and Economic Empowerment Schemes:
Pradhan Mantri Virasat Ka Samvardhan (PMVIKAS):
- PMVIKAS focuses on conserving and promoting the rich cultural heritage of minority communities.
- The scheme provides support to traditional crafts, art forms, and cultural practices, thereby empowering artisans and craftsmen.
NMDFC Scheme:
- The NMDFC Scheme offers concessional loans to minorities to foster economic ventures and entrepreneurship.
- By facilitating access to financial resources, the scheme promotes economic self-reliance and sustainable livelihoods among minority groups.
Special Schemes:
Jiyo Parsi:
- This unique scheme addresses the population decline of the Parsi community in India.
- It implements measures to encourage Parsi families to have more children and sustain their community’s cultural legacy.
Qaumi Waqf Board Taraqqiati Scheme (QWBTS) and Shahari Waqf Sampatti Vikas Yojana (SWSVY):
- These schemes focus on developing and utilizing waqf properties for the welfare of minority communities.
- They aim to enhance infrastructure and facilities in waqf properties to better serve the community’s needs.
Infrastructure Development Schemes:
Pradhan Mantri Jan Vikas Karyakram (PMJVK):
- Aims at creating better infrastructure in minority-concentrated areas.
- Provides improved amenities, healthcare facilities, education centers, and skill development opportunities.
Source: PIB GOV.
The Cinematograph (Amendment) Bill 2023
Tags: GS – 2: Governance (Statutory, Regulatory & Various Quasi-Judicial Bodies)
Why in News:
Recently, The Rajya Sabha passed the Cinematograph (Amendment) Bill 2023 that introduces stringent anti-piracy provisions, expanding the scope of the law from censorship to also cover copyright.
Cinematograph (Amendment) Bill 2023:
- Introduced by the Ministry of I&B, the Bill seeks to amend the Cinematograph Act 1952.
- The Cinematograph Act 1952 authorises the Central Board of Film Certification (CBFC) to require cuts in films and clear them for exhibition in cinemas and on television/ refuse the exhibition of a film.
- Under the Act, film may be certified for exhibition:
- without restriction (‘U’),
- without restriction, but subject to guidance of parents or guardians for children below 12 years of age (‘UA’),
- only to adults (‘A’),
- only to members of any profession or class of persons (‘S’).
Key Provisions of the Amendment Bill:
- Introduction of New Certifications: The bill proposes three new certifications under the ‘UA’ (Parental Guidance) category: UA 7+, UA 13+, and UA 16+. These certifications indicate that children younger than the specified age limits can watch such movies with parental guidance. [in line with the Shyam Benegal committee (2017)]
- Separate certificate for television/other media: Films with an ‘A’ or ‘S’ certificate will require a separate certificate for exhibition on television, or any other media prescribed by the central government. The Board may direct the applicant to carry appropriate deletions or modifications for the separate certificate.
- Unauthorised recording and exhibition to be punishable: The Bill prohibits carrying out or abetting – the unauthorised recording and unauthorised exhibition of films – in order to stop piracy. This offence will be punishable with: imprisonment between 3 months and 3 years, and a fine between 3 lakh rupees and 5% of the audited gross production cost.
- Certificates to be always valid: Under the Act, the certificate issued by the Board is valid for 10 years. The Bill provides that the certificates will be perpetually/always valid.
- Revisional powers of the central government: The Act empowers the central government to examine and make orders in relation to films that have been certified or are pending certification. The Board is required to dispose of matters in conformity to the order. The Bill removes this power of the central government.
Significance of the Bill:
- It will make the certification process more effective, as per the demand of current time.
- It will comprehensively curb the menace of film piracy, and thus help in faster growth of the film industry and boost job creation in the sector.
Concerns with the Bill:
- OTT platforms out of the purview of the Bill which makes a way for uncut movie to be broadcasted.
- It places the onus on parents and guardians to determine if the material is appropriate for viewers of a particular age range.
Source: Indian Express
The Offshore Areas Mineral (Development and Regulation) Amendment Bill, 2023
Tags: GS – 2: Governance (Government Policies and Interventions for Development in various sectors)
Why in News:
Recently, The Offshore Areas Mineral (Development and Regulation) Amendment Bill 2023 was introduced in Lok Sabha to amend the offshore areas mineral law.
The Offshore Areas Mineral (Development and Regulation) Amendment Bill 2023:
- It has been prepared by the Ministry of Mines, seeks to amend the Offshore Areas Mineral (Development and Regulation) Act 2002, to allow auction of minerals mined offshore.
- To mine rocks under the sea: Under the original Act, not even a single rock could be not mined out from the sea bed mainly due to pending litigations. The Bill allows the use of the national wealth in the sea for the use of the people of the country.
- To facilitate private sector participation: In the mining of non-atomic minerals in India’s territorial waters and continental shelf, private companies might be encouraged to contribute cutting-edge technologies for the execution of complex mining operations.
- To provide an auction of minerals mined offshore: The original Act does not allow the auction of such minerals.
- To improve transparency in the allocation of mineral resources.
- To grant an exploration licence or production lease: Only to a government company in case the quality of minerals in that particular area is equal to or above the threshold value decided by the Centre.
- To propose area under a production lease: Such areas shall comprise contiguous standard blocks and shall not exceed an area of 15 minutes latitude by 15 minutes longitude.
- To remove discretion in the grant of renewals: The provisions for renewal of production leases have been removed and the period of production lease has been increased to 50 years.
Significance of the Bill:
- The bill encourages the participation of the public-private sector. This will bring the necessary expertise and technology to explore and mine the mineral resources present in the EEZ.
- The Bill provides for India to harness its maritime resources to its optimal capacity.
Source: Economic Times
Jharkhand issues PESA draft rules for consultations
Tags: GS-II: Bills/Acts
In News:
Jharkhand issues PESA draft rules for consultations
About Jharkhand PESA rules:
- Jharkhand government has recently published draft rules for implementing the Provisions of the Panchayats Extension to Scheduled Areas (PESA) Act.
- Scheduled Areas in Jharkhand are identified by the Fifth Schedule of the Constitution and the draft aims to ensure self-governance through gram sabhas for people living in Scheduled Areas.
- PESA recognizes tribal communities’ right to govern themselves through their own systems of self-government and acknowledges their traditional rights over natural resources.
- Major provisions:
- The draft rules outline the rights of gram Sabhas under the 5th Schedule areas in the state, including resolving traditional and family disputes and hearing certain cases under the IPC.
- Gram sabhas will have fundamental responsibilities of maintaining peace and order, following the principles of the Constitution.
- It mandates the establishment of eight standing committees, including Education and Social Justice, under the gram Sabha.
- These committees must have at least 50% women and a minimum of 40% people from Scheduled Tribe (ST) communities.
- The Education and Social Justice Committee will focus on education, economic upliftment of Scheduled Castes, Scheduled Tribes and primitive tribes, providing protection from social injustice.
- The gram sabhas will preserve customary law, social and religious practices of the Scheduled Tribe communities and align State Government rules with their practices.
- They will have the authority to hear issues mentioned in Parishisht 1 of the Indian Penal Code, 1860, but for serious crime-related issues, it must inform the nearest police station in-charge.
- Overall, the bill is a progressive step for social inclusion and governance of tribal populations of Jharkhand but it must pass through the test of constitutionality before converted into an act.
Source: Indian Express
Registration of Births and Deaths (RBD) Amendment Bill, 2023
Tags: GS-II: Acts/Bills
In News:
Union government introduces Registration of Births and Deaths (RBD) Amendment Bill, 2023 in parliament
About Registration of Births and Deaths (RBD) Amendment Bill, 2023:
- The Registration of Births and Deaths (RBD) Amendment Bill, 2023, was recently introduced in the Lok Sabha to amend the existing Registration of Births and Deaths Act, 1969.
- Major proposals:
- The bill proposes the digitization of birth records, creating comprehensive digital birth certificates to be used to prove a person’s date and place of birth for various purposes.
- The Bill mandates all births and deaths to be registered on a centralized portal known as the Centre’s Civil Registration System (CRS).
- States will be obligated to register births and deaths on the CRS and share the data with the Registrar General of India.
- The Bill proposes to collect the Aadhaar numbers of parents and informants, if available, during birth registration.
- Medical institutions will be required to provide a certificate stating the cause of death to the Registrar and a copy to the nearest relative.
- The centralized register will facilitate updating other databases for efficient and transparent delivery of public services and social benefits.
- These certificates can be used for applications for educational institutions, driving licenses, government jobs, passports, Aadhaar, voter enrolment etc.,
- The database generated will also be used to registration of marriage and update the National Population Register (NPR) and property registration records.
- Overall, the amendment will go a long way in streamlining the registration process for adopted, orphaned, surrogate children, and children of single parents or unwed mothers.
Source: The Hindu
Cooling Solutions
Tag: GS-3 Environmental conservation; Indigenous development in Science and Technology
In News:
According to NITI Aayog, around 65% of the energy demand in India comes from space cooling and heating. And it is projected that India will see an 11-fold increase in cooling demand in buildings by 2037-38, compared to the 2017-18 baseline.
About Cooling Solutions:
- Recognising increasing power demands for space cooling and heating, India launched the Cooling Action Plan (ICAP) in 2019.
- It is predicted that a potential reduction of around 20% in cooling load could be achieved by 2037-38, through climate-appropriate building envelopes.
- An additional 30% reduction in cooling energy can be achieved through improvements in cooling equipment efficiency and better servicing and operation and maintenance practices.
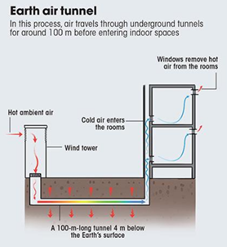
Customised Cooling Solutions:
Large-scale spaces with cooling solutions that are low in energy consumption, applicable in varying climatic conditions and could reduce the need for conventional air conditioners in India are:
- Tapping the earth’s potential: Temperature just 4 m below the Earth’s surface remains relatively constant throughout the year which can work as a heat sink or a heat source depending on the season. NIIT University in Neemrana, Rajasthan, has used this potential, wherein ambient air is filtered and passed through 100-m-long tunnels embedded inside Earth. This cools the air without adding humidity by 10-12°C.
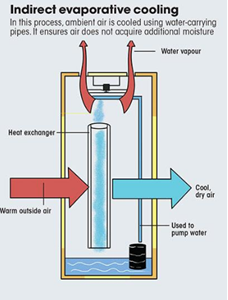
- Evaporative Cooling: It involves passing hot air through a medium that is saturated with water. The air transfers heat to the water, causing it to evaporate and turn into vapour. As a result, the air becomes cool and moist, providing thermal comfort. IIT Gandhinagar has constructed its dining halls which use this principle.
- Cooling sans humidifying: It uses an indirect evaporative cooling system where the incoming air stream is cooled using water carrying pipes. The air, however, does not directly touch the water; it only interacts with the pipes containing it. Thus, heat is exchanged between the air and the water, without acquiring moisture.
- Dehumidifying: Filtering ambient air through a desiccant (a substance that can absorb moisture) can dehumidify air and then the dehumidified air would be cooled through evaporative cooling. Nalanda University in Bihar uses this technique.
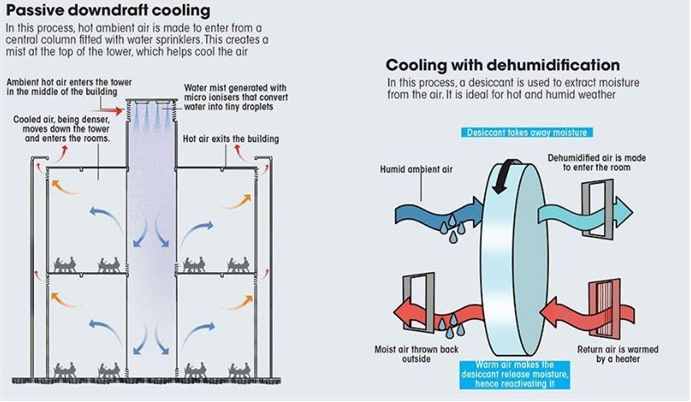
Source: Down to Earth
India’s Rice Export Ban
Tag: GS-3 Issues related to external trade
In News:
India recently decided to ban the export of all types of rice, except Basmati and parboiled rice. As per IMF, this move could exacerbate food prices and inflation globally.
About the Rice Export Ban:
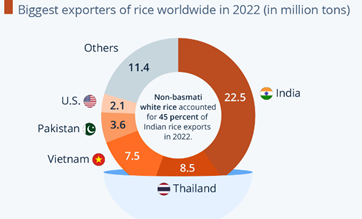
- India is the world’s biggest rice exporter, accounting for 40% of global trade by volume. In 2022, it shipped 22m tonnes to more than 140 countries. Non-basmati white rice constitutes approximately 25% of the total rice exported from the country
- Most of the exports consist of non-basmati rice especially popular in poor places such as Bangladesh, Nepal and parts of sub-Saharan Africa.
- Previously, India has implemented restrictions on non-basmati white rice exports to ensure sufficient availability in the domestic market at reasonable prices.
- According to the rice-price index, published monthly by the FAO, rice prices rose by 14% in the year to June.
Implications of ban of rice exports:
- Global Supply Shortage: The ban will remove almost 10 million tons of non-basmati white rice from the world market, leading to a decrease in overall rice supply.
- Rise is global rice prices: The reduction in supply is likely to create a surge in world rice prices. Other rice-exporting countries like Thailand, Vietnam, Pakistan, US, and Myanmar cannot fill the gap left by India’s absence.
- Domestic Supply Concerns: The ban is a response to domestic supply concerns caused by subnormal monsoon rainfall in major growing states.
- Loss of credibility as a reliable trade partner: The ban raises questions about the credibility of official output estimates, especially when India recorded all-time-high production of both wheat and rice in 2022-23.
- Hindrances to Market Building Efforts: Building markets takes time and effort, and the sudden ban can undo the progress made in establishing India as a reliable rice supplier in various regions.
- Potential of a Domino effect where other rice producing countries could ban rice exports as witnessed during the 2008 rice ban by Vietnam.
Source: The Hindu
Intelligent Traffic Management System
Tags: General Studies –3 Science & Technology
Why in news?
Cameras equipped with Artificial Intelligence (AI) will be deployed at 25 locations in Mysuru as part of the Intelligent Traffic Management System.
About:
- An advanced traffic management system (TMS) is a context-aware solution that relies on real-time data from connected road infrastructure and predictive analytics to effectively coordinate traffic across city arteries.
- The system will automatically capture violations such as helmetless riding, triple-riding on two-wheelers, driver-on-call, seat belt violation, and signal jump.
- Once a violation is captured, a challan will be generated, and a notice will be sent to the vehicle owner’s address.
- A similar type of Traffic Management System is operational in cities like Bengaluru, Ahmedabad etc.
Source: The Hindu
Bharat Mandapam
Tags: General Studies –2 Government Policies & Infrastructure
Why in news?
Recently, Prime Minister Narendra Modi inaugurated the international exhibition-cum-convention Centre (IECC) complex named Bharat Mandapam at Pragati Maidan in New Delhi.
About:
- Prime Minister also unveiled the G-20 coin and G-20 stamp at the grand opening ceremony.
- The new convention complex will help showcase and promote India as a global business destination.
IECC complex
- The IECC complex is India’s largest MICE (meetings, incentives, conferences, and exhibitions) destination and features state-of-the-art facilities, including a convention centre, exhibition halls, and an amphitheatre.
- The architectural design of the convention centre incorporates elements from India’s traditional art and culture, representing the nation’s rich heritage and modern achievements.
- The term ‘Bharat Mandapam’ is derived from Lord Basaveshwara’s concept of ‘Anubhav Mantapa,’ which was a significant institution in the 12th century.
- Anubhav Mantapa is considered one of the earliest parliaments in human history, where poets and socio-spiritual reformers known as Sharanas discussed and deliberated on various reforms.
- The members of the Anubhav Mantapa were not elected by the people; instead, they were chosen or nominated by the higher authorities of the Mantapa
Source: Economic Times
World Cities Culture Forum (WCCF)
Tags: General Studies – 1 Groupings & Agreements Involving India and/or Affecting India’s Interests
Why in news?
Recently, the World Cities Culture Forum (WCCF) has inducted Bengaluru as a member, making it the first Indian city to join the platform.
About:
● WCCF was founded in 2012 by Justine Simons OBE, London’s Deputy Mayor for Culture & the Creative Industries.
● With 40 member cities already in its portfolio, Bengaluru becomes the 41st member of the forum.
● The city’s inclusion was attributed to its dedication to an inclusive and globalized culture.
● Bengaluru being the latest addition is set to join the league of cities like New York, London, Paris, Tokyo and Dubai among others.
● The WCCF will collaborate with the Unboxing BLR Foundation, and together, they plan to organize a ‘city festival’ to facilitate the exchange of cultural learning as part of the forum’s global outreach.
Additional Information:
● Bengaluru is seen as a microcosm of the new aspirational India, showcasing a vibrant design and theatre community, numerous museums, and a cosmopolitan food culture, which will be highlighted and structurally presented through the WCCF platform.
Source: Times of India
Byculla railway station (Mumbai)
Tags: General Studies –1 History
Why in news?
Recently, the heritage Byculla Railway station which has been restored to its original glory, received the UNESCO award.
About:
● The 169-year-old Byculla railway station in Mumbai is one of the oldest railway stations in India still in use.
● The restoration work of the Byculla Railway Station was undertaken by ‘I Love Mumbai,’ an NGO.
● Designated as a Grade-I heritage structure, Byculla Railway Station holds immense architectural and historical value.
o This status emphasizes the importance of preserving the station’s original design and features for future generations to appreciate and learn from.
Additional Information:
● Additionally, the Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj Vastu Sangrahalaya (CSMVS), Stepwells of Golconda (Hyderabad), and Domakonda Fort (Telangana) also won the highest award of excellence in the UNESCO Asia Pacific awards in 2022 in different categories.
● Byculla Railway Station was one of the original stations inaugurated when the Bombay–Thane railway commenced operations in April 1853.
● The first train was run by the Great Indian Peninsula Railway (now Central Railway) between Bori Bunder (now Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj Terminus) and Thane, a distance of 34 km (21 mi), on 16 April 1853.
Source: Indian Express
Persons with Disabilities
Tags: General Studies – 2 Government Policies & Interventions
Why in news?
Recently, the Centre is facing criticism from rights activists and the Opposition for omitting disability-related questions in the sixth round of the National Family Health Survey (NFHS).
About:
● The government’s response to the Parliamentary committee’s earlier recommendations explained that data on PwDs is primarily derived from decennial censuses and sample surveys on disability.
● The government also introduced Unique Disability ID (UDID) cards for individuals covered under disability schemes, but the committee found this approach insufficient, as the number of issued UDID cards did not match the estimated PwD population.
● The committee emphasized the need for innovative solutions and recommended that the government collaborate with State governments and other departments/organizations involved in PwD welfare schemes to arrive at a realistic assessment of the PwD population in the country.
Persons with Disabilities
● Persons with Disabilities (PWDs) refer to individuals who have long-term physical, mental, intellectual, or sensory impairments that may hinder their full and effective participation in society on an equal basis with others.
● As per Census 2011, at the all-India level, disabled persons constitute 2.21% of the total population.
Constitutional Framework for Disabled in India:
o Article 41 of the Directive Principles of State Policy (DPSP) states that the State shall make effective provision for securing the right to work, to education and to public assistance in cases of unemployment, old age, sickness and disablement, within the limits of its economic capacity and development.
o The subject of ‘relief of the disabled and unemployable’ is specified in the state list of the Seventh Schedule of the constitution.
Source: The Hindu
INDIAai
Tags: General Studies –3 Science & Technology
Why in news?
Recently, the INDIAai and Meta India signed a memorandum of understanding (MoU) to establish a framework for collaboration and cooperation in the field of artificial intelligence (AI) and emerging technologies.
About:
● It is the National artificial intelligence Portal of India which was launched on 28th May 2020.
● It is a knowledge portal, research organization, and ecosystem-building initiative focused on preparing the nation for an AI-driven future.
● It is a joint venture between the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY), the National e-Governance Division (NeGD), and NASSCOM.
● It is the single central knowledge hub on artificial intelligence and allied fields for aspiring entrepreneurs, students, professionals, academics, and everyone else.
More Information:
● NeGD: It was created in 2009 as an Independent Business Division under the Digital India Corporation (a not-for-profit company set up by MeitY).
● NASSCOM: It is a not-for-profit industry association and the apex body for the IT and IT-enabled products and services sector in India.
Source: PIB Gov.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are daily current affairs?
A: Daily current affairs refer to the most recent and relevant events, developments, and news stories that are happening around the world on a day-to-day basis. These can encompass a wide range of topics, including politics, economics, science, technology, sports, and more.
Q: Why is it important to stay updated with daily current affairs?
A: Staying updated with daily current affairs is crucial because it helps individuals make informed decisions in their personal and professional lives. It enables people to understand the world around them, stay aware of significant events, and engage in informed discussions about important issues.
Q: Where can I access daily current affairs information?
A: There are various sources for daily current affairs, including newspapers, news websites, television news broadcasts, radio programs, and dedicated apps or newsletters. Social media platforms are also widely used to share and access current affairs information.
Q: How can I effectively incorporate daily current affairs into my routine?
A: To incorporate daily current affairs into your routine, consider setting aside specific times each day to read or watch news updates. You can also subscribe to newsletters or follow news apps to receive curated content. Engaging in discussions with peers or participating in online forums can further enhance your understanding of current events.
Q: What are some tips for critical analysis of daily current affairs?
A: When analyzing daily current affairs, it’s essential to cross-reference information from multiple sources to ensure accuracy. Additionally, consider the source’s credibility and bias, if any. Develop the ability to identify the main points and implications of news stories, and critically evaluate the significance and impact of the events reported.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here

