Explore UPSC Prelims Topic Wise Questions on Physics, focusing on the fascinating realm of Optics. Immerse yourself in a curated collection of questions meticulously designed to deepen your understanding of optical phenomena. From the behavior of light waves to the principles of reflection, refraction, and optical instruments, delve into the intricacies of this fundamental branch of physics. Each question offers a unique opportunity to hone your analytical skills and apply theoretical knowledge to practical scenarios. Whether you’re aiming to comprehend the basics or seeking advanced insights, these topic-wise questions cater to aspirants at every level of preparation. Strengthen your grasp of Optics, a crucial subject for the UPSC Prelims examination, and equip yourself with the confidence to tackle challenging problems effectively. Start your journey towards mastering Physics for UPSC Prelims today and unlock the door to a successful career in the civil services.
Contents
- 1 Q1. Assertion (A) A diamond sparkles more than a glass imitation cut to the same shape. Reason (R) The refractive index of diamond is less than that of glass. (1995)
- 2 Q2. Optical fibre works on the principle of (1995)
- 3 Q3. An air bubble in water will act like a (1995)
- 4 Q4. Suppose a rocketship is receding from the Earth at a speed of 2/10th the velocity of light. A light in the rocketship appears blue to the passengers on the ship. What colour would it appear to an observer on the Earth? (1995)
- 5 Q5. When a mirror is rotated by an angle 6, the reflected rays will rotate by (1996)
- 6 Q6. Total internal reflection can take place when light travels from (1996)
- 7 Q7. Consider the following statements. (1996)
- 8 Q8. Consider the following statements. (1999)
- 9 Q9. Endoscopy, a technique used to explore the stomach or other inner parts of the body is based on the phenomenon of (1999)
- 10 Q10. Consider the following natural phenomena. (2002)
- 11 Q11. Diffusion of light in the atmosphere takes place due to (2003)
- 12 Q12. Consider the following statements. (2007)
- 13 Q13. Assertion (A) In the visible spectrum of light, red light is more energetic than green light. Reason (R) The wavelength of red light is more than that of green light. (2008)
- 14 Q14. Recently, LASIK (Laser-Assisted in Situ Keratomileusis) procedure is being made popular for vision correction. Which one of the following statements in this context is not correct? (2010)
- 15 Q15. Which one of the following reflects back more sunlight as compared to the other three (2010)
- 16 In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
Q1. Assertion (A) A diamond sparkles more than a glass imitation cut to the same shape. Reason (R) The refractive index of diamond is less than that of glass. (1995)
Codes
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but Ris false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Ans. (c)
Experiment A is true, but assertion R is false.
Diamond indeed exhibits more sparkle than a glass imitation cut to the same shape due to its higher refractive index. However, assertion R mistakenly claims that A is false. Diamond’s refractive index is higher than that of glass, enabling it to bend light more effectively.
Q2. Optical fibre works on the principle of (1995)
(a) total internal reflection
(b) reflection
(c) scattering
(d) interference
Ans. (a)
Optical fiber operates based on the principle of total internal reflection, where light is reflected back into the denser medium from the rarer medium when the angle of refraction exceeds 90°.
In optical fibers, light rays undergo multiple total internal reflections due to their fabrication, ensuring that light reflected at one side of the inner surface strikes the other side at an angle greater than the critical angle (i). Even if the fiber is bent, light can travel along its length without any significant loss of energy.
Reflection, scattering, and interference are not applicable to optical fibers.
Q3. An air bubble in water will act like a (1995)
(a) convex mirror
(b) convex lens
(c) concave mirror
(d) concave lens
Ans. (d)
An air bubble in water indeed behaves like a concave lens. The refractive index of air is lower than that of water, and the speed of light in air is greater than in water. Consequently, when light transitions from water (denser medium) to air (rarer medium), it bends toward the normal. However, when the light exits the air bubble (from rarer to denser medium), it bends away from the normal. overall, the air bubble in water will act as a concave lens due to the combination of the refractive index differences and the bending of light as it enters and exits the bubble.
Q4. Suppose a rocketship is receding from the Earth at a speed of 2/10th the velocity of light. A light in the rocketship appears blue to the passengers on the ship. What colour would it appear to an observer on the Earth? (1995)
(a) Blue
(b) Orange
(c) Yellow
(d) Yellow-orange
Ans. (c)
Imagine a spacecraft is moving away from Earth at a rate of 0.2 times the speed of light. To the travelers onboard, a light within the spacecraft appears blue.
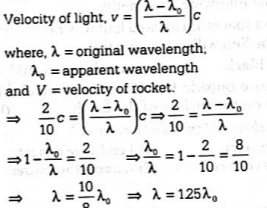
The wavelength of blue light is 450 nm to 475 nm. The wavelength of light on the Earth.
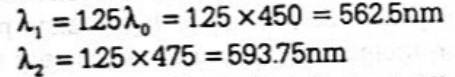
This range of wavelength is of yellow colour.
So, Yellow colour would appear to an observer on the Earth.
Q5. When a mirror is rotated by an angle 6, the reflected rays will rotate by (1996)
(a) 0°
(b) θ/2
(c)θ
(d) 2θ
Ans. (d)
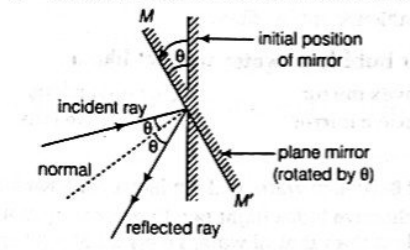
If a mirror undergoes a rotation of θ degrees, the reflected ray will rotate by 2θ degrees accordingly. As depicted in the diagram, when the mirror is rotated by θ degrees, the perpendicular drawn at the point of incidence (the normal) also rotates by θ degrees. Adhering to the laws of reflection, which dictate that the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection, we can conclude. The light reflected will also form an angle “e” with the normal. Thus, the total angle, which is the sum of the angle between the incident ray and the normal, and the angle between the normal and the reflected ray, equals 2θ degrees.
Q6. Total internal reflection can take place when light travels from (1996)
(a) diamond to glass
(b) water to glass
(c) air to water
(d) air to glass
Ans. (a)
Total Internal Reflection (TIR) can occur when light transitions from diamond to glass. When light travels from a denser to a rarer medium, it bends away from the normal. As the angle of incidence increases in the denser medium, so does the angle of refraction in the rarer medium. At a specific angle, known as the critical angle, the angle of refraction becomes 90°. When the angle of incidence surpasses this critical angle, the light ray reflects back into the same medium after interacting with the interface. This occurrence is termed total internal reflection.
Q7. Consider the following statements. (1996)
A person in a spaceship located half way between the Earth and the Sun will notice that the
1. sky is jet black.
2. stars do not twinkle.
3. temperature outside the spaceship is much higher than that on the surface of the Earth.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
(a) Only 3 is correct
(b) 1 and 2 are correct
(c) 1 and 3 are correct
(d) 1, 2 and 3 are correct
Ans. (d)
All the statements are accurate for the given scenario.
The sky appears jet black to an individual in a spaceship positioned halfway between the Earth and the Sun because no scattering occurs. Scattering of light happens when the size of the molecules in the sky is significantly smaller compared to the wavelength of the light. In this scenario, molecules in the medium absorb incoming light and then emit it in all directions. However, in the higher atmosphere or in space, molecules are absent, leading to no scattering.
Stars don’t exhibit twinkling in space due to the absence of atmospheric conditions such as wind and air currents, which typically alter the position of star images, causing them to twinkle. The position of star images changes due to refraction, where light rays bend as they transition from one transparent medium to another.
The temperature outside the spaceship is notably higher than on the Earth’s surface as it increases when approaching the Sun.
Q8. Consider the following statements. (1999)
1. If a person looks at a coin which is in a bucket of water, the coin will appear to be closer than it real is.
2. If a person under water looks at a coin above, the water surface, the coin will appear to be at a higher level than it really is.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 1 alone
(c) 2 alone
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans. (a)
Both statements are accurate. When a person looks at a coin submerged in a bucket of water, the coin appears closer than its actual position. This phenomenon occurs because light passing from a denser medium (water) to a rarer medium (air) bends away from the normal. As the coin is situated within the water, the light emanating from it at the bottom of the water-filled bucket bends away from the normal due to refraction, causing the coin to appear closer than its true position. Similarly, when a person underwater looks at a coin above the water’s surface, the coin appears to be at a higher level than it actually is, also due to refraction of light at the water-air interface.
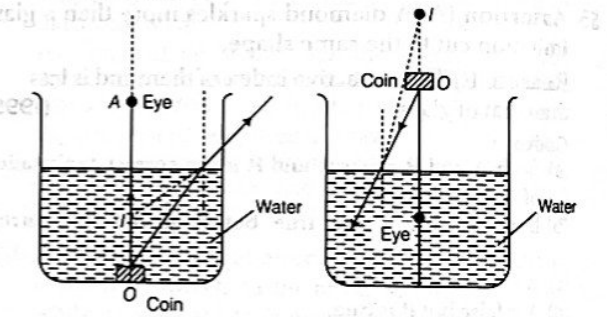
Indeed, if an object, like a coin, is placed in a rarer medium such as air and observed from a denser medium like water, the rays of light will bend towards the normal upon refraction at the interface between the two media. Consequently, the apparent height of the object will be greater than its actual height.
Q9. Endoscopy, a technique used to explore the stomach or other inner parts of the body is based on the phenomenon of (1999)
(a) total internal reflection
(b) interference Beer
(c) diffraction
(d) polarisation
Ans. (a)
Endoscopy, a method employed to examine the stomach and other internal body parts, relies on the principle of total internal reflection. In medical practice, doctors utilize endoscopy to inspect a person’s digestive tract. It involves a flexible tube equipped with a light source and camera, providing a real-time view of the digestive tract on a monitor. This application parallels optical fiber technology, where optical fibers serve as light conduits enabling visual examination of internal organs such as the stomach and intestines.
Q10. Consider the following natural phenomena. (2002)
1. Terrestrial heating
2. Reflection of light
3. Refraction of light
4. Diffraction of light
Due to which of these phenomena is mirage formed?
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 2, 3 and 4
(c) 1 and 3
(d) Only 4
Ans. (c)
Mirages form in deserts and on hot, tarred roads due to terrestrial heating and light refraction. In the scorching summer, the sand or road surfaces absorb intense sunlight, becoming extremely hot. Consequently, the air layers near the surface heat up, becoming less dense, while higher layers remain cooler and denser. Light refraction occurs differently in these distinct layers, causing the angle of incidence to surpass the critical angle in each case, leading to total internal reflection. This phenomenon creates the illusion of water, known as a mirage. Notably, this optical illusion does not involve light reflection or diffraction.
Q11. Diffusion of light in the atmosphere takes place due to (2003)
(a) carbon dioxide
(b) dust particles
(c) helium
(d) water vapours
Ans. (b)
Light diffusion in the atmosphere occurs due to the presence of dust particles. The Earth’s atmosphere consists of a heterogeneous mixture containing fine particles such as smoke, microscopic water droplets, suspended dust particles, and air molecules. When a beam of light encounters these fine particles, its path becomes visible, and the diffused light from these particles is reflected back to us. This phenomenon is termed the scattering of light. The color of the scattered light is contingent upon the size of the scattering particles.
Q12. Consider the following statements. (2007)
1. If magenta and yellow coloured circles intersect, then the intersected area will have red colour.
2. If cyan and magenta coloured circles intersect, then the intersected area will have blue colour.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) Only 1
(b) Only 2
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans. (c)
Both statements are accurate. According to the color triangle, the intersection of magenta and yellow colored circles results in the formation of red color. Similarly, the intersection of cyan and magenta colored circles produces blue color.
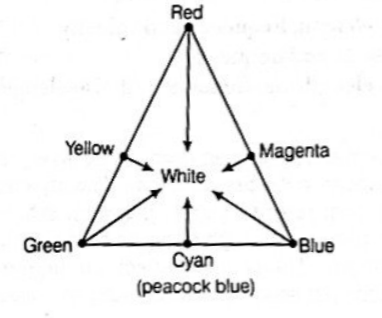
In science, red, green, and blue are termed primary colors because none of them can be created from other colors of light. However, they produce different colors when appropriately combined. The colors resulting from the addition of two primary colors are termed secondary colors; they include yellow, cyan (a shade of blue), and magenta. When the three primary colors are mixed together, they produce white light, much like the secondary colors. A primary color and its opposite secondary color on the color triangle, such as blue and yellow, combine to create white light. Any two colors that produce white light are referred to as complementary colors.
Q13. Assertion (A) In the visible spectrum of light, red light is more energetic than green light. Reason (R) The wavelength of red light is more than that of green light. (2008)
Codes
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the corred explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Ans. (d)
Statement A is false, but statement R is true.
The energy of light radiation is inversely proportional to wavelength, meaning shorter wavelengths correspond to higher energy photons. Therefore, the wavelength of red light is longer than that of green light, implying that red light has lower energy compared to green light.
Q14. Recently, LASIK (Laser-Assisted in Situ Keratomileusis) procedure is being made popular for vision correction. Which one of the following statements in this context is not correct? (2010)
(a) LASIK procedure is used to correct refractive errors of the eye
(b) It is a procedure that permanently changes the shapes of the cornea
(c) It reduces a person’s dependence on glasses or contact lenses
(d) It is a procedure that can be done on the person of any age
Ans. (d)
Statement (d) is not accurate in the context of LASIK procedure.
The medical community has approved LASIK for individuals aged 18 years and older. Moreover, it is crucial that the person’s eye prescription remains stable for at least one year before undergoing surgery. LASIK is a type of refractive surgery designed to correct myopia (nearsightedness), hyperopia (farsightedness), and astigmatism.
Q15. Which one of the following reflects back more sunlight as compared to the other three (2010)
(a) Sand desert
(b) Paddy cropland
(c) Land covered with fresh snow
(d) Praise land
Ans. (c)
Land covered with fresh snow indeed reflects more sunlight compared to the other three types of land surfaces. Fresh snow and ice have high albedo, meaning they reflect a significant portion of sunlight. In fact, they can reflect up to 95% of the sunlight that falls on them.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here

