
In today’s daily current affairs briefing for UPSC aspirants, we explore the latest developments that hold relevance for the upcoming civil services examination. Our focus today includes a critical analysis of recent policy changes, international affairs, and national developments, all of which play a pivotal role in shaping the socio-political and economic landscape of India. Stay informed and stay ahead in your UPSC preparations with our daily current affairs updates, as we provide you with concise, well-researched insights to help you connect the dots between contemporary events and the broader canvas of the civil services syllabus.
Contents
- 1 Road Safety in India
- 2 Government’s Advocacy for Ownership of Data
- 3 Antimicrobial Resistance
- 4 Indira Gandhi Peace Prize
- 5 Onattukara sesame
- 6 Krishnaraja Sagar Dam
- 7 Northeast Monsoon
- 8 Ahoms
- 9 Maldives
- 10 Somalia
- 11 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 11.1 Q: What are daily current affairs?
- 11.2 Q: Why is it important to stay updated with daily current affairs?
- 11.3 Q: Where can I access daily current affairs information?
- 11.4 Q: How can I effectively incorporate daily current affairs into my routine?
- 11.5 Q: What are some tips for critical analysis of daily current affairs?
- 12 In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
Road Safety in India
Tag: GS-3 GS- 2 Infrastructure, Government Policies & Interventions
In News:
Every year,300,000 individuals are estimated to lose their lives on Indian roads, as reported by the World Health Organization (WHO). This equates to over 34 people per hour, every day.
About Road Safety in India
Overview
- Road transport is the primary mode of transportation in India, both in terms of traffic share and its contribution to the national economy.
- To address the growing demand for road transport, there has been an increase in both the number of vehicles and the length of the road network.
- However, the expansion in road infrastructure, motorization, and urbanization has resulted in a negative externality – a rise in road accidents and fatalities.
Causes
- Several factors contribute to the surge in road accidents, including infrastructural deficits such as poor road conditions, visibility issues, and substandard road design.
- Negligence and risks like over speeding, driving under the influence, fatigue, and lack of protective gear are significant contributors.
- Distractions, especially the use of mobile phones while driving, and overloading vehicles to cut transportation costs also play a role.
- Weak vehicle safety standards in India have been highlighted, revealing failures in crash tests for popular car models.
- Lack of awareness about safety features like airbags and Anti-lock Braking System (ABS) is another factor contributing to road accidents.
Impacts
Economic
- Road accidents lead to a significant economic impact, causing a 3% loss in India’s GDP, much of which could be prevented.
Social
- The burden on households is substantial, with each road accident death resulting in the depletion of nearly seven months’ household income for poor families.
- Vulnerable Road Users (VRUs), particularly poor working-age males, bear a disproportionate share of road crash deaths and injuries.
Gender-Specific Impact
- The impact on women in victimized families is notable, with about 50% experiencing a severe decline in household income after a crash.
- Approximately 40% reported changes in their working patterns, and around 11% took up extra work to cope with the financial crisis.
- Rural households, especially those with lower incomes, faced more severe income declines than their urban or higher-income counterparts, according to the World Bank’s 2021 report, “Traffic Crash Injuries and Disabilities: The Burden on Indian Society.”
How can road safety be ensured?
Transparent Enforcement
- Implementing E-challan can reduce corruption in the handling of traffic infringement fines.
Speed Detection Technologies
- Introducing proven speed detection devices like radar and speed detection camera systems can enhance traffic control efforts.
- Cities like Chandigarh and New Delhi have already adopted digital still cameras, speed cameras, and radar guns for speed detection.
Enhanced Safety Measures
- Implementing speed humps, raised platforms, roundabouts, and optical markings can significantly decrease road accidents.
Stringent Regulations and Increased Penalties
- To deter traffic rule violations, imposing substantial fines on violators, especially those driving under the influence of substances like alcohol or drugs, can be effective.
Mandatory Vehicular Safety Standards
- Enforcing essential vehicle safety features, including electronic stability control, effective car crash standards, and advanced braking systems, should be made obligatory.
- The recently introduced Bharat NCAP by the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways is a step in this direction.
Community Involvement:
- Bystanders play a crucial role in post-crash care. Encouraging them to activate emergency care systems and perform simple life-saving actions until professional help arrives is essential.
Training and Skill Development
- Organizing training courses and workshops to enhance skills in road safety audits and road safety engineering is crucial for improving overall road safety.
Initiatives to enhance road safety
International Initiatives
- Brasilia Declaration on Road Safety (2015)-Signed at the second Global High-Level Conference on Road Safety in Brazil, the declaration, of which India is a signatory, aims to achieve Sustainable Development Goal 3.6—halving global deaths and injuries from road traffic accidents by 2030.
- Decade of Action for Road Safety 2021-2030-The UN General Assembly adopted a resolution with the target of preventing at least 50% of road traffic deaths and injuries by 2030. Aligned with the Stockholm Declaration, this global plan emphasizes a holistic approach to road safety.
- International Road Assessment Programme (iRAP)-A registered charity dedicated to saving lives through safer roads.
India’s Legislative Measures
- Motor Vehicles Amendment Act, 2019-This Act increases penalties for various traffic violations, addresses defective vehicles and juvenile driving, establishes a Motor Vehicle Accident Fund for compulsory insurance, and proposes the creation of a National Road Safety Board.
- Carriage by Road Act, 2007-Regulates common carriers, limiting their liability and addressing the declaration of the value of goods for determining liability in case of loss or damage caused by negligence or criminal acts.
- Control of National Highways (Land and Traffic) Act, 2000-Focuses on controlling land within National Highways, ensuring right of way, and managing traffic on these highways, including removal of unauthorized occupation.
- National Highways Authority of India Act, 1998-Constitutes an authority for the development, maintenance, and management of National Highways (NHs).
Source: TH
Government’s Advocacy for Ownership of Data
Tag: GS- 3 IT & Computers, GS- 2 Government Policies & Interventions
In News:
Reports are suggesting that the Indian Government is contemplating to instruct tech giants such as Facebook, Google, and Amazon to provide anonymized personal data for a government-supported database.
About Anonymized data
- An anonymized data set refers to any collection of data that lacks personally identifiable information.
- This may encompass aggregated information, such as the general health data of a specific demographic, weather and climate data for a region, and traffic data, among other examples.
- This type of data is distinct from personal data, which involves information related to an identified or identifiable individual, such as email and biometrics.
- The use of anonymized data serves various purposes, including statistical analysis, market research, product development, and more, all while ensuring the privacy of the individuals whose data was utilized.
Why is the Government Contemplating Access to Data Held by Major Tech Companies?
- This action is a component of an upcoming Digital India Bill, which includes a provision compelling major tech firm to deposit all non-personal data they possess into a government-supported database known as the India Datasets Platform.
- According to the working group established by the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology, the India Datasets Platform is envisioned as a unified national platform for sharing and exchanging data among various stakeholders, including governments, private companies, Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs), academia, and others.
- The non-personal data housed by the India Datasets Platform could be monetized, playing a pivotal role in generating economic benefits.
- In May 2022, the government released the draft National Data Governance Framework Policy, wherein it “encouraged” private companies to share non-personal data with startups and Indian researchers.
- The government’s argument is rooted in the assertion that big tech companies have profited from constructing algorithms based on non-personal data of Indians, and therefore, they should not assert exclusive ownership over it.
About Digital India Bill
- The Digital India Bill of 2023, if approved, will serve as the successor to the Information Technology Act of 2000 and is a pivotal component of a comprehensive legal framework that encompasses various legislative measures.
- This holistic approach includes initiatives like the Digital Personal Data Protection Act, 2023, the draft Indian Telecommunication Bill, 2022, and a policy addressing the governance of non-personal data.
- The primary objective of the bill is to enhance the artificial intelligence (AI) ecosystem in India by establishing a robust foundation for data-driven innovation and development.
- It is designed to create thorough oversight over India’s digital landscape, effectively addressing contemporary challenges such as cybercrime, data protection, deepfakes, competition among internet platforms, online safety, and the potential adverse impacts of artificial intelligence (AI).
| UPSC Previous Year Questions Prelims (2021) Q. ‘Right to Privacy’ is protected under which Article of the Constitution of India? (a) Article 15 (b) Article 19 (c) Article 21 (d) Article 29 Ans: (c) Prelims (2018) Q. Right to Privacy is protected as an intrinsic part of Right to Life and Personal Liberty. Which of the following in the Constitution of India correctly and appropriately imply the above statement? (a) Article 14 and the provisions under the 42nd Amendment to the Constitution. (b) Article 17 and the Directive Principles of State Policy in Part IV. (c) Article 21 and the freedoms guaranteed in Part III. (d) Article 24 and the provisions under the 44th Amendment to the Constitution. Ans: (c) Mains (2017) Q. Examine the scope of Fundamental Rights in the light of the latest judgement of the Supreme Court on Right to Privacy. |
Source: IE
Antimicrobial Resistance
Tag: GS-3 Science and Tech.
In News:
Antimicrobial resistance remains a substantial obstacle to worldwide public health, profoundly impacting the effectiveness of medications and the treatment of infectious diseases.
About Antimicrobial Resistance

- Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) is the acquired resistance of microorganisms to drugs, making infections harder to treat and increasing health risks.
- Recognized as a top global health threat by the WHO, “superbugs” with AMR contribute to newborn deaths in India and heightened mortality rates in Covid patients with drug-resistant infections.
- NDM-1, a multi-drug resistance determinant, originated in South Asia, impacting regions worldwide.
- Urgent global action is needed to address AMR’s severe consequences on public health.
AMR: Indian Scenario
- Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) poses a significant concern in developing nations, especially in countries like India, where the burden of infectious diseases is high, and healthcare spending is limited.
- India is among the nations with the highest burden of bacterial infections, making the impact of AMR more pronounced.
- The National Health Policy 2017 in India recognizes the challenge of antimicrobial resistance, highlighting the need for effective action.
- The Ministry of Health & Family Welfare (MoHFW) has identified AMR as a top priority, collaborating with the World Health Organization (WHO).
- Surveillance programs for drug resistance have been instituted in various disease areas, and regulations on antimicrobial sale have been enforced since March 2014.
- India, with its large population, rising incomes, high infectious disease burden, and easy access to antibiotics, is a significant contributor to the global generation of resistance genes.
- The emergence of New Delhi Metallo-beta-lactamase-1 (NDM-1) and multi-drug resistant typhoid from South Asia has global implications.
Initiatives to curb AMR in India
National Initiatives on AMR
- National Programme (2012)- Launched in 2012, this program strengthens the AMR Surveillance Network by establishing labs in State Medical Colleges.
- National Action Plan (2017)-The National Action Plan on AMR, initiated in April 2017, adopts a One Health approach and involves various stakeholder ministries/departments.
- AMR Surveillance and Research Network (2013)-Launched in 2013, this network aims to generate evidence and capture trends in drug-resistant infections.
Research and International Collaboration
- ICMR Initiatives-The Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) collaborates internationally to develop new drugs/medicines for AMR, fostering medical research.
- International Collaborations-ICMR, in partnership with the Research Council of Norway (RCN) and the Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF) in Germany, engages in joint research on AMR.
Antibiotic Stewardship Program
- AMSP Pilot Project– ICMR has initiated the Antibiotic Stewardship Program (AMSP) on a pilot basis across India. This program aims to control the misuse and overuse of antibiotics in hospital wards and ICUs.
Regulatory Actions
- DCGI Ban (Fixed Dose Combinations)-The Drug Controller General of India (DCGI) has banned 40 Fixed Dose Combinations (FDCs) deemed inappropriate.
| UPSC Previous Year Questions Prelims (2019) Q. Which of the following are the reasons for the occurrence of multi-drug resistance in microbial pathogens in India? Genetic predisposition of some people Taking incorrect doses of antibiotics to cure diseases Using antibiotics in livestock farming Multiple chronic diseases in some people Select the correct answer using the code given below. (a) 1 and 2 (b) 2 and 3 only (c) 1, 3 and 4 (d) 2, 3 and 4 Ans: (b) |
Source: TH
Indira Gandhi Peace Prize
Tag: GS-2 Polity
In News:
The 2022 Indira Gandhi Prize for Peace, Disarmament, and Development was jointly awarded to the Indian Medical Association and the Trained Nurses Association of India.
About Indira Gandhi Peace Prize
- Established in 1986, the Indira Gandhi Prize for Peace, Disarmament and Development is dedicated to the memory of the former Prime Minister.
- This prestigious award, presented by a trust in her name, includes a monetary prize of Rs 25 lakh along with a citation.
- The accolade is conferred upon individuals or organizations actively contributing to global peace and development, leveraging scientific discoveries to enhance freedom and improve humanity.
- The recipients are recognized for their efforts in shaping a new international economic order.
- The prize underscores a commitment to the values championed by Indira Gandhi, fostering a legacy of positive impact on the world stage.
About Indian Medical Association
- The Indian Medical Association (IMA) stands as the largest representative organization of doctors practicing modern medicine in India.
- With a membership exceeding 3.5 lakh doctors, it operates through 28 State Branches, 5 Union Territory Branches, and 1702 local branches spanning almost every district in the country.
- In its early years, various regional doctors’ associations existed, prompting a conference discussion on consolidating them under one umbrella.
- The term “Indian Medical Association” was coined in 1928, marking the inception of an organization that has played a significant role in India’s freedom struggle.
- IMA’s global impact is evident through its role in establishing the World Medical Association (WMA) in 1946, making it a founding member.
- Over the years, IMA has actively participated in WMA deliberations, hosting important events such as the III World Conference on Medical Education in 1966 and the WMA General Assembly in 2009.
- Dr. Ketan Desai from IMA served as WMA President in 2015. IMA has led the Confederation of Medical Associations in Asia and Oceania (CMAAO) on multiple occasions.
- Post-independence, IMA has expanded its presence across the nation, boasting a vast membership of healthcare professionals, active local branches, and a continuous commitment to the well-being of both doctors and the wider community.
| UPSC Previous Year Questions Prelims (2019) Q. Which of the following are the reasons for the occurrence of multi-drug resistance in microbial pathogens in India? Genetic predisposition of some people Taking incorrect doses of antibiotics to cure diseases Using antibiotics in livestock farming Multiple chronic diseases in some people Select the correct answer using the code given below. (a) 1 and 2 (b) 2 and 3 only (c) 1, 3 and 4 (d) 2, 3 and 4 Ans: (b) |
Source: TH
Onattukara sesame
Tag: GS-3 Environment, GS-3 Agriculture
In News:
The Onattukara Vikasana Agency, the registered proprietor of GI-tagged sesame seeds, intends to expand sesame cultivation from the existing 600 hectares to 2,000 hectares.
About Onattukara sesame

- Onattukara Ellu and its oil are renowned for their distinctive health advantages.
- The notably elevated antioxidant content in Onattukara Ellu plays a crucial role in combating free radicals that can harm the body’s cells.
- Additionally, the substantial presence of unsaturated fat in Onattukara Ellu contributes to its heart-healthy properties, making it particularly beneficial for individuals with cardiovascular conditions.
- Moreover, this traditional ingredient is known for its potential to enhance overall well-being and promote a balanced and nutritious diet.
- The unique combination of antioxidants and unsaturated fats underscores the holistic health benefits associated with the consumption of Onattukara Ellu and its oil.
| UPSC Previous Year Questions Prelims (2015) Q. Which of the following has/have been accorded ‘Geographical Indication’ status? Banaras Brocades and Sarees Rajasthani Daal-Bati-Churma Tirupathi Laddu Select the correct answer using the code given below: (a) 1 only (b) 2 and 3 only (c) 1 and 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3 Ans: (c) Exp: A Geographical Indication (GI) is a sign used on products that have a specific geographical origin and possess qualities or a reputation that are due to that origin. Darjeeling tea was the first product in India to get a GI tag. Banaras Brocades and Sarees and Tirupathi Laddu have got GI tag while Rajathan’s Daal-Baati-Churma does not. Hence, 1 and 3 are correct. Therefore, option (c) is the correct answer. Prelims (2018) Q. India enacted the Geographical Indications of Goods (Registration and Protection) Act, 1999 in order to comply with the obligations to (2018) (a) ILO (b) IMF (c) UNCTAD (d) WTO Ans: (d) Exp: Geographical indications (GIs) are a type of intellectual property (IP). The World Trade Organisation (WTO) recognises intellectual property rights under TRIPS (Trade Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights) Agreement. Under Article 22(1) of the TRIPS Agreement, the GIs are defined as “indications which identify a good as originating in the territory of a member, or a region or locality in that territory, where a given quality, reputation or other characteristic of the good is essentially attributable to its geographic origin”. Therefore, option (d) is the correct answer. |
Source: TH
Krishnaraja Sagar Dam
Tag: GS-3 Environment
In News:
Recently, the cumulative storage in Krishnaraja Sagar (KRS), Kabini, Hemavathi, and Harangi stood at 59.07 thousand million cubic feet (tmcft), which is 51.56% of the gross capacity of 114.57 tmcft.
About Krishnaraja Sagar Dam

- Constructed in 1932 across the Kaveri River, the Krishna Raja Sagar Dam was commissioned to serve the districts of Mysore and Mandya in Karnataka.
- Named after the then ruler of the Mysore Kingdom, Krishnaraja Wodeyar IV, this engineering marvel is credited to one of India’s greatest engineers, Sir M. Vishweshwaraiah.
- Celebrated as Engineers Day on his birthday, September 15th, the dam not only stands as a testament to his ingenuity but also fulfils crucial roles.
- The reservoir, a key creation of Sir M. Vishweshwaraiah, serves as the primary source of drinking water for Mysore city and a significant portion of Bangalore.
- Additionally, the water released from this dam plays a vital role in meeting the water needs of the state of Tamil Nadu.
About Kaveri River
- Originating from the Brahmagiri Hill in the Western Ghats of southwestern Karnataka, the river travels in a southeasterly course through the states of Karnataka and Tamil Nadu.
- As it descends the Eastern Ghats, the river forms a series of magnificent falls.
- Prior to reaching its endpoint south of Cuddalore,
- Tamil Nadu, the river bifurcates into numerous distributaries, creating an expansive delta known as the “garden of southern India.”
- Noteworthy tributaries contributing to the river’s flow include Arkavathi, Hemavathi, Lakshmana Theertha, Shimsa, Kabini, and Harangi.
Source: TH
Northeast Monsoon
Tag: GS-3 Environment
In News:
The northeast monsoon is expected to further intensify briefly over Kerala due to the influence of twin cyclonic circulations over the Bay of Bengal.
What is Northeast Monsoon?
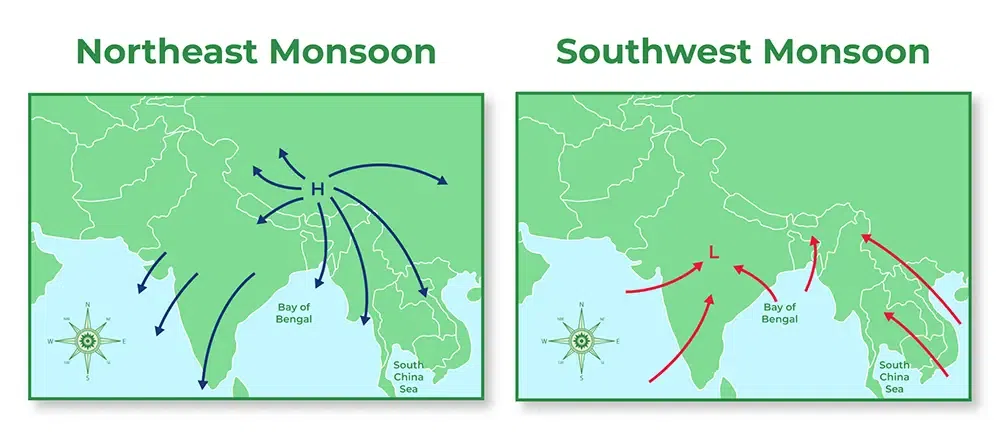
The Winter Monsoon is a relatively small-scale monsoon phenomenon that primarily impacts the Southern Peninsula. This seasonal weather pattern is specifically referred to as the winter monsoon.
Several factors contribute to the onset of the Northeast Monsoon
- Change in Wind Pattern-Following the complete withdrawal of the Southwest monsoon around mid-October, there is a swift transition in the wind pattern from south-westerly to north-easterly direction.
- Cyclonic Activities-The period from October to December, post the Southwest monsoon season, marks the peak time for cyclonic activity in the North Indian Ocean region, covering the Arabian Sea and the Bay of Bengal.
- Winds associated with low-pressure systems, depressions, or cyclones influence the winter monsoon, impacting the rainfall.
- Global Climate Parameters-Northeast Monsoon (NEM) rainfall is influenced by global climate parameters like El Nino/La Nina, Southern Oscillation Index (SOI), Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD), and Madden-Julian Oscillation (MJO).
- Positive indicators such as El Nino, positive IOD, and MJO in phases 2-4 with amplitude greater than one are generally associated with favourable NEM rainfall.
- Additionally, La Nina and positive SOI during the latter part of the season also support good NEM activity.
Regions that are prominently affected by the Northeast Monsoon
- Tamil Nadu, Puducherry, Karaikal, Yanam, coastal Andhra Pradesh, Kerala, north interior Karnataka, Mahe, and Lakshadweep.
- Tamil Nadu, in particular, receives approximately 48% of its annual rainfall during these months, playing a crucial role in agricultural activities and reservoir management in the state.
Source: TH
Ahoms
Tag: GS-1 Art and Culture
In News:
A 19-minute animation film, cantered on an iconic Ahom general has been chosen for the Indian Panorama section at the International Film Festival of India (IFFI) 2023.
About Ahoms
- For a span of 598 years, from 1228 to 1826, the Ahom dynasty held sway over the Ahom kingdom in what is now Assam, India.
- The dynasty was established by Sukaphaa or Tsue-Ka-Pha, a Shan prince from Mong Mao who reached Assam after crossing the Patkai Mountains.
- While foreign medieval chronicles referred to the monarchs of this dynasty as Asam Raja, their subjects addressed them as Chaopha or Swargadeo.
- Under the reign of Suhungmung in the 16th century, the Ahom kingdom took on a multiethnic character, significantly influencing the political and social landscape of the entire Brahmaputra valley.
- However, the kingdom faced challenges, particularly with the onset of the Moamoria uprising, leading to a weakened state and frequent assaults by Burmese troops.
- The culmination of this era came with the Burmese invasion of Assam in 1826 and its subsequent annexation by the British East India Company under the Treaty of Yandabo.
- This marked the conclusion of the Ahom dynasty’s rule.
- Following the victory in the First Anglo-Burmese War and the signing of the Treaty of Yandabo in 1826, the East India Company assumed control of the region.
Source: TH
Maldives
Tag: GS-2 IR
In News
About Maldives
The Maldives, officially known as the Republic of Maldives, is a tropical paradise located in the Indian Ocean, southwest of Sri Lanka and India. Comprising 26 atolls and over 1,000 coral islands, the Maldives is renowned for its stunning white-sand beaches, crystal-clear turquoise waters, and vibrant coral reefs
India-Maldives Relations
Security Partnership
- Cooperation in defence encompasses Joint Exercises like “Ekuverin,” “Dosti,” “Ekatha,” and “Operation Shield” initiated in 2021.
- India plays a significant role in meeting approximately 70% of the defence training requirements for the Maldivian National Defence Force (MNDF).
- Additionally, a drug detoxification and rehabilitation centre in Addu, supported by India, is part of 20 community development projects covering healthcare, education, fisheries, tourism, sports, and culture.
Rehabilitation Centre
- A contract was signed for the Addu reclamation and shore protection project, and an Indian-assisted drug detoxification and rehabilitation centre in Addu is among 20 high-impact community development projects in various sectors.
Economic Cooperation
- Tourism is a cornerstone of the Maldivian economy, with India emerging as its third-largest trade partner in 2021.
- The Greater Male Connectivity Project (GMCP), signed with Afcons, the largest-ever infrastructure project in the Maldives, aims to boost economic ties.
- The Bilateral USD Currency Swap Agreement between the RBI and the Maldives Monetary Authority was signed in 2019.
Infrastructure Projects
- Under an Indian credit line, the Hanimaadhoo International Airport Development project is set to enhance facilities.
- The National College for Policing and Law Enforcement (NCPLE), inaugurated in 2022, is India’s largest grant project in the Maldives.
Greater Male Connectivity Project
- This significant project involves a 6.74 km-long bridge and causeway linking Male with Villingli, Gulhifalhu, and Thilafushi islands, using renewable energy.
- Funded by a USD 100 million grant and a USD 400 million Line of Credit from India, it represents the largest infrastructure undertaking in the Maldives.
Source: TH
Somalia
Tag: GS-2 IR
In News:
The heavy seasonal downpours in Somalia, exacerbated by the concurrent influence of two climate phenomena—El Niño and the Indian Ocean Dipole—may impact approximately 1.6 million individuals.
About Somalia
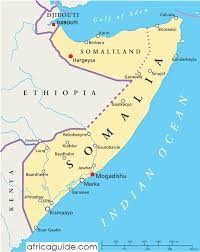
- Situated in the Horn of Africa, Somalia shares borders with the Gulf of Aden to the north, the Indian Ocean to the east, Kenya and Ethiopia to the west, and Djibouti to the northwest.
- Mogadishu serves as the capital and largest city of Somalia.
- The country boasts diverse landscapes encompassing arid plains, plateaus, highlands, and mountain ranges. In the northern part, the Golis Mountains dominate the scenery, while the southern region features savannas and grasslands.
- Somalia predominantly experiences an arid to semi-arid climate characterized by hot temperatures and limited rainfall. The coastal areas enjoy a more moderate climate influenced by the Indian Ocean.
- Off the coast of Somalia, several islands are found, including the Bajuni Islands and the Socotra Archipelago, which comprises Socotra, Abd al Kuri, and Samha. It’s important to note that the administration of the Socotra Archipelago falls under Yemen.
Source: TH
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are daily current affairs?
A: Daily current affairs refer to the most recent and relevant events, developments, and news stories that are happening around the world on a day-to-day basis. These can encompass a wide range of topics, including politics, economics, science, technology, sports, and more.
Q: Why is it important to stay updated with daily current affairs?
A: Staying updated with daily current affairs is crucial because it helps individuals make informed decisions in their personal and professional lives. It enables people to understand the world around them, stay aware of significant events, and engage in informed discussions about important issues.
Q: Where can I access daily current affairs information?
A: There are various sources for daily current affairs, including newspapers, news websites, television news broadcasts, radio programs, and dedicated apps or newsletters. Social media platforms are also widely used to share and access current affairs information.
Q: How can I effectively incorporate daily current affairs into my routine?
A: To incorporate daily current affairs into your routine, consider setting aside specific times each day to read or watch news updates. You can also subscribe to newsletters or follow news apps to receive curated content. Engaging in discussions with peers or participating in online forums can further enhance your understanding of current events.
Q: What are some tips for critical analysis of daily current affairs?
A: When analyzing daily current affairs, it’s essential to cross-reference information from multiple sources to ensure accuracy. Additionally, consider the source’s credibility and bias, if any. Develop the ability to identify the main points and implications of news stories, and critically evaluate the significance and impact of the events reported.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here

