Social capital refers to the network of social connections, norms, and trust that exist within a community or society. It encompasses the relationships and interactions among individuals, groups, and institutions, fostering cooperation, collaboration, and mutual support. In the realm of governance, social capital plays a pivotal role in enhancing effectiveness, legitimacy, and accountability. By cultivating strong social ties and shared values, social capital facilitates communication, consensus-building, and collective action among citizens and policymakers. This leads to improved decision-making processes, greater responsiveness to community needs, and increased citizen participation in governance. Moreover, social capital fosters a sense of belonging and solidarity, reducing social conflict and promoting social cohesion. Overall, the presence of robust social capital contributes to the establishment of inclusive, transparent, and accountable governance structures that better serve the interests of society as a whole.
Contents
Answer
Robert Putnam in his book – “Bowling alone” defined social capital as “features of social organisations such as networks, norms, and social trust that facilitate action and cooperation for mutual benefit.” Social capital is a valuable resource that can contribute to various aspects of community life, including economic development, effective governance, and overall societal well-being.
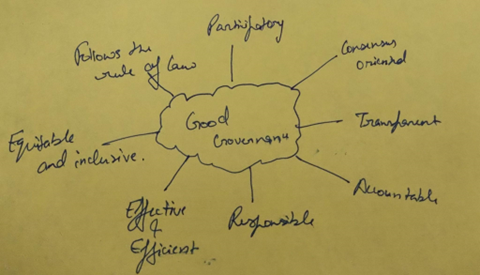
Social capital enhances good governance in the following manner
- Trust and Cooperation: Social capital fosters trust and cooperation among individuals and groups within a society. In a community where people have strong social ties and shared values, there is a greater likelihood of cooperation and mutual support. Trust is a crucial element in good governance, as it promotes transparency and accountability.
- Civic Engagement: High levels of social capital encourage civic engagement, where individuals actively participate in political processes due to their strong social networks.
- For example – Gram Sabha, where social capital facilitates informed decision-making through active public participation and public deliberation.
- Community Resilience – Especially during natural disasters, communities with high social capital respond to crises better.
- Whether it was the 2018 floods or the COVID Pandemic, the state of Kerala emerged as a standard setter in terms of effective relief and response operations.
- Effective Policy Implementation – initiatives like MGNREGA have been more successful in areas with strong social networks that ensure proper implementation and prevent misuse of funds through regular social audits.
- For e.g. – MKSS conducts Jan Sunwai in Rajasthan
- Providing Policy Input: Social capital enables citizens to offer valuable input to policymakers. Through their social connections, individuals can convey their concerns, suggestions, and needs to government officials. This make the government more responsive.
Social capital empowers individuals and communities to actively participate in the governance process, ultimately leading to more responsive, equitable, and effective governance at all levels of society.
Building and maintaining social capital is therefore an important aspect of promoting a healthy and well-functioning society.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here


