In today’s daily current affairs briefing for UPSC aspirants, we explore the latest developments that hold relevance for the upcoming civil services examination. Our focus today includes a critical analysis of recent policy changes, international affairs, and national developments, all of which play a pivotal role in shaping the socio-political and economic landscape of India. Stay informed and stay ahead in your UPSC preparations with our daily current affairs updates, as we provide you with concise, well-researched insights to help you connect the dots between contemporary events and the broader canvas of the civil services syllabus.
Contents
- 1 Vishwakarma Scheme
- 2 Climate change causing deluge across the world
- 3 Medical Textiles
- 4 Natural Polyphenols to Combat Alzheimer’s Disease
- 5 Santiniketan
- 6 Banning Glue pads for rodent control
- 7 Rubber
- 8 Critical Raw Materials Act
- 9 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 9.1 Q: What are daily current affairs?
- 9.2 Q: Why is it important to stay updated with daily current affairs?
- 9.3 Q: Where can I access daily current affairs information?
- 9.4 Q: How can I effectively incorporate daily current affairs into my routine?
- 9.5 Q: What are some tips for critical analysis of daily current affairs?
Vishwakarma Scheme
Tags: GS – 2: Social Justice (Welfare Schemes for vulnerable sections)
In News:
Recently, Prime Minister Narendra Modi launched the PM Vishwakarma scheme in New Delhi on the occasion of Vishwakarma Jayanti, to give government support to workers engaged in traditional crafts and skills.
About the Scheme:
- The scheme was earlier announced during the speech on Independence Day.
- The scheme focuses on uplifting and empowering people engaged in traditional crafts.
- It has a dual purpose:
- Providing financial support to artisans and craftspeople
- Preserving and celebrating India’s age-old traditions, culture, and diverse heritage through local products, art, and crafts.
- The scheme is fully funded by the Union Government with an allocation of Rs 13,000-15,000 crore.
- Families associated with 18 such different sectors like Carpenters, Boat Makers, Armourers, Blacksmiths, etc. will be helped.
- The scheme is to help enhance the skills of workers employed in these fields and help them avail loans easily to aid their earnings.
- The Vishwakarma workers will be registered for free through Common Services Centres using the biometric-based PM Vishwakarma portal.
- They will then be provided recognition through the PM Vishwakarma certificate and ID card, given skill upgradation involving basic and advanced training, a toolkit incentive of ₹15,000, collateral-free credit support up to ₹1 lakh (first tranche) and ₹2 lakh (second tranche) at a concessional interest rate of 5%, incentive for digital transactions and marketing support.
- A toolkit booklet has also been released in 12 Indian languages, with accompanying video elements, to aid the knowledge of workers on new technologies in their field.
- Five lakh families will be covered in the first year and 30 lakh families over five years.
- The scheme also aims to ensure that Vishwakarma are integrated with the domestic and global value chains.
Significance of the Scheme:
- Preservation of traditional skills and practices: It strives to support and maintain a customary family-based practice of transferring knowledge from one generation to the next. This epitomises India’s cultural tradition, in which skill and knowledge are passed down through families.
- Quality upgradation: By providing skill upgradation, training, and toolkit incentives, it focuses to enhance the quality of products and services offered by artisans.
- Integration into Value Chains: The scheme is designed to integrate artisans and craftspeople into both domestic and global value chains. By doing this artisans can sell their products to a broader customer base, potentially increasing their income and sustaining their livelihoods.
- Wider Market Access: The scheme focuses on marketing support and incentives for digital transactions helps artisans expand their market reach. It assists them in tapping into domestic and international markets, thereby creating more opportunities for growth and recognition.
Challenges associated with the implementation of the scheme:
- Addressing the disparity: Artisans in rural areas may face different challenges compared to those in urban areas. Addressing these disparities and ensuring that all eligible artisans can participate in the scheme is essential.
- Effective monitoring and evaluation mechanisms are critical to prevent misuse of funds and ensure that artisans are not excluded from the scheme.
- Digital Literacy: Providing training and resources for digital literacy is a challenge (particularly for those who may not be familiar with digital technologies) that needs to be addressed to maximize the scheme’s impact.
Climate change causing deluge across the world
Tags: GS – 3: Disaster Management (Flood), GS – 3: Ecology and Environment (Climate Change)
In News: Recently, more than 11,000 people were killed and 30,000 were displaced in Libya after torrential rains caused once-in-a-century floods that burst dams and swept away buildings.
Floods due to the Mediterranean storm Daniel:
- More than 11,000 people were killed and 30,000 were displaced in Libya.
- Severe rainfall inundated parts of central Greece, north-western Turkey, southern Brazil, central and coastal Spain, southern China, Hong Kong and the southwestern US.
- While a Mediterranean storm called Daniel led to floods in Libya, Greece and Turkey, a cyclone wreaked havoc in Brazil and another storm known as Typhoon Haikui caused flooding in Hong Kong and China.
- These extreme weather events took place against the backdrop of soaring global temperatures.
Relation between flood and climate change:
- Although it is unclear if climate change is directly causing floods, experts say that it is undoubtedly making many of the elements that do so.
- Heavier Precipitation: Since more water vapour is evaporated from land, the oceans, and other bodies of water at higher temperatures, a warmer atmosphere may contain more moisture. The atmosphere can store around 7% extra moisture, according to experts, for every 1-degree Celsius increase in average temperature. As a result, precipitation becomes more intense, persistent, and/or frequent during storms, increasing the risk of catastrophic floods.
- Amplification of Drought: The earth has gotten both drier and wetter as a result of rising average temperature. Droughts can be made worse by warmer air sucking moisture from the soil. On the other hand, warm air can store more moisture, which allows it to carry more water into a wet area.
- Rising Sea Levels: The melting of glaciers and ice sheets brought on by higher global temperatures has raised sea levels, increasing the danger of flooding in coastal areas. According to a 2022 report by NOAA Climate, the global mean sea level has risen about 21–24 centimetres since 1880.
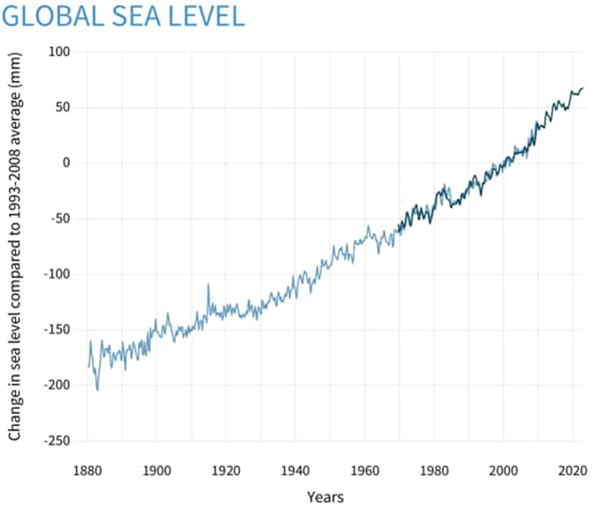
Hard to attribute floods to climate change:
- Particularly for the most devastating floods, which occur less frequently, there are few historical records.
- There are too many variables involved to point out one to be held responsible for flooding in a location (such as regional weather patterns, soil characteristics, and geography of the affected area).
- In the same way, researchers are still trying to determine how climate change and tornadoes are related. However, not all severe weather events are like this.
- There is enough evidence to show that global warming has increased the number of hot days.
Other factors that affect flooding:
- Local conditions like topography and how wet the soil is contributing to the flood development. E.g., drier soils are more capable of absorbing most of the rainfall in comparison to wetter soils — however, both really dry and really wet soils can’t absorb much water.
- Weather patterns: In the 2022 Australian floods much of the eastern coast of the country was inundated due to persistent heavy rainfall.
- Deforestation: A 2007 study done by researchers from Australia’s Charles Darwin University and the National University of Singapore found that with every 10% increase in trees being cut down, the flood risk increases by up to 28%.
- Inadequate maintenance of infrastructure: In Libya’s port city of Derna, the severity of floods was so huge because heavy rainfall caused two of the city’s dams to burst — they collapsed under the pressure of water gathered behind them during the storm.
- Human encroachment into floodplains: In July, Delhi witnessed its worst floods in history. The Yamuna River rose to 208.66 meters, submerging the Ring Road and leaving Kashmere Gate, Civil Lines, ITO, and Rajghat waterlogged. The main reason behind the deluge was excessive encroachment.
https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-climate/climate-change-affects-floods-8941878/
Medical Textiles
Tag: GS-3 Science and Tech
In News: Recently, the Ministry of Textiles organized the ‘Meditex 2023’ International Conference on Scope and Opportunities in Medical Textiles.
About
- Medical textile is a result of the combination of textile technology and medical science known as Medical textiles or Med-tech.
- Some examples of medical textiles are hygienic materials hospital bed sheets, curtains surgical masks, gowns, etc.
- Medical textiles are used in operation theaters, even surgical threads, bandages, artificial bones, ligaments, artificial kidneys, and livers, there are touches of technological and smart textiles everywhere.
Features of Medical Textiles
- Textile materials must be non-toxic.
- Must be resistant to allergens and cancer.
- Textile materials must be biologically compatible.
- Complete good dimensional stability.
- It has air permeability and waterproofing properties.
- Resistant to acid and alkali.
- The quality of the fabric should be good.
- Re-wash and reusable.
Types of Fibers Used in Medical Textiles
Commodity Fiber:
- Natural and Regenerated Fibers: Cotton, Silk, Wood Pulp, Viscose.
- Synthetic fibers: polyester polypropylene, polyethylene, polyamide, PTFA, carbon, glass, silica.
Specialty Fiber:
- Collagen, calcium alginate, chitin, chitosan.
https://pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=1957224
Natural Polyphenols to Combat Alzheimer’s Disease
Tag: GS-3 Science and Technology
In News:
Potential treatment route for Alzheimer’s disease found in natural polyphenol
About
- Naturally occurring plant-based polyphenols (PPs) like tannic acid found in twigs of trees like Chestnut and Oak can modulate the ferroptosis- Alzheimer’s Disease axis to yield a safe, cost-effective strategy for combating Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and reduce the societal burden of this debilitating neurodegenerative disorder.
- Ferroptosis, an iron-dependent form of programmed cell death, has emerged as a significant contributor to the development of AD. Several hallmarks of AD, such as abnormal iron build up, lipid peroxidation, reactive oxygen species (ROS), and reduced activity of the antioxidant enzyme glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4), align with the characteristics of ferroptosis.
Santiniketan
Tag: GS-1 History
In News:
Recently, Rabindranath Tagore’s Santiniketan was declared as a Unesco World Heritage.
About
- The UNESCO World Heritage designation acknowledges the cultural and educational significance of Santiniketan, preserving its unique architectural heritage and raising global awareness of Rabindranath Tagore’s legacy.
- Santiniketan had its origins as an ashram established by Debendranath Tagore, the father of Rabindranath Tagore, with the vision of creating a sanctuary for meditation and fostering unity among people, regardless of their caste or creed.
- The architectural style of Santiniketan represents a departure from the British colonial and European modernist influences of the early 20th century.
- It draws inspiration from ancient, medieval, and folk traditions across Asia, embracing a form of pan-Asian modernity.
- Architectural structures of Santiniketan, dating back to the 19th century, bear historical significance in the founding of Santiniketan and its association with the universal spirit, symbolizing a revival of religious ideals in Bengal and India.

Banning Glue pads for rodent control
Tag: GS-3 Environment
In News:
Recently, Delhi has joined several Indian states in banning glue pads for rodent control.
About
- Glue pads are widely criticized as a cruel method of rodent control because they subject trapped animals to prolonged suffering, as they slowly die from starvation and extreme pain while stuck in the strong adhesive.
- Rat poison, often used as an alternative to glue pads, is similarly considered inhumane. It poses risks not only to the targeted rodents but also to the wider ecosystem. Animals that consume poisoned rats, such as cats, snakes, mongooses, and predatory birds, can be harmed by the toxins, leading to unintended consequences and harm to non-target species.
- The Animal Welfare Board of India (AWBI) took a stand against the use of glue pads for rodent control by releasing advisory notices in both 2011 and 2021, effectively banning their use.

Rubber
Tag: GS-1 Geography
In News:
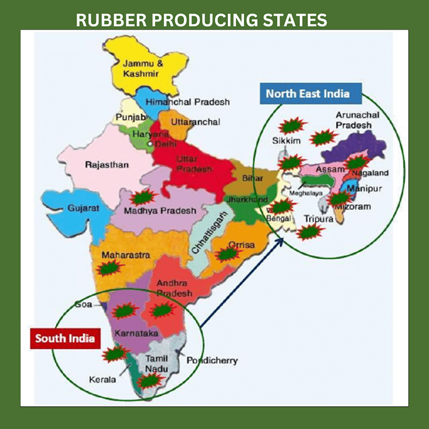
Rubber Board to increase the area under rubber in Northeast.
About
- The Rubber Board of India is embarking on a project aimed at expanding the area under natural rubber cultivation in the northeastern states of India.
- This initiative excludes Sikkim but includes the state of West Bengal.
- The objective is likely to promote and support the cultivation of natural rubber in the northeastern region, which could have economic and environmental benefits for the area and the rubber industry as a whole.
About Natural Rubber
- Natural rubber is a polymer derived from isoprene, an organic compound. It is a cohesive, elastic solid obtained from the latex of several tropical trees, with Hevea brasiliensis being the most significant source.
- Rubber trees typically have an economic lifespan of approximately 32 years in plantation settings.
- Natural rubber can be sourced from various plants, with the most common being the Pará rubber tree (Hevea brasiliensis). This tree thrives when cultivated and produces latex for several years.
- Congo rubber is obtained from vines within the Landolphia genus. These vines cannot be successfully cultivated, leading to the extensive harvesting of wild plants in the Congo for their latex.
- Additionally, rubber can be derived from dandelion milk, which contains latex and can be utilized in rubber production.
Condition Required
- Rubber is a tropical tree. It requires high temperature throughout the year – ranging between 20°-35°C or average monthly mean of 27°C. Less than 20°C temperature is detrimental. Similarly, rubber also requires heavy rainfall.
- The annual average rainfall of not less than 200 cm is optimum. Rubber tree thrives well when the distribution of rainfall is uniformly high all over the year. The equatorial regions of the world are suitable for rubber cultivation.
- Rubber is grown in literate or loamy soil, mostly in slope and undulated land or slightly high elaborated flat land where there is no possibility of water stagnation, and having well drainage facilities
Critical Raw Materials Act
Tag: GS-1 Geography
In News:
EU Parliament votes in favor of Critical Raw Materials Act
About
- Critical raw materials refer to natural resources that hold a strategic value for a country or region because of their economic, industrial, and geopolitical significance.
- These resources play a vital role in various industries, encompassing technology, manufacturing, energy, and defence, and their accessibility can profoundly affect a nation’s economic stability and competitive edge.
- Critical raw materials encompass rare earth elements, lithium, cobalt, graphite, platinum group metals, and specific minerals and metals pivotal for advanced technologies and the development of clean energy solutions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are daily current affairs?
A: Daily current affairs refer to the most recent and relevant events, developments, and news stories that are happening around the world on a day-to-day basis. These can encompass a wide range of topics, including politics, economics, science, technology, sports, and more.
Q: Why is it important to stay updated with daily current affairs?
A: Staying updated with daily current affairs is crucial because it helps individuals make informed decisions in their personal and professional lives. It enables people to understand the world around them, stay aware of significant events, and engage in informed discussions about important issues.
Q: Where can I access daily current affairs information?
A: There are various sources for daily current affairs, including newspapers, news websites, television news broadcasts, radio programs, and dedicated apps or newsletters. Social media platforms are also widely used to share and access current affairs information.
Q: How can I effectively incorporate daily current affairs into my routine?
A: To incorporate daily current affairs into your routine, consider setting aside specific times each day to read or watch news updates. You can also subscribe to newsletters or follow news apps to receive curated content. Engaging in discussions with peers or participating in online forums can further enhance your understanding of current events.
Q: What are some tips for critical analysis of daily current affairs?
A: When analyzing daily current affairs, it’s essential to cross-reference information from multiple sources to ensure accuracy. Additionally, consider the source’s credibility and bias, if any. Develop the ability to identify the main points and implications of news stories, and critically evaluate the significance and impact of the events reported.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here
Visit our YouTube Channel – here


