In recent times, the escalating incidence of extreme rainfall events has cast a shadow of peril over communities residing in low-lying areas and floodplains across the country. The repercussions of these climatic anomalies have been nothing short of devastating, subjecting vulnerable populations to unprecedented challenges and adversities. As flash floods become increasingly frequent, their ferocity compounds the severity of the impact, wreaking havoc on infrastructure, livelihoods, and the overall well-being of those caught in their destructive path. The urgency to address this emergent issue has become paramount, necessitating a comprehensive discussion on the multifaceted consequences and the imperative for proactive measures to mitigate the looming threats posed by these extreme weather events.
Contents
Answer
The Central Water Commission (CWC) estimates that over 40 million people in India are at risk of flooding every year, number of flood-affected districts in India has increased from 161 in 1980 to 354 in 2020.
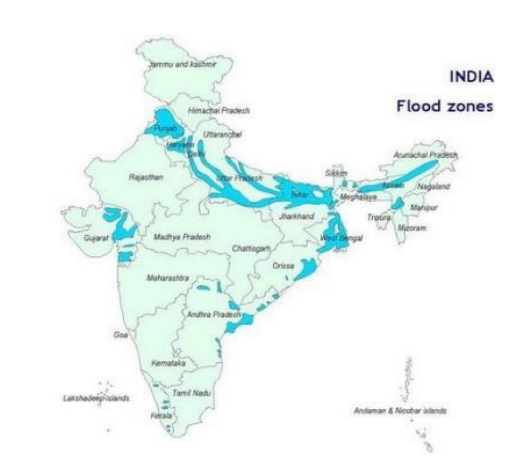
Incidence of extreme rainfall events and flash floods have increased in recent times due to following reasons
Climate change
- Causing changes in atmospheric circulation patterns (like expanding of the Hadley cell, which means that it is reaching further into the mid-latitudes leading to more extreme rainfall events heavy thunderstorms and hurricanes.), causing intense rainfall events. Kerala floods 2018 caused by heavy monsoon rains, which have become more intense due to climate change.
Land use changes
- Deforestation can lead to the loss of trees, which play an important role in absorbing rainwater
- A study by the World Resources Institute found that deforestation increases the risk of flooding by up to 80%
Urbanisation
- Concretisation can make areas more vulnerable to flooding
- Can lead to increased runoff, which can overwhelm drainage systems and cause flooding.
- Increased waste generation leading to choked drainage system, thus floods.
- lead to the loss of wetlands and other green spaces, which play an important role in absorbing rainwater.
- United Nations-the number of people living in flood-prone areas is expected to increase by 20% by 2050, due to urbanization and climate change.

Devastating consequences for people living in low-lying areas and flood plains of the country are as follows
- Floods cause loss of life and livelihood. People living in these areas are often poor and marginalised living in slum and squatter settlements, they have fewer resources to cope with the impacts of floods.

- Floods cause widespread damage to property and infrastructure, including homes, schools, hospitals, and roads, make it difficult for people to access essential services and rebuild their lives’. The World Bank estimates that the global cost of flood damage is between $100 and $200 billion per year
- lead to the spread of waterborne diseases, such as cholera and typhoid. floods contaminate water sources and make it difficult for people to access clean water.Eg. In 2020, the Assam floods in India led to an outbreak of typhoid, which affected over 100,000 people.
- Destroy crops and livestock, leading to food shortages and famine.Eg. The FAO estimates that floods destroy about 10% of the global cereal crop each year.
The National Flood Control Programme (NFCP), The Flood Plain Zoning (FPZ) Atlas of India, The Flood Warning System (FWS), The Flood Insurance Programme (FIP) are steps in the right direction to tackle floods.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here