
In today’s daily current affairs briefing for UPSC aspirants, we explore the latest developments that hold relevance for the upcoming civil services examination. Our focus today includes a critical analysis of recent policy changes, international affairs, and national developments, all of which play a pivotal role in shaping the socio-political and economic landscape of India. Stay informed and stay ahead in your UPSC preparations with our daily current affairs updates, as we provide you with concise, well-researched insights to help you connect the dots between contemporary events and the broader canvas of the civil services syllabus.
Contents
- 1 India-US 2+2 Ministerial Dialogue
- 1.1 In News:
- 1.2 About 2+2 Meeting
- 1.3 About India’s 2+2 dialogue
- 1.3.1 Défense Collaboration
- 1.3.2 Infantry Combat Vehicles and Future Plans
- 1.3.3 Advancements in defence Technology Cooperation
- 1.3.4 Membership in Combined Maritime Forces
- 1.3.5 Maritime Security
- 1.3.6 Space and Semiconductor Collaboration
- 1.3.7 Discussion on Chinese Aggression
- 1.3.8 India-Canada Row
- 1.3.9 Israel-Hamas War
- 1.4 Way Forward
- 2 OECD Report: Towards Eliminating Plastic Pollution by 2040
- 3 Sovereign green bond
- 4 Code of Conduct for Judiciary
- 5 GPS anklets
- 6 EX-BONGOSAGAR
- 7 Zaglossus Attenboroughi
- 8 Traditional Seed Preservation Practices in North East
- 9 Smart Cities Mission
- 10 Arrow-3 Missile Defence System
- 11 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 11.1 Q: What are daily current affairs?
- 11.2 Q: Why is it important to stay updated with daily current affairs?
- 11.3 Q: Where can I access daily current affairs information?
- 11.4 Q: How can I effectively incorporate daily current affairs into my routine?
- 11.5 Q: What are some tips for critical analysis of daily current affairs?
- 12 In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
India-US 2+2 Ministerial Dialogue
Tag: GS- 2 Bilateral Groupings & Agreements
In News:
The 5th Edition of the India-US 2+2 Ministerial Dialogue recently occurred, focusing on progress in bilateral cooperation areas such as defence, semiconductors, emerging technology, space, and health.
About 2+2 Meeting
- The 2+2 meetings involve two high-level representatives, each holding portfolios in Foreign and Defence ministries, from both countries.
- This framework aims to expand dialogue, allowing a deeper understanding of strategic concerns and sensitivities.
- This mechanism helps build a more robust and integrated strategic relationship amid a dynamically evolving global landscape.
- India’s 2+2 Partners
- The United States stands as India’s oldest and most crucial 2+2 talks partner.
- Furthermore, India has engaged in 2+2 meetings with ministers from Australia, Japan, the United Kingdom, and Russia.
About India’s 2+2 dialogue
Défense Collaboration
- The two nations aimed to jointly develop and produce defence systems, strengthening their partnership in defence technologies.
- Ongoing negotiations include deals for MQ-9B unmanned aerial vehicles and the licensed manufacture of General Electric’s F-414 jet engine in India, aligning with India’s goal of enhancing its defence capabilities.
- The finalization of a Security of Supply Arrangement (SOSA), a key priority in the roadmap, is anticipated to enhance the defence industrial ecosystems and supply chain resilience.
Infantry Combat Vehicles and Future Plans
- Discussions on infantry combat vehicles, particularly the Stryker, were part of the defence industry cooperation roadmap.
- Formal cooperation in infantry combat systems awaits the finalization of the Indian military’s needs and a production plan through collaboration between Indian and U.S. industry and military teams.
Advancements in defence Technology Cooperation
- Both sides assessed the progress of the India-U.S. defence Industrial Ecosystem, INDUS-X, launched in June 2023, focusing on expanding the strategic technology partnership and defence industrial cooperation.
Membership in Combined Maritime Forces
- India’s decision to become a full member of the Combined Maritime Forces, based in Bahrain, was welcomed, underscoring India’s commitment to regional maritime security.
Maritime Security
- Both nations emphasized their commitment to maritime security in the Indo-Pacific region, recognizing the importance of safeguarding vital sea lanes and promoting stability.
Space and Semiconductor Collaboration
- Progress under the India-US Initiative on Critical and Emerging Technology (iCET) was welcomed, aiming to build science and technology collaborations in commercial and defence sectors, especially in emerging technologies like quantum, telecom, biotechnology, Artificial Intelligence, and semiconductors.
- The early meeting of the Strategic Trade Dialogue Monitoring Mechanism was also welcomed.
Discussion on Chinese Aggression
- The U.S. highlighted that the bilateral relationship extends beyond addressing challenges posed by China.
India-Canada Row
- The ongoing dispute between India and Canada, particularly regarding security concerns related to a Khalistan separatist based in the U.S. and Canada, was addressed.
- India communicated its position on core security concerns.
Israel-Hamas War
- India reiterated its stance on the Israel-Hamas Conflict, advocating for a two-state solution and the early resumption of dialogue.
- Humanitarian assistance has been provided, emphasizing adherence to international humanitarian law and condemning civilian casualties.
Way Forward
- The collaboration between the two nations is crucial in upholding a free, open, and rule-based Indo-Pacific region.
- The extraordinary demographic dividend presents extensive opportunities for U.S. and Indian companies in technology transfer, manufacturing, trade, and investment.
- India is becoming a prominent player in a global system experiencing unprecedented transformation.
- Leveraging its current position, India intends to explore opportunities that advance its essential interests.
| UPSC Previous Year Questions Mains (2019) Q. ‘What introduces friction into the ties between India and the United States is that Washington is still unable to find for India a position in its global strategy, which would satisfy India’s National self-esteem and ambitions’. Explain with suitable examples. (Q. ‘What introduces friction into the ties between India and the United States is that Washington is still unable to find for India a position in its global strategy, which would satisfy India’s National self-esteem and ambitions’. Explain with suitable examples. |
Source: PIB
OECD Report: Towards Eliminating Plastic Pollution by 2040
Tag: GS-3 Environment
In News:
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) issued an interim report which disclosed that 21 million tonnes of plastics entered the environment worldwide in 2022.
Key Highlights of the Report
- Considering the climate policies implemented as of 2021 (used as a reference), there is a projected 50% increase in the release of (macro)plastics into the environment by 2040.
- However, if prompt, rigorous, and globally coordinated policy measures are taken (incurring a cost equivalent to just 0.5% of global GDP), plastic waste generation in 2040 could be reduced by a quarter compared to the baseline.
- Adverse Outcomes of Persistent Plastic Utilization and Increasing Waste Levels includes:
- Environmental Consequences encompass the buildup of plastic in oceans, causing harm to marine life, and the disturbance of ecosystems due to plastic pollution.
- Climate Ramifications involve greenhouse gas emissions stemming from plastic production and the energy-intensive procedures involved in plastic recycling.
- Health Implications involve microplastics entering the food chain (resulting in bioaccumulation) and impacting human health, as well as respiratory issues arising from the incineration of plastic waste.
- Economic Repercussions include the expenses related to cleaning up plastic pollution and the decline in tourism revenue in areas affected by plastic debris.
Recommendations proposed in the report
Control Production and Demand:
- Enforce targeted taxes and regulations on disposable plastics, as demonstrated by India’s ban on Single-Use plastics in 2022.
- Constrain production and demand to sustainable levels by exploring alternatives to plastics, following India’s LiFE approach.
Foster Circular Design:
- Enhance the plastic production process through eco-design criteria. Establish product standards that encourage reuse.
Improve Recycling:
- Bolster material loops by enhancing separate collection, sorting, and recycling of plastic waste.
- Implement measures such as extended producer responsibility.
Seal Leakage Routes:
- Mitigate environmental losses by implementing effective waste collection and disposal methods.
About OECD
- The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development is an intergovernmental organization established in 1961 with 38 member countries.
- Its primary purpose is to promote economic progress and global trade.
- Functioning as a forum, its member nations are characterized by their commitment to democracy and market economies.
- The organization serves as a platform for comparing policy experiences, addressing common issues, identifying best practices, and coordinating both domestic and international policies among its members.
- Most OECD members are high-income economies categorized as “very high” in the Human Development Index, representing developed countries.
- Collectively, they have a population of 1.38 billion
- As of 2017, OECD member countries accounted for 62.2% of global nominal GDP (US$49.6 trillion) and 42.8% of global GDP (Int$54.2 trillion) at purchasing power parity.
- The OECD holds the status of an official United Nations observer.
| UPSC Previous Year Questions Prelims (2021) Q. Bisphenol A (BPA), a cause of concern, is a structural/key component in the manufacture of which of the following kinds of plastics? (a) Low-density polyethylene (b) Polycarbonate (c) Polyethylene terephthalate (d) Polyvinyl chloride Answer: B Exp: BPA stands for bisphenol A, an industrial chemical that has been used to make certain plastics and resins since the 1950s. BPA is found in polycarbonate plastics and epoxy resins. Polycarbonate plastics are often used in containers that store food and beverages, such as water bottles. Prelims (2021) Q. Triclosan considered harmful when exposed to high levels for a long time, is most likely present in which of the following? (a) Food preservatives (b) Fruit-ripening substances (c) Reused plastic containers (d) Toiletries Answer: D Exp: Triclosan is an antibacterial and antifungal agent present in some consumer products, including toothpaste, soaps, detergents, toiletries toys, and surgical cleaning treatment |
Source: DTE
Sovereign green bond
Tag: GS-3 Economy
In News:
The initial issuance of sovereign green bonds (SGrB) for the Financial Year 2024 saw a successful auction of five-year maturity bonds, drawing considerable investor interest.
About Sovereign green bond
- A sovereign green bond is a financial tool issued by a sovereign entity, inter-governmental group, alliance, or corporation.
- The funds raised from these bonds are specifically allocated to projects categorized as environmentally sustainable.
- In the context of India, sovereign green bonds exemplify the nation’s dedication to constructing a low-carbon economy.
- They effectively reduce the capital cost associated with green projects by attracting new investors and mobilizing private capital for sustainable development initiatives.
- India’s inaugural foray into the sovereign green bond market financed expenditures in various areas, including grid-scale solar and wind projects, as well as decentralized solar initiatives such as solar water pumps for agriculture.
- This demonstrates a strategic utilization of green bonds to promote environmentally friendly ventures in the country.
Source: Business Line
Code of Conduct for Judiciary
Tag: GS-2 Indian Polity
In News:
The U.S. Supreme Court has issued its inaugural code of conduct, consisting of nine pages outlining ethics rules for its justices.
About Code of Conduct
A code of conduct is a set of guidelines that delineate the standards, rules, and responsibilities or appropriate practices for an individual, group, or organization. It may be either voluntary or mandatory.
Criticism of Code of Conduct
- The code lacks an enforcement mechanism, relying on justices to voluntarily comply with its “rules and principles.” Rules alone are deemed incomplete without a mechanism for assurance.
- There have been recent appeals for the U.S. Congress to enact legislation that would establish enforceable ethical guidelines for the Supreme Court.
Ethical Concerns in the Indian Judiciary
- In 2022, the Madurai bench of the Madras High Court sentenced YouTuber Savukku Shankar to six months in prison.
- This decision followed his accusations against Justice GR Swaminathan, alleging influence in a case and making general claims of corruption within the higher judiciary.
- In 2018, a press conference was held by four of the senior-most judges of the Supreme Court, expressing dissent against the then Chief Justice of India (CJI).
- In 2020, former Chief Justice of India (CJI) Ranjan Gogoi was nominated to the Rajya Sabha. During his tenure, the bench headed by him delivered pivotal judgments in cases such as Ayodhya, Sabarimala, and Rafale.
Solutions
- Adherence to the Bangalore Principles of Judicial Conduct (2002) is essential, emphasizing the importance of maintaining independence from inappropriate influences, steering clear of conflicts of interest, and upholding the rule of law.
- The concern known as the “Uncle Judges Syndrome” is tackled by the Law Commission of India in its 230th Report.
- The commission recommends that individuals with family members practicing in a High Court should not be appointed as judges in the same High Court.
Source: BBC
GPS anklets
Tag: GS-3 science and technology
In News:
Marking a precedent in India, Ghulam Mohammad Bhat, who is facing charges under the Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Act in Jammu and Kashmir, has been granted bail under the condition of wearing a Global Positioning System (GPS) tracking device.
About GPS tracker
- The GPS tracker, a compact wearable device, is securely attached around the ankle, offering instantaneous location updates.
- It is designed to be tamper-proof, triggering an alarm if any attempt is made to interfere with it.
- Additionally, it cannot be removed by the wearer or any unauthorized individual without causing damage.
- This tracker can be worn on either the ankle or arm, resulting in variations known as GPS anklets and GPS bracelets.
- While the use of GPS trackers as a condition for bail is standard practice in countries such as the United States, the United Kingdom, and Malaysia, this represents the inaugural occurrence of such a measure in India.
About GPS
- The Global Positioning System (GPS) is a satellite-based navigation system employing satellites, receivers, and algorithms to coordinate location, velocity, and time data.
- Originally developed by the U.S. military, GPS has evolved into a widely utilized technology for air, sea, and land travel.
- One of the key advantages of GPS is its operational capability in diverse weather conditions, offering continuous service worldwide 24 hours a day.
- Remarkably, GPS does not entail subscription fees or setup charges.
- Certain GPS receivers exhibit exceptional accuracy, enabling them to pinpoint their location with precision down to 1 centimetre.
- Originally conceived for military purposes, GPS has transcended its military origins to become an indispensable tool for various civilian applications, including navigation, mapping, surveying, and numerous location-based services.
Source: IE
EX-BONGOSAGAR
Tag: GS-2 International Relations
In News:
The Indian Navy and Bangladesh Navy conducted the 4th edition of the Bilateral Exercise BONGOSAGAR-23 and the 5th edition of the Coordinated Patrol (CORPAT) in the Northern Bay of Bengal.
About EX-BONGOSAGAR
- Participating in the exercise were Indian Navy Ships Kuthar, Kiltan, and Maritime Patrol Aircraft Dornier, alongside Bangladesh Navy Ships Abu Bakr, Abu Ubaidah, and MPA.
- Notably, the CORPAT-23 incorporated inaugural Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief (HADR) drills, specifically concentrating on a Search and Rescue scenario at sea.
Source: PIB
Zaglossus Attenboroughi
Tag: GS-3 Environment
In News:
After being missing for six decades, an elusive echidna identified as Zaglossus Attenborough, previously feared extinct, has been rediscovered in a remote area of Indonesia.
About Zaglossus Attenboroughi
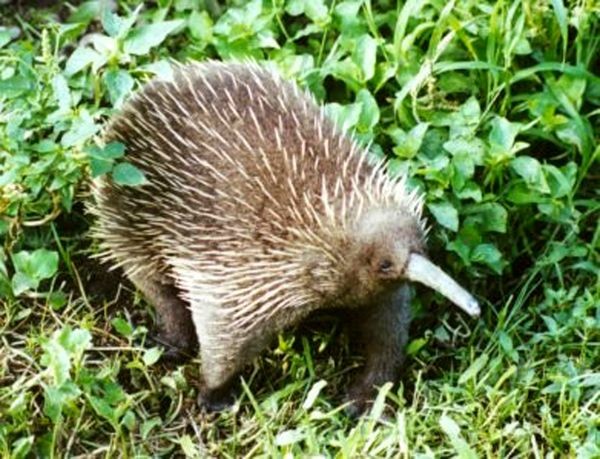

- The Zaglossus Attenborough, commonly known as Attenborough’s long-beaked echidna, was last sighted in 1961.
- This species of long-beaked echidna, named in honour of renowned British naturalist David Attenborough, is particularly challenging to locate due to its nocturnal and elusive nature.
- It has exclusively been documented in the extremely remote Cyclops Mountains within Indonesia’s Papua region.
- Also referred to as Sir David’s long-beaked echidna or the Cyclops long-beaked echidna, this unique creature is one of three species belonging to the Zaglossus genus found on the island of New Guinea.
- Specifically, it resides in the Cyclops Mountains, near the cities of Sentani and Jayapura in the Indonesian province of Papua.
- Given its restricted habitat and elusive behaviour, the Attenborough long-beaked echidna is a critically endangered species, as classified by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN).
- The nomenclature reflects not only its distinctive features but also pays tribute to the naturalist Sir David Attenborough.
Source: TH
Traditional Seed Preservation Practices in North East
Tag: GS-3 Environment
In News:
The Ao and Sümi Naga communities in Nagaland adhere to practices handed down through generations, specifically Traditional Seed Preservation Practices. These involve safeguarding seeds from productive harvests to be used in subsequent cycles.
About Ao and Sümi Naga communities
Ao Naga community
- The Ao Naga tribe primarily inhabits Nagaland’s Mokokchung district, spanning from Tsüla (Dikhu) Valley to Tsürang (Disai) Valley.
- Thought to have originated from Southeast Asian nations like Indonesia, Malaysia, and Myanmar, the Ao Nagas are part of the Naga tribes with roots in Mongoloid ancestry.
- Within the Ao tribe, the Mongsen and the Chongli are distinctive racial groups.
- The Aos were the pioneering Nagas to embrace Christianity and Western education.
Sümi Naga Community
- The Sümi Naga people represent another indigenous community in Nagaland, renowned for their unique cultural practices and robust agricultural heritage.
- They observe various festivals, including Tuluni, Ahuna, and Tsükhenye, often revolving around agricultural cycles and featuring traditional dances, songs, and feasts.
- Similar to several other Naga tribes, the Sümi Naga traditionally engaged in jhum or shifting cultivation, cultivating crops such as rice, millet, beans, lentils, pepper, and tobacco.
About Shifting cultivation
- Shifting cultivation, referred to locally as ‘Jhum,‘ is a prevalent crop cultivation method among the indigenous communities of Northeast India.
- Also known as slash-and-burn agriculture, this practice involves farmers clearing land by cutting vegetation and burning forests and woodlands to create open areas for agriculture.
- This method offers a quick and straightforward way to prepare the land for cultivation.
- The burning of residual materials contributes essential nutrients to the soil, facilitating cultivation.
- Beyond providing sustenance, fodder, fuel, and livelihood, this practice is intricately tied to the identity of the families involved.
- However, due to the felling of forests and trees, shifting cultivation can lead to soil erosion and potentially impact the course of rivers.
Source: DTE
Smart Cities Mission
Tag: GS- 2 Government Policies & Interventions, Welfare Schemes, Infrastructure
In News:
The most recent data from the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs sheds light on the current status of India’s Smart Cities Mission.
Key Highlights of the Data
- Leading the completion of projects, fund utilization, and overall criteria, Surat in Gujarat stands out as the top-performing city.
- Agra (Uttar Pradesh), Ahmedabad (Gujarat), Varanasi (Uttar Pradesh), and Bhopal (Madhya Pradesh) also secure positions in the top five cities, showcasing commendable progress
- The remaining top 10 includes Tumakuru (Karnataka), Udaipur (Rajasthan), Madurai (Tamil Nadu), Kota (Rajasthan), and Shivamogga (Karnataka).
- Addressing regional disparities, Union Territories (UTs) and cities in Northeastern states find themselves in the bottom 10.
- The cities at the bottom include Kavaratti (Lakshadweep), Puducherry, Port Blair (Andaman and Nicobar Islands), Imphal (Manipur), Shillong (Meghalaya), Diu, Guwahati (Assam), Aizawl (Mizoram), Gangtok (Sikkim), and Pasighat (Arunachal Pradesh).
- Sources attribute the slower progress in smaller cities to capacity constraints, emphasizing the need for tailored strategies to address the unique challenges faced by these urban centers.
- In terms of the overall project landscape, approximately 22% of total projects (1,745 out of 7,947) that constitute 33% of the total cost (Rs 1.70 lakh crore) are still ongoing. The completion of the majority of projects (6,202) underscores the scale and financial investment involved.
Source: IE
Arrow-3 Missile Defence System
Tag: GS-2 IR
In News:
Israel confirmed using its advanced Arrow 3 missile interceptor against Iran-backed Houthi rebels.
About Arrow-3 Missile Defence System
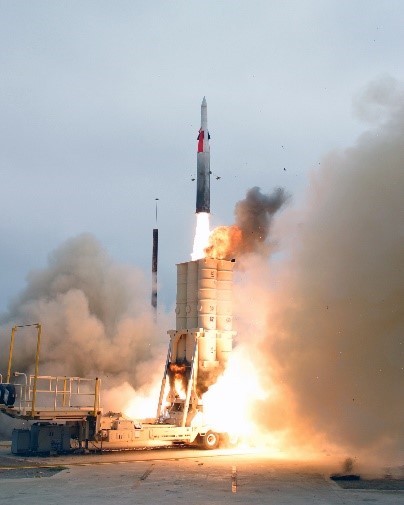

- The Arrow 3, also known as Hetz 3, stands as an Ex atmospheric hypersonic anti-ballistic missile jointly funded, developed, and produced by the collaborative efforts of Israel and the United States.
- Spearheaded by Israel Aerospace Industries and Boeing, this missile is under the oversight of the Israeli Ministry of Defence’s “Homa” administration and the U.S. Missile defence Agency.
- The Arrow 3 is a crucial component of anti-ballistic missile defence, specifically designed to intercept long-range missiles.
- A joint venture between Israel Aerospace Industries (IAI) and Boeing, with collaboration from the U.S. Missile defence Agency.
- Engineered to intercept threats at high altitudes and extended ranges compared to its predecessor, Arrow 2.
- Possesses the capability to intercept incoming missiles outside Earth’s atmosphere
- Relies on kinetic energy to neutralize incoming threats, eliminating the need for explosive warheads.
- Capable of intercepting threats at distances exceeding 1,500 kilometres.
- Able to engage targets at altitudes surpassing Earth’s atmosphere, typically above 100 km.
- Travel speeds estimated at Mach 9 or greater (9 times the speed of sound).
- Equipped with advanced sensors and tracking systems for precise target acquisition and interception.
- Can engage multiple incoming threats simultaneously.
- Deemed highly effective against various ballistic missiles, including intermediate-range and intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs).
Source: TOI
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are daily current affairs?
A: Daily current affairs refer to the most recent and relevant events, developments, and news stories that are happening around the world on a day-to-day basis. These can encompass a wide range of topics, including politics, economics, science, technology, sports, and more.
Q: Why is it important to stay updated with daily current affairs?
A: Staying updated with daily current affairs is crucial because it helps individuals make informed decisions in their personal and professional lives. It enables people to understand the world around them, stay aware of significant events, and engage in informed discussions about important issues.
Q: Where can I access daily current affairs information?
A: There are various sources for daily current affairs, including newspapers, news websites, television news broadcasts, radio programs, and dedicated apps or newsletters. Social media platforms are also widely used to share and access current affairs information.
Q: How can I effectively incorporate daily current affairs into my routine?
A: To incorporate daily current affairs into your routine, consider setting aside specific times each day to read or watch news updates. You can also subscribe to newsletters or follow news apps to receive curated content. Engaging in discussions with peers or participating in online forums can further enhance your understanding of current events.
Q: What are some tips for critical analysis of daily current affairs?
A: When analyzing daily current affairs, it’s essential to cross-reference information from multiple sources to ensure accuracy. Additionally, consider the source’s credibility and bias, if any. Develop the ability to identify the main points and implications of news stories, and critically evaluate the significance and impact of the events reported.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here

