The emergence of linguistic regions and states in India is a fascinating journey deeply intertwined with the complex tapestry of the country’s history, culture, and diversity. India, known for its rich linguistic landscape, witnessed a significant transformation in the mid-20th century, marked by the reorganization of states along linguistic lines. This restructuring was a response to the diverse linguistic identities that coexisted within the nation, aiming to provide a more inclusive and representative political framework. The linguistic reorganization not only altered the administrative map of the country but also played a pivotal role in shaping the socio-political dynamics of post-independence India. Examining the factors that led to the emergence of linguistic regions and states provides valuable insights into the intricate process of nation-building in a country as linguistically diverse as India.
Contents
Answer
The emergence of linguistic regions and states in India is a significant chapter in the country’s post-independence history. However, an important determinant of the origin of linguistic regions is the linguistic and cultural diversity within the country, which had its roots in the historical linguistic hearths of India.
The emergence of linguistic regions and states in India due to India’s cultural diversity and linguistic hearths:
- Dravidian Linguistic Hearth (South India):
- The ancient Dravidian culture is associated with the Indus Valley Civilization, one of the world’s oldest urban civilizations.
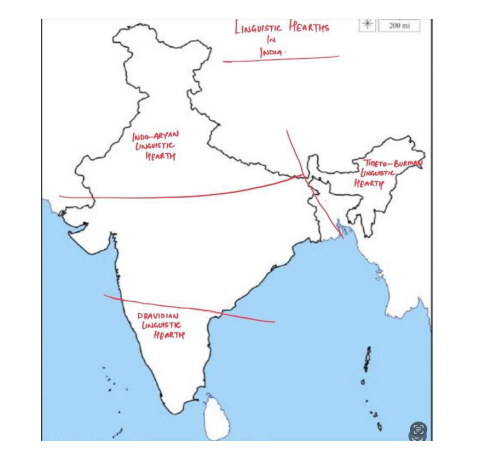
- Gave rise to languages like Tamil, Telugu, Kannada, and Malayalam.
- Linguistic diversity in South India played a crucial role in the demand for linguistic states.
- Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, and Kerala were created to preserve the distinct Dravidian languages and cultures.
- Indo-Aryan Linguistic Hearth (North India):
- Roots of the Indo-Aryan linguistic hearth can be traced back to the ancient Indo-European migrations that took place around the 2nd millennium BCE
- Gave rise to languages like Hindi, Bengali, Punjabi, and Gujarati.
- The demand for linguistic states emerged due to the desire to promote regional languages.
- Uttar Pradesh, West Bengal, Punjab, and Gujarat were among the states formed based on linguistic lines.
- Tibeto-Burman Linguistic Hearth (Northeast India):
- Northeast India is home to a linguistic hearth of Tibeto-Burman languages like Assamese, Bodo, and Manipuri.
- The region saw the formation of states such as Assam, Manipur, and Nagaland to protect the linguistic and cultural identities of the people in the Northeast. The emergence of linguistic regions and states in India as a result of post-independence linguistic rearrangements:
- Following independence, the Indian government recognized the importance of linguistic identity in governance and administration.
- led to the reorganization of states in 1956-linguistic reorganization. thereby fostering a stronger sense of cultural and linguistic identity.
- Key milestones in this process
- Creation of states like Andhra Pradesh (Telugu-speaking)
- Karnataka (Kannada-speaking)
- Kerala (Malayalam-speaking).
The linguistic reorganization of states and the emergence of linguistic regions have helped preserve and promote various regional languages, cultures, and traditions.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here