
In today’s daily current affairs briefing for UPSC aspirants, we explore the latest developments that hold relevance for the upcoming civil services examination. Our focus today includes a critical analysis of recent policy changes, international affairs, and national developments, all of which play a pivotal role in shaping the socio-political and economic landscape of India. Stay informed and stay ahead in your UPSC preparations with our daily current affairs updates, as we provide you with concise, well-researched insights to help you connect the dots between contemporary events and the broader canvas of the civil services syllabus.
Contents
- 1 The problem of manual scavenging in India
- 2 Demographic dividend – India biggest strength
- 3 Plea to make Scheduled Caste status ‘religion-neutral’
- 4 Ferocious black holes reveal ‘time dilation’ in early universe
- 5 Gravity Hole
- 6 Nature Restoration Law
- 7 Mo Jungle Jami Yojana
- 8 Infochemicals
- 9 Regulation of the Digital Market
- 10 Cucumber Mosaic Virus (CMV) and Tomato Mosaic Virus (ToMV)
- 11 Zaporizhzhya Nuclear Power Plant, Ukraine
- 12 New methane source
- 13 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 13.1 Q: What are daily current affairs?
- 13.2 Q: Why is it important to stay updated with daily current affairs?
- 13.3 Q: Where can I access daily current affairs information?
- 13.4 Q: How can I effectively incorporate daily current affairs into my routine?
- 13.5 Q: What are some tips for critical analysis of daily current affairs?
- 14 In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
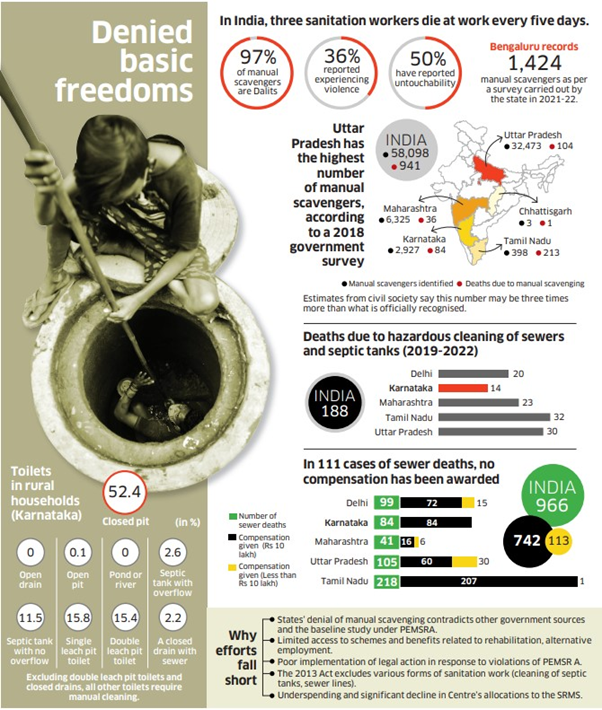
The problem of manual scavenging in India
Tag: GS-2 Social Justice
In News:
Recently Union Social Justice Ministry panel claims Problem of manual scavenging eliminated in the country.
About
Manual scavenging is the practice of manually cleaning human excreta from dry latrines, sewers, and septic tanks. It is a hazardous and dehumanizing occupation that is often done by Dalits.
The practice of manual scavenging has been banned in India since 1993, but it continues to persist in many parts of the country. There are a number of reasons why manual scavenging is still prevalent in India, including:
- Inefficient sewage management systems: In India, most municipalities do not have the latest machines for cleaning the sewage systems. This means that manual scavengers are often hired to enter the sewers and septic tanks to clean them.
- Ineffective implementation of policies: Government programs have focused on providing financial assistance to manual scavengers, but they have not done enough to address the social and economic factors that keep people in this occupation.
- Lack of social mobility: Manual scavengers are often stigmatized by the community and denied access to education and employment opportunities. This makes it difficult for them to escape this occupation.
Effects of manual scavenging:
- Social discrimination: Manual scavengers are often stigmatized by the community and seen as “untouchable.” This can lead to social exclusion and discrimination, making it difficult for manual scavengers to access education, employment, and other opportunities.
- Caste-based inequalities: The caste system is a major factor in the social and economic exclusion of manual scavengers. Manual scavengers are often from the lowest castes, and this can make it difficult for them to escape this occupation.
- Health problems: Manual scavengers are exposed to toxic gases and bacteria that can lead to serious health problems, including respiratory infections, skin diseases, and even death.
- Death: As per the National Commission for Safai Karamcharis (NCSK) database, 608 manual scavengers have died between 2013 and 2017 while cleaning septic tanks.
| Government Initiative to eliminate manual scavenging |
| The Prohibition of Employment as Manual Scavengers and their Rehabilitation (Amendment) Bill 2020 The Prohibition of Employment as Manual Scavengers and their Rehabilitation Act, 2013 The Building and Maintenance of Insanitary Latrines Act of 2013 Prevention of Atrocities Act, 1989 Safaimitra Suraksha Challenge Swachhta Abhiyan App |
There are a number of things that can be done to end manual scavenging in India. These include:
- Investing in modern sewage management systems: This would reduce the need for manual scavenging and create safer working conditions for sanitation workers.
- Enforcing the ban on manual scavenging: The government needs to crack down on employers who hire manual scavengers and ensure that the law is enforced effectively.
- Providing education and employment opportunities: The government needs to provide education and employment opportunities to manual scavengers so that they can escape this occupation.
- Changing social attitudes: The government needs to work to change social attitudes towards manual scavengers and challenge the stigma associated with this occupation.
How can India curb manual scavenging?
Manual scavenging is a hazardous and dehumanizing practice that has been banned in India since 1993. However, it still persists in many parts of the country. There are a number of things that can be done to curb manual scavenging, including:
- Proper identification: The government needs to identify all manual scavengers and provide them with the necessary support.
- Proactive involvement of stakeholders: The government needs to work with all stakeholders, including the community, NGOs, and government officials, to develop and implement a comprehensive plan to end manual scavenging.
- Mass awareness: The government needs to raise awareness about the dangers of manual scavenging and the legal implications of engaging in this practice.
- Rehabilitation and compensation of manual scavengers: The government needs to provide rehabilitation and compensation to manual scavengers who have been injured or killed in the course of their work.
- Investing in proper human waste management: The government needs to invest in proper human waste management systems that will reduce the need for manual scavenging. Example: Swacch Bharat and Swasth Bharat
- Robotic scavenging: The government can use robots to clean sewers and septic tanks, which will reduce the need for manual scavenging. Example: Bandicoot Robot
- Towards social integration: The government needs to work to integrate manual scavengers into mainstream society and provide them with the same opportunities as everyone else.
Source: The Hindu
Demographic dividend – India biggest strength
Tag: GS-1 Population related issues; GS-2 Development and management of Human Resources
In News:
The current demographic dividend of India, entails a huge potential to make its next 25 years a golden period, provided the effective utilisation of its human resources.
About the demographic dividend of India and the world:
- According to the United Nations Population Fund (UNFPA), demographic dividend means, “the economic growth potential that can result from shifts in a population’s age structure, mainly when the share of the working-age population (15 to 64) is larger than the non-working-age share of the population.
- India has an average age of 29 years, thus has a youthful population which presents a unique advantage for the country’s economic growth.
- Globally most of the developed countries are ageing with the US, China, France, Germany and Japan having an average age of 38, 38, 42, 45 and 48 years, respectively.
- India’s old-age dependency ratio will reach 37% in 2075, whereas the same will be 55.8% in France, 75.3 % in Japan, 49.3% in US, 53% in the UK and 63.1% in Germany
Lessons from the Asian Success stories:
- Harnessing of demographic dividend: Asian countries like China, Japan, South Korea, Malaysia, and Singapore have effectively utilised their favourable demographics to drive economic growth and development.
- Shift towards labour intensive productions: Importance of capitalising on labour-intensive manufacturing sectors to create employment opportunities could be witnessed in the case of China.
- Structural Transformations: Countries like Japan, Singapore etc. have undergone structural transformations by transitioning from labour-intensive industries to more advanced sectors to successfully reap the advantage of demographic dividend.
What needs to be done to efficiently use India’s demographic dividend?
- Increased opportunities: There is a need to create opportunities for the existing labour force and the new entrants into the labour market by improving their productivity.
- Increase Marginal Productivity of labour: There is a need to shift a major chunk of the 45.5% of the labour force engaged in agriculture with negligible labour productivity and often being disguised unemployment.
- Focus on labour intensive sectors such as textiles, toys, footwear, auto components, sports goods, mining and construction and agricultural processing to absorb unskilled and uneducated labourers.
- Absorption in tertiary sectors like restaurants, hotels, healthcare and caregiving services have huge potential.
- Industry and Infrastructure Development: India should accelerate infrastructure development to support economic growth and enhance competitiveness. This includes investment in transportation, energy, digital connectivity, and other critical infrastructure sectors.
- Push to MSMEs: MSMEs need support in improving competitiveness, achieving scale, digital infrastructure, technology up-grade and branding to be part of a larger supply chain and the global value chains.
- Skilling and Education: Benefits of demographic dividend can only be reaped if the labour force is more productive and efficient through skilling, re-skilling, up-skilling and education.
- Social Security and Healthcare: India should work towards improving access to quality healthcare services and implementing robust social security programs.
Initiatives of Indian government to reap the demographic dividend:
- Skill development initiatives: Various programmes like Jan Shikshan Sansthan, Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana, and National Apprenticeship Promotion Scheme to improve employability have been launched. The MSDE Vision 2025 further aims to improve the linkage between education and skill.
- Healthcare reforms: The Ayushman Bharat and Swachh Bharat Mission seek to improve health equity in India. The PM Janaushadhi Pariyojana has made drugs affordable and accessible, enhancing overall public health.
- Education policy: The National Education Policy 2020, alongside the Samagra Shiksha programme, is focused on providing inclusive, equitable, and quality education at all school levels, ensuring a productive labour force in the future.
- Support for MSMEs: Recognizing MSMEs as the backbone of Indian manufacturing, the government has supported them through various PLI incentives and credit facilities like Mudra.
- Flagship programmes like Skill India, Make in India, and Start-up India etc. have been introduced to enhance the productivity of the labour force and to foster innovation and entrepreneurship.
Source: Indian Express
Plea to make Scheduled Caste status ‘religion-neutral’
Tags: GS – 1: Castes and Religion
Why in News:
Recently, The Supreme Court has taken on board a plea to stop using religious identity as a criterion to afford or deny communities a place within the Scheduled Caste bracket.
About the Petition:
- It has challenged the Constitution (Scheduled Castes) Order 1950 issued under Article 341(1) of the Constitution.
- Paragraph 3 of the Constitution (Scheduled Castes) Order, 1950 mandates that anybody who is not a Hindu, Sikh or Buddhist cannot be granted Scheduled Caste status.
- Since the word ‘religion’ is not mentioned in Article 341(1) of the Constitution, the ban concerning Christians and Muslims in the 1950 Order should be deleted.
Constitutional Provision:
- Article 341(1) authorises the President to declare certain castes and classes as Scheduled Castes in a State (after consultation with the Governor) or a Union Territory.
Arguments in favour of the petition:
- The change in religion does not change social exclusion or backwardness.
- Justice Ranganath Mishra Commission (2007) recommended that Scheduled Caste reservation be provided for Dalit converts to Christianity and Islam. The Centre had rejected the report.
- A new Commission (under G. Balakrishnan) has been established in 2022 to report on granting Scheduled Caste status to persons who have historically belonged to the SC but have converted to religions other than Hinduism, Buddhism and Sikhism.
Source: The Hindu
Ferocious black holes reveal ‘time dilation’ in early universe
Tags: GS – 3: Science and Technology (Space)
Why in News:
Scientists observed a ferocious black hole that demonstrate “time dilation” in the early universe.
Quasars:
- Quasars are extremely active supermassive black holes found at the centres of galaxies.
- A black hole is a place in space where gravity pulls so much that even light cannot get out.
- Mass of these quasars are millions to billions of times that of the Sun.
- They draw in matter with their strong gravitational pull and emit intense radiation, including high-energy particle jets.
- They are surrounded by a glowing disk of matter.
Key findings of the study:
- Scientists observed the light coming from 190 quasars.
- These quasars were from a time about 1.5 billion years after the Big Bang.
- They found that time passed only about a fifth as quickly as it does today, around 12.3 billion years ago when the universe was much younger. This shows that time used to pass more slowly in the early universe compared to now.
- This supports Einstein’s theory of relativity, which states that time and space are intertwined.
Source: Indian Express
Gravity Hole
Tags: GS-I: Geography
In News:
Indian Ocean harbours a colossal and enigmatic phenomenon known as the “Gravity Hole”
About Gravity Hole:
- Indian Ocean is home to a massive and mysterious geoid low (IOGL) phenomenon also known as the “Gravity Hole”
- Important features:
- It is formed by plumes generated beneath the Indian Ocean due to the perturbation of the African Large Low Shear Velocity province, also known as the “African blob.”
- It spans over 2 million square miles and lies more than 600 miles beneath the Earth’s crust.
- The IOGL is a significant gravity anomaly, with a deep depression hidden beneath the ocean’s surface.
- It is believed that it may be the remnants of an ancient sea that disappeared millions of years ago.
- A recent study proposes that the IOGL comprises slabs from the Tethys Ocean which used to separate the supercontinents of Gondwana and Laurasia, which sank into the Earth’s depths long ago.
- Overall, Gravity Hole in the Indian Ocean is one of the most significant gravitational anomalies on Earth and further research is needed to uncover more secrets about this intriguing phenomenon.
Source: Hindustan Times
Nature Restoration Law
Tags: GS-2: Environmental Laws
In News:
IUCN Urges Europe to implement nature restoration law
About Nature Restoration Law:
- The Nature Restoration Law is a proposed legislation aimed at promoting and implementing nature restoration efforts.
- It is being advocated by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) and urged to be implemented by the European Union (EU).
- The law emphasizes the restoration of natural ecosystems, including land, sea, agriculture, forest, marine, freshwater, and urban systems.
- The EU Council has already agreed to restore 20% of its land and sea by 2030 as a part of the proposed law.
- Important features:
- The law sets legally binding targets for nature restoration and aims to restore entire ecosystems by 2050.
- It highlights the economic benefits of investing in nature restoration, with an estimated eight-fold return and benefits worth 38 Euros for every Euro spent.
- Nature restoration is considered crucial for building resilience against climate-related challenges such as droughts, wildfires, and floods.
- It’s compliance is essential for meeting climate and biodiversity targets under Kunming-Montreal biodiversity framework, Paris agreement, and EU’s European Green Deal.
- Overall, timely implementation of laws on natural restoration is crucial for strengthening the resilience and sustainability of the EU’s economy and environment.
Source: Down to Earth
Mo Jungle Jami Yojana
Tag: GS-3, Environment
In News:
Recently, Odisha government announced the launch of a scheme to effectively implement the provisions of The Scheduled Tribes and other Traditional Forest Dwellers (Recognition of Forest Rights) Act 2006.
About
Mo Jungle Jami Yojana (MJJY) is aims to provide land ownership and access to forest resources to the Scheduled Tribe and forest-dwelling population, improving their livelihoods and food security.
The MJJY will be implemented across 32000 villages of 32 districts in Odisha and will benefit approximately 7.4 lakh tribal families.
The scheme includes the following components:
- Digitization of records: The records of all forest villages will be digitized to make them easily accessible to the beneficiaries.
- Conversion of unsurveyed and zero area villages into revenue villages: The unsurveyed and zero area villages will be converted into revenue villages so that the beneficiaries can get land titles.
- Establishment of Forest Rights Cells: Forest Rights Cells will be established at the tahsil and district level with professional human resources to oversee the implementation of the scheme.
- Provision of land titles: All eligible claimants, including single women and Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs), will receive land titles.
- Provision of basic development facilities: The scheme also includes the provision of basic development facilities such as water, schools, transportation, and health care to the forest villages.
Source: Down to Earth
Infochemicals
Tag: GS-3, Environment
In News:
Climate change is causing a communication breakdown in the animal world
About
- Infochemicals are chemical signals that are used by animals to communicate with each other. They can be used for a variety of purposes, such as finding mates, avoiding predators, or marking territory.
- Climate change is causing a breakdown in animal communication by altering the production and release of infochemicals. For example, rising temperatures can change the way that plants produce volatile organic compounds (VOCs), which are a type of infochemical that is used by insects to find food and mates.
Additional Information about Infochemicals:
- They are produced by a wide variety of animals, including insects, mammals, and birds.
- They can be volatile, meaning that they evaporate easily and can be carried by air currents.
- They can be detected by animals over long distances.
- They can be used to send a variety of messages, such as “I am here,” “This is my territory,” or “I am looking for a mate.”
Source: Down to Earth
Regulation of the Digital Market
Tag: GS-3, Economy
In News:
MCA to oversee all competition issues in digital market; MeitY to handle sector-specific and technical issues
About
- India’s digital market is experiencing rapid growth and transformation. It encompasses various sectors such as e-commerce, digital payments, online services, social media, and digital advertising. It is expected to touch $ 1 trillion by 2025-26.
- The government is working towards introducing legislation including Digital India Act and Digital Competition Law to regulate the growing digital market.
| Regulation |
| Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA) oversees all competition issues in the digital market. Ministry of Information Technology (MeitY) handles sector-specific and technical issues in the digital market. |
Source: The Hindu
Cucumber Mosaic Virus (CMV) and Tomato Mosaic Virus (ToMV)
Tag: GS-3, Science
In News:
Recently, Tomato crop was impacted by attacks of the cucumber mosaic virus (CMV), while growers in Karnataka and other South Indian states have blamed the tomato mosaic virus (ToMV) for crop losses.
About
- Cucumber mosaic virus (CMV) and tomato mosaic virus (ToMV) are two of the most common and destructive viruses that affect vegetable crops. Both viruses are transmitted by aphids, and they can cause a wide range of symptoms, including leaf mottling, stunting, and fruit deformation.
- CMV is a widespread virus that can infect a wide range of plant species, including cucumbers, tomatoes, peppers, and melons. The symptoms of CMV infection can vary depending on the plant species, but they often include yellowing and mottling of the leaves, stunted growth, and reduced yields.
- ToMV is also a widespread virus that can infect a wide range of plant species, including tomatoes, potatoes, eggplants, and peppers. The symptoms of ToMV infection are similar to those of CMV infection, but they can be more severe. ToMV-infected plants often have severely distorted leaves, stunted growth, and reduced yields.
There is no cure for CMV or ToMV infection, but there are a number of steps that can be taken to prevent infection, including:
- Planting resistant varieties of crops
- Using insecticidal soaps or oils to control aphids
- Rotating crops
- Cleaning and disinfecting tools and equipment
If a crop is infected with CMV or ToMV, it is important to remove and destroy the infected plants to prevent the spread of the virus.
| Feature | Cucumber Mosaic Virus (CMV) | Tomato Mosaic Virus (ToMV) |
| Genus | Cucumovirus | Tobamovirus |
| Transmission | Aphids | Aphids |
| Symptoms | Yellowing and mottling of leaves, stunted growth, reduced yields | Severely distorted leaves, stunted growth, reduced yields |
| Control | Planting resistant varieties, using insecticidal soaps or oils, rotating crops, cleaning and disinfecting tools and equipment | Planting resistant varieties, using insecticidal soaps or oils, rotating crops, cleaning and disinfecting tools and equipment |
Source: Indian Express
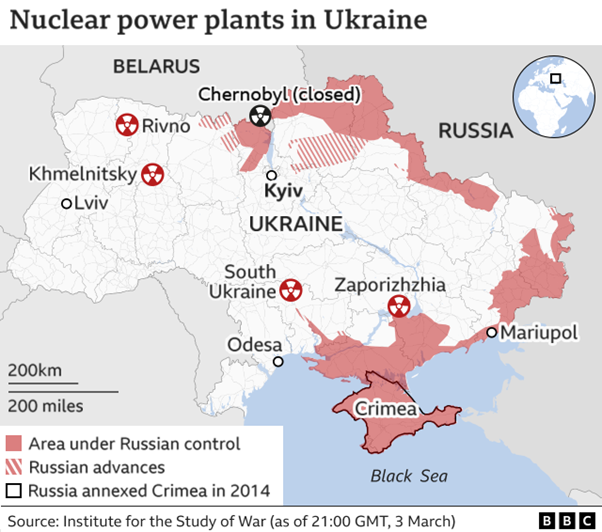
Zaporizhzhya Nuclear Power Plant, Ukraine
Tag: GS-1 Geography
In News:
According to a recent report by an NGO, there are concerning risks associated with the Zaporizhzhya nuclear power plant, which is situated in a region affected by conflict.
About
- Zaporizhzhya Nuclear Power Plant is the largest nuclear power plant in Europe and among the 10 largest in the world.
- It is located in southeastern Ukraine, near the city of Enerhodar.
- It has six VVER-1000 reactors, which can generate a total of 6,000 megawatts of electricity.
- The plant provides about 20% of Ukraine’s electricity.
- It was built by the Soviet Union in the 1980s.
Source: The Hindu
New methane source
Tag: GS-3, Environment
In News:
Climate change has exposed a new source of methane in the Arctic: groundwater springs.
About
- A new source of methane has been discovered in the Arctic, in the form of groundwater springs. These springs are emitting more than 2,000 tonnes of methane annually, which is a potent greenhouse gas.
- The methane is thought to have been trapped under glaciers for thousands of years. As the glaciers retreat due to climate change, the methane is being released into the atmosphere.
- The release of methane from groundwater springs is a new and concerning development. Methane is a more potent greenhouse gas than carbon dioxide, so its release could accelerate climate change.
Source: Down to Earth
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are daily current affairs?
A: Daily current affairs refer to the most recent and relevant events, developments, and news stories that are happening around the world on a day-to-day basis. These can encompass a wide range of topics, including politics, economics, science, technology, sports, and more.
Q: Why is it important to stay updated with daily current affairs?
A: Staying updated with daily current affairs is crucial because it helps individuals make informed decisions in their personal and professional lives. It enables people to understand the world around them, stay aware of significant events, and engage in informed discussions about important issues.
Q: Where can I access daily current affairs information?
A: There are various sources for daily current affairs, including newspapers, news websites, television news broadcasts, radio programs, and dedicated apps or newsletters. Social media platforms are also widely used to share and access current affairs information.
Q: How can I effectively incorporate daily current affairs into my routine?
A: To incorporate daily current affairs into your routine, consider setting aside specific times each day to read or watch news updates. You can also subscribe to newsletters or follow news apps to receive curated content. Engaging in discussions with peers or participating in online forums can further enhance your understanding of current events.
Q: What are some tips for critical analysis of daily current affairs?
A: When analyzing daily current affairs, it’s essential to cross-reference information from multiple sources to ensure accuracy. Additionally, consider the source’s credibility and bias, if any. Develop the ability to identify the main points and implications of news stories, and critically evaluate the significance and impact of the events reported.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here

