
In today’s daily current affairs briefing for UPSC aspirants, we explore the latest developments that hold relevance for the upcoming civil services examination. Our focus today includes a critical analysis of recent policy changes, international affairs, and national developments, all of which play a pivotal role in shaping the socio-political and economic landscape of India. Stay informed and stay ahead in your UPSC preparations with our daily current affairs updates, as we provide you with concise, well-researched insights to help you connect the dots between contemporary events and the broader canvas of the civil services syllabus.
Contents
- 1 India-Middle East-Europe Corridor (IMEC)
- 2 Complexity in Federal Relations
- 3 UNESCO’s City of Literature
- 4 The Bharatiya Nagarik Suraksha Sanhita, 2023
- 5 PVTGs
- 6 Chhath Pooja
- 7 FATF
- 8 Global South
- 9 WMO
- 10 Trade Deficit
- 11 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 11.1 Q: What are daily current affairs?
- 11.2 Q: Why is it important to stay updated with daily current affairs?
- 11.3 Q: Where can I access daily current affairs information?
- 11.4 Q: How can I effectively incorporate daily current affairs into my routine?
- 11.5 Q: What are some tips for critical analysis of daily current affairs?
- 12 In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
India-Middle East-Europe Corridor (IMEC)
Tag: GS-2 IR, Global Groupings, Groupings & Agreements Involving India and/or Affecting India’s Interests
In News:
The Economic Corridor connecting India, the Middle East, and Europe is described by Finance Minister as a mutually beneficial arrangement for all participating states.
About IMEC
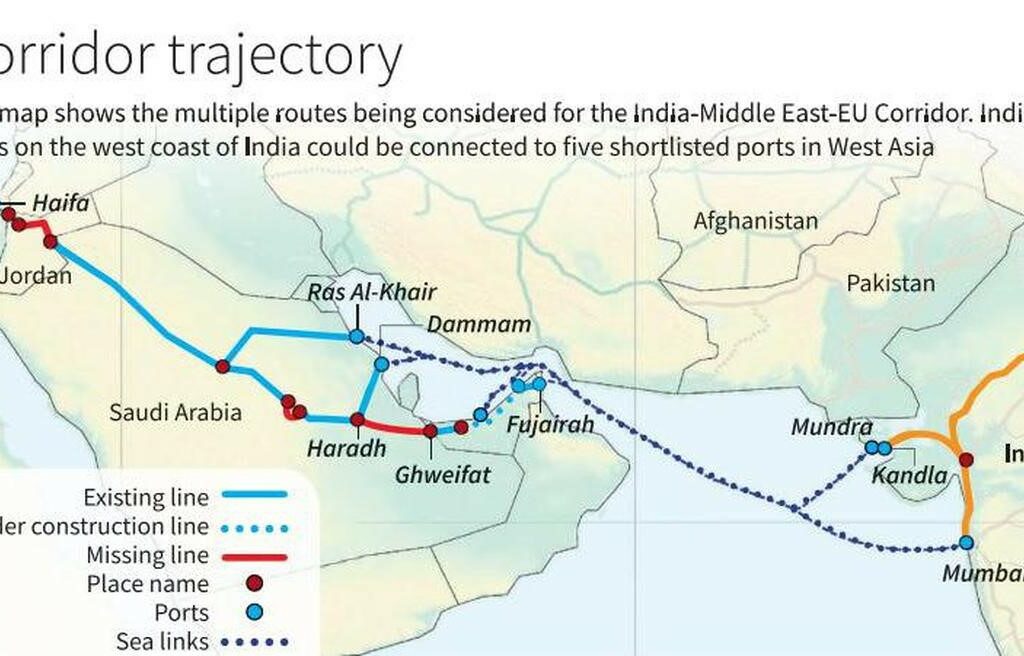
- The India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC) involves two corridors: the East Corridor connecting India to the Arabian Gulf and the Northern Corridor linking the Gulf to Europe.
- It encompasses railroad, ship-to-rail networks, and road transport routes, along with an electricity cable, hydrogen pipeline, and high-speed data cable.
- Key signatories include India, the US, Saudi Arabia, UAE, EU, Italy, France, and Germany.
- The initiative aims to establish a comprehensive transportation network to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and promote economic unity.
- The primary objective is to facilitate trade and connectivity, providing a reliable cross-border ship-to-rail transit network once completed.
Impacts of IMEC
Geopolitical Implications:
- IMEC serves as a counter to China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), countering its influence in the Eurasian region.
- It strengthens ties across continents, offering the U.S. a strategic opportunity to maintain influence amid China’s rise.
- Bypassing Pakistan, IMEC breaks its veto over India’s overland connectivity to the West.
- The corridor deepens India’s strategic engagement with the Arabian Peninsula, promoting intra-regional connectivity and potentially contributing to peace in the region.
Economic Benefits:
- IMEC enhances trade opportunities, making India’s trade with Europe 40% faster compared to the Suez Canal route.
- It stimulates industrial growth by creating an efficient transport network for the seamless movement of goods.
- Job creation is expected to surge across sectors due to expanded economic activities.
- The corridor ensures energy security and resource access, stabilizing India’s energy sector.
- Facilitating Special Economic Zones (SEZs) along the route can attract foreign investment, promote manufacturing, and drive economic growth.
Major Challenges in IMEC
Logistical and Connectivity Complexity
- Managing the intricate coordination and planning involved in developing a multimodal transport corridor across rail, road, and sea routes among various countries presents significant challenges.
Construction Challenges and Rail Network Gaps
- Substantial investment and construction efforts are required to address missing rail links, especially in the Middle East, posing a substantial obstacle.
Cross-Border Coordination Struggles
- Coordinating policies and regulations across multiple countries with diverse interests and administrative procedures emerges as a major hurdle in realizing this transcontinental corridor.
Potential Opposition and Competitive Forces
- The likelihood of opposition or competition from existing transport routes, notably Egypt’s Suez Canal, introduces diplomatic challenges and may affect traffic and revenue.
Financial Obstacles and Cost Estimations
- Securing financing for the construction, operation, and maintenance of the corridor proves to be a significant challenge, with estimated costs ranging from USD 3 billion to USD 8 billion for each IMEC route.
The Path Ahead
- Ensuring smooth operations requires achieving technical compatibility and standardization in gauges, train technologies, container dimensions, and other critical aspects across diverse countries.
- Smooth implementation hinges on balancing geopolitical interests among participating nations and addressing potential political sensitivities, particularly concerning Israel.
- Critical aspects of the project include addressing environmental impact concerns, ensuring sustainability, and adhering to green and eco-friendly practices in both construction and operation.
- Essential to the project’s success is the implementation of robust security measures to safeguard cargo and infrastructure from potential threats, theft, piracy, and other security risks.
Source: TH
Complexity in Federal Relations
Tag: GS- 2 Federalism Co-operative Federalism
In News:
In India, historical disputes between the Central and State governments over economic policies have intensified in recent years, becoming persistent frictions in the federal system.
About Federalism
- Federalism is a governance system dividing powers between central and state governments, fostering diversity and regional autonomy.
- India’s Constitution establishes a quasi-federal system, blending features of both federation and union.
- Legislative powers are distributed through Union, State, and Concurrent Lists.
- India’s federalism, evolving from a unitary British system to a federal one post-independence, addresses challenges like princely state integration, linguistic reorganization, regional movements, and fiscal and cooperative federalism.
- It entails complex center-state relations, resource sharing, and inter-state coordination.
Different Models of Federal Systems
Holding Together Federation
- Powers are shared among constituent parts, emphasizing diversity.
- Central authority holds significant powers.
- Examples include India, Spain, and Belgium.
Coming Together Federation
- Independent states unite to form a larger entity.
- States enjoy more autonomy than in the holding together type.
- Examples include the USA, Australia, and Switzerland.
Asymmetrical Federation
- Some constituent units have more powers or special status due to historical or cultural reasons.
- Examples include Canada (Quebec), Russia (Chechnya), and Ethiopia (Tigray).
Challenges confronting Indian federalism
Regional Dynamics
- Emergence of regional parties based on linguistic, ethnic, and religious factors poses a threat to national integration.
- Instances include calls for Gorkhaland in West Bengal and Bodoland in Assam.
Power Division Issues
- Ambiguities and imbalances in the distribution of powers between the Centre and states.
- The Centre’s extensive powers can result in interference, exemplified by the imposition of President’s rule in Arunachal Pradesh and Uttarakhand in 2016.
Lack of Fiscal Federalism
- Inequities and opacities in fiscal relations.
- States rely on the Centre for financial support with constrained taxation authority.
- Grievances arise over insufficient compensation for GST-related revenue losses.
Disparity in Representation
- Disproportional representation in parliamentary and federal bodies.
- The influence of states in national decision-making is impacted by variations such as Uttar Pradesh’s 80 Lok Sabha seats compared to Sikkim’s one.
Centralized Amendment Authority
- The exclusive power of Parliament to amend the Constitution.
- Instances include the independent decision to revoke Article 370 and reorganize Jammu and Kashmir in 2019 without consulting the state government.
- The establishment of Telangana in 2014 resulted in protests and violence due to opposition from Andhra Pradesh.
How to Promote Federalism? and Institutions engaged in Promotion
Preserving Diversity and Pluralism
- Federalism is essential for safeguarding India’s diverse society, culture, language, and religion against pressures for homogenization from the Centre or dominant groups.
- Example: Protecting regional languages and cultures.
Safeguarding Autonomy and Rights
- Federalism is crucial for protecting and enhancing the autonomy and rights of states and sub-national units, countering centralization and external interference.
- Example: States’ autonomy in formulating education policies.
Improving Governance Quality and Efficiency
- Federalism is necessary to empower states and sub-national units to formulate and implement policies, ensuring quality and efficient service delivery.
- Example: State-driven healthcare initiatives.
Promoting Balanced and Inclusive Development
- Federalism promotes equitable distribution of resources and opportunities, fostering balanced and inclusive development across all regions and sections of India.
- Example: Allocating resources based on regional needs.
Fostering Harmony and Cooperation
- Federalism encourages dialogue and consultation over confrontation, sustaining harmony and cooperation among different levels or units of government.
- Example: Resolving inter-state water disputes through dialogue.
Institutions Promoting Federalism
The Supreme Court
- Acts as the constitutional guardian and interpreter, resolving disputes between the Centre and states.
- Example: Adjudicating on disputes related to state autonomy.
The Inter-State Council
- Constitutional body promoting coordination and cooperation among the Centre and states.
- Example: Facilitating dialogue on water-sharing issues between states.
The Finance Commission
- Recommends revenue distribution between the Centre and states, enhancing state resources.
- Example: Allocating funds for state-specific development projects.
The NITI Aayog
- Functions as a think tank, involving states in economic and social development policies.
- Example: Collaborative policymaking for sustainable development.
To strengthen federalism in India, focus should be on
- Enhancing Devolution
- Increase the transfer of powers and resources to states and local bodies.
- Representation and Participation
- Involve states more in national decision-making, fostering greater representation.
- Cooperative and Competitive Federalism
- Encourage collaboration and competition among states, promoting best practices.
- Addressing Regional Imbalances
- Tackle regional imbalances through special assistance, fair resource allocation, and regional development councils.
- Respecting Federal Principles
- Adhere to constitutional provisions, avoid unilateral actions, and resolve disputes through dialogue or judicial mechanisms.
| UPSC Previous Year Questions Prelims (2017) Q. Which one of the following is not a feature of Indian federalism? (a) There is an independent judiciary in India. (b) Powers have been clearly divided between the Centre and the States. (c) The federating units have been given unequal representation in the Rajya Sabha. (d) It is the result of an agreement among the federating units. Ans: (d) Prelims (2017) Q. Local self-government can be best explained as an exercise in (a) Federalism (b) Democratic decentralization (c) Administrative delegation (d) Direct democracy Ans: (b) Mains (2014) Q. Though the federal principle is dominant in our constitution and that principle is one of its basic features, but it is equally true that federalism under the Indian Constitution leans in favour of a strong Center, a feature that militates against the concept of strong federalism. Discuss. |
Source: TH
UNESCO’s City of Literature
Tag: GS 1 Art and culture
In News:
How Kerala Secured a Spot on UNESCO’s City of Literature List: The Journey from Edinburgh to Kozhikode
About UNESCO’s City of Literature
- UNESCO City of Literature is a designation awarded by UNESCO (United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization) as part of its Creative Cities Network program.
- The program recognizes cities around the world that have made significant efforts to nurture and promote literature, fostering a culture of reading, writing, and literary exchange.
- The UNESCO City of Literature designation aims to:
- Promote Literature and Culture
- Cities designated as UNESCO Cities of Literature are recognized for their commitment to supporting literature and promoting cultural diversity.
- Encourage Collaboration
- The program encourages cities to collaborate on literary initiatives, fostering international cooperation and cultural exchange among cities with a shared dedication to literature.
- Empower Local Writers
- Designated cities actively support local writers and literary communities, providing them with platforms to showcase their work and contribute to the city’s cultural life.
- Strengthen Publishing and Educational Initiatives
- UNESCO Cities of Literature often focus on enhancing publishing activities, organizing literary events, and promoting educational programs to strengthen literary traditions and knowledge.
- Preserve Literary Heritage
- These cities are committed to preserving their literary heritage, including historical sites, libraries, and literary archives.
- Promote Literature and Culture
- The designation is not only an acknowledgment of a city’s past literary achievements but also a commitment to ongoing efforts to nurture literary creativity, promote cultural exchange, and foster a vibrant literary environment.
- Each City of Literature is unique in its approach to achieving these goals, contributing to the global network of cities dedicated to advancing literature and creativity.
- Some international examples of UNESCO Cities of Literature include Edinburgh, Melbourne, Dublin, and Iowa City.
Source: TH
The Bharatiya Nagarik Suraksha Sanhita, 2023
Tag: GS-2 Constitutional Amendments
In News:
The 2023 proposed Bharatiya Nagarik Suraksha Sanhita (BNSS) Bill, intended to replace the Code of Criminal Procedure (CrPC), extends additional immunity to armed forces personnel.
About The Bharatiya Nagarik Suraksha Sanhita, 2023
- Introduced in the Lok Sabha on August 11, 2023, the Bharatiya Nagarik Suraksha Sanhita, 2023 repeals the Code of Criminal Procedure, 1973.
- This Code outlines the procedures for arrest, prosecution, and bail related to offenses under various Acts, including the Indian Penal Code, 1860.
- While the new Bill largely preserves the existing provisions of the Code.

Key Highlights of the Bill
- Copy of FIR-Accused and victim entitled to a free copy of the FIR within 14 days of the accused’s production.
- Zero FIR-Permits filing a zero FIR from any part of the country, allowing for the transfer to the relevant jurisdiction.
Expedited Procedures
- Accused can be examined through electronic means like video conferencing.
- Mandatory summary trials for petty cases.
- Streamlined magisterial system for efficiency.
Greater Use of Technology
- Electronic forms for trials, appeals, depositions, summons, warrants, etc.
- Audio-video recording for search, seizure, victim’s statement, etc.
- Designated officers for online and in-person notification of arrests (e-FIR).
- Sedition-Outlines Executive Magistrate’s procedure for seditious matters.
- Use of Handcuffs-Permitted for habitual offenders, escapees, and serious crimes.
- Safeguards Against Arrests-No arrest without permission for offenses punishable with less than 3 years or for individuals above 60 years.
- Cognizable Cases-Preliminary inquiry within 14 days for offenses attracting 3-7 years.
- Mercy Petitions-Submit within 30 days to the Governor after disposal of the convict’s petition.
- Sanction to Prosecute-Government to decide on sanction within 120 days; not required for sexual offenses, trafficking, etc.
- Arms in Procession-Prohibits district magistrates from carrying arms in public processions or drills.
- Samples Without Arrest-Magistrate can order sample collection without arrest for investigation purposes.
- Detention-Police can detain or remove individuals resisting preventive actions.
Pros of the Bill
- The Bill establishes specific timelines for various procedures, a feature not found in the CrPC.
- It also sets a deadline for medical officers to submit their investigation reports.
- Furthermore, it defines and clarifies certain procedures, such as the requirement to present an arrested person before any magistrate within 24 hours, irrespective of jurisdiction.
Cons of the Bill
- Procedural Complexity-The proposed code does not simplify existing procedures under the current law.
- Electronic Recording-Emphasizes electronic modes for recording statements, but the requirement for physical signatures may hinder true electronic recording.
Delays in Investigation
- Mandating a DSP-level officer’s preliminary inquiry may cause delays in gathering crucial evidence.
- Allowing investigations during the trial may lead to further delays.
- Impact on Fundamental Rights-Permission for the use of handcuffs against certain offenders may impact basic fundamental rights.
Lack of Clarity
- Despite defining bail, there is ambiguity in the factors considered for granting bail in non-bailable offenses.
- Section 484’s vague language on bail criteria may lead to arbitrariness.
- Unaddressed Definitions-The Bill lacks clarity on transit bail, and certain definitions, such as for remand, remain unaddressed.
Source: TH
PVTGs
Tag: GS-2 vulnerable Section
In News:
The Pradhan Mantri Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PM PVTG) Mission, amounting to ₹24,000 crores, was launched for the comprehensive development of approximately 28 lakh PVTGs in the nation.
About PVTGs
- In India, the tribal population constitutes 8.6% of the total population, with Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs) facing increased vulnerability within this demographic.
- More developed and assertive tribal groups tend to receive a significant portion of tribal development funds, leaving PVTGs in greater need of targeted developmental funds.
- The Dhebar Commission in 1973 categorized Primitive Tribal Groups (PTGs) as a distinct category, identifying them as less developed among tribal communities.
- In 2006, the Government of India renamed PTGs as PVTGs.
- In 1975, the government initiated the identification of the most vulnerable tribal groups, declaring 52 such groups. Subsequently, in 1993, an additional 23 groups were included, bringing the total number of PVTGs to 75 out of 705 Scheduled Tribes.
- PVTGs share common characteristics, including homogeneity, small population size, relative physical isolation, absence of a written language, simple technology, and a slower rate of change.
- Among the 75 listed PVTGs, Odisha has the highest number.
Source: TH
Chhath Pooja
Tag: GS-1 Art and culture
In News:
The central government criticized the government in Delhi for the occurrence of toxic white froth in the Yamuna preceding Chhath Puja, alleging that it has negatively impacted public sentiments.
About Chhath Pooja
- Chhath is a Hindu festival devoted to expressing gratitude to the Sun god and his consort, Usha, for the blessings bestowed upon Earth.
- The Goddess revered during the Chhath Puja is known as Chhathi Maiya, also recognized as Usha, the wife of the sun god.
- The term “chhath” translates to the sixth, symbolizing the festival’s celebration on the sixth day of the Hindu lunar month Kartika in the Bikram Sambat calendar.
- The festival spans four days and involves sacred bathing, fasting, prolonged periods of standing in water, and the offering of prayers and food to the setting and rising sun.
- Primarily observed in the Mithila Province of Nepal, Terai-Madhesh region of Nepal, and the Indian states of Bihar, Jharkhand, and Uttar Pradesh, Chhath is celebrated with great fervor.
- Although the main worshippers, known as Parvaitin, are predominantly women, the festival is not gender-specific, and many men also participate.
- Chhath holds significance in areas with a migrant population from these regions.
Source: TH
FATF
Tag: GS- 2 Groupings & Agreements Involving India and/or Affecting India’s Interests, India and its Neighbourhood GS – 3 Money Laundering, Terrorism in Hinterland & Border Areas
In News:
A team from the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) is currently assessing whether India has established and effectively implemented the necessary legal framework to combat money laundering and terrorist financing.
About FATF
- The Financial Action Task Force (FATF) is a global watchdog established in 1989 to combat money laundering and terrorist financing.
- Initially focused on money laundering, it expanded its mandate after the 9/11 attacks to include terrorist financing and later added efforts to counter the financing of Weapons of Mass Destruction (WMD).
- The FATF issues recommendations, with over 200 jurisdictions committing to them.
- The FATF Plenary, meeting three times a year, is its decision-making body.
- India, a member since 2010, joined as an observer in 2006.
- The President, T. Raja Kumar, leads the FATF.
- The Secretariat is at the OECD headquarters in Paris.
- The Grey List identifies jurisdictions under increased monitoring, while the Black List includes non-cooperative countries supporting terror funding and money laundering.
- As of now, Iran, North Korea, and Myanmar are blacklisted.
- The consequences of being listed include economic sanctions, loan difficulties, and international trade reductions.
- Recently, Pakistan was removed from the Grey List, receiving international approval for its actions against designated terrorists.
| UPSC Previous Year Questions Mains (2021) Q. Discuss how emerging technologies and globalisation contribute to money laundering. Elaborate measures to tackle the problem of money laundering both at national and international levels. Q. Analyse the complexity and intensity of terrorism, its causes, linkages and obnoxious nexus. Also suggest measures required to be taken to eradicate the menace of terrorism. |
Source: TH
Global South
Tag: GS- 2 Groupings & Agreements Involving India and/or Affecting India’s Interests
In News:
The second Voice of Global South Summit is scheduled for inauguration, marking the second time of India hosting the summit in less than a year.
About Global South
- The Global South encompasses developing nations primarily located in Africa, Asia, and Latin America, characterized by higher poverty levels and challenging living conditions compared to the wealthier nations of the Global North.
- Coined in 1969, the term replaced the pejorative “Third World” label, gaining prominence after the dissolution of the Soviet Union.
- The Global South signifies geopolitical and economic commonalities among nations, often influenced by a history of imperialism and colonial rule, particularly evident in African countries.
Significance of the Global South
- The Global South has witnessed a substantial shift in wealth and political influence, challenging traditional economic power dynamics.
- Projections suggest that, by 2030, three of the four largest economies will be from the Global South, notably led by China and India.
- The combined GDP of BRICS nations already surpasses that of G-7 nations.
- This shift is reshaping global geopolitics, with Asian nations anticipated to play a prominent role in the “Asian Century.”
Source: TH
WMO
Tag: GS-3 International Treaties & Agreements, Government Policies & Interventions
In News:
Concentrations of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere reached unprecedented levels in 2022, and the WMO cautioned that the upward trend shows no signs of abating.
About WMO
- The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) is an intergovernmental organization comprising 192 Member States and Territories.
- India is one of the member countries of the WMO.
- It traces its roots back to the International Meteorological Organization (IMO), formed following the 1873 Vienna International Meteorological Congress.
- Officially established through the ratification of the WMO Convention on March 23, 1950, the WMO serves as the specialized agency of the United Nations dedicated to meteorology (weather and climate), operational hydrology, and related geophysical sciences.
- The organization’s headquarters is situated in Geneva, Switzerland.
Source: TH
Trade Deficit
Tag: GS-3 Economy
In News:
What is Trade Deficit and what are its impacts?
A trade deficit occurs when a country imports more goods and services than it exports.
Trade deficit can have several impacts
- Current Account Imbalance: A trade deficit contributes to a current account deficit, which is the broader measure of the country’s economic transactions with the rest of the world. It includes trade in goods and services, as well as investment income and transfers.
- Currency Depreciation: Continuous trade deficits can put pressure on the country’s currency. If the demand for foreign goods and services exceeds the demand for the domestic currency, the value of the currency may depreciate against other currencies. This can lead to higher import costs and inflation.
- Foreign Exchange Reserves: To finance a trade deficit, a country may need to dip into its foreign exchange reserves. If the deficit is persistent, it can deplete these reserves, reducing the country’s ability to withstand economic shocks.
- Impact on Domestic Industries: A trade deficit can affect domestic industries, especially those that face intense competition from imported goods. If cheaper foreign products flood the market, it may lead to the decline of certain domestic industries, impacting employment and economic growth.
- Interest Rates and Inflation: To attract foreign capital and finance the trade deficit, a country may need to offer higher interest rates. This can impact domestic interest rates and contribute to inflationary pressures.
- Macroeconomic Stability: Persistent trade deficits can affect the overall macroeconomic stability of a country. It may lead to imbalances in the economy, making it more susceptible to external shocks and economic downturns.
- Deindustrialization: A prolonged trade deficit can lead to a situation where a country relies heavily on imports for its consumption needs and loses competitiveness in certain industries. This deindustrialization can have long-term consequences for the economy.
- Policy Responses: Governments may respond to trade deficits by implementing protectionist measures such as tariffs or subsidies to domestic industries. While these measures aim to reduce imports and boost domestic production, they can also lead to trade tensions with other countries.
| UPSC Previous Year Questions Prelims (2011) Q. Consider the following actions which the Government can take: Devaluing the domestic currency. Reduction in the export subsidy. Adopting suitable policies which attract greater FDI and more funds from FIIs. Which of the above action/actions can help in reducing the current account deficit? (a) 1 and 2 (b) 2 and 3 (c) 3 only (d) 1 and 3 Ans: (d) Prelims (2014) Q. With reference to Balance of Payments, which of the following constitutes/constitute the Current Account? Balance of trade Foreign assets Balance of invisibles Special Drawing Rights Select the correct answer using the code given below: (a) 1 only (b) 2 and 3 (c) 1 and 3 (d) 1, 2 and 4 Ans: (c) |
Source: BL
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are daily current affairs?
A: Daily current affairs refer to the most recent and relevant events, developments, and news stories that are happening around the world on a day-to-day basis. These can encompass a wide range of topics, including politics, economics, science, technology, sports, and more.
Q: Why is it important to stay updated with daily current affairs?
A: Staying updated with daily current affairs is crucial because it helps individuals make informed decisions in their personal and professional lives. It enables people to understand the world around them, stay aware of significant events, and engage in informed discussions about important issues.
Q: Where can I access daily current affairs information?
A: There are various sources for daily current affairs, including newspapers, news websites, television news broadcasts, radio programs, and dedicated apps or newsletters. Social media platforms are also widely used to share and access current affairs information.
Q: How can I effectively incorporate daily current affairs into my routine?
A: To incorporate daily current affairs into your routine, consider setting aside specific times each day to read or watch news updates. You can also subscribe to newsletters or follow news apps to receive curated content. Engaging in discussions with peers or participating in online forums can further enhance your understanding of current events.
Q: What are some tips for critical analysis of daily current affairs?
A: When analyzing daily current affairs, it’s essential to cross-reference information from multiple sources to ensure accuracy. Additionally, consider the source’s credibility and bias, if any. Develop the ability to identify the main points and implications of news stories, and critically evaluate the significance and impact of the events reported.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here

