Prepare for the UPSC Prelims with comprehensive Physics questions focused on Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) and Waves, specifically Sound. This curated collection of topic-wise questions delves into the fundamental principles of SHM and wave phenomena, offering a thorough understanding essential for success in the exam. Covering various aspects, including concepts, applications, and problem-solving, these questions provide a structured approach to mastering the Physics syllabus. Whether you’re revising key topics or aiming for in-depth preparation, this resource offers a valuable tool for enhancing your knowledge and exam readiness. Strengthen your grasp on SHM and Wave (Sound) topics, ensuring confidence and proficiency on exam day. Dive into these targeted questions to sharpen your skills and excel in the UPSC Prelims examination.
Contents
- 1 Q1. When the same note is played on a sitar and a flute, the sound produced can be distinguished from each other because of the difference in (1995)
- 2 Q2. A girl is swinging on a swing in sitting position. When the same girl stands up, the period of swing will (1997)
- 3 Q3. A noise level of 100 decibel would correspond to (2000)
- 4 Q4. Consider the following statements. (2001)
- 5 Q5. Which one of the following statements is not correct? (2003)
- 6 Q6. In which one among the following is the speed of sound maximum? (2006)
- 7 Q7. Consider the following statements. (2007)
- 8 Q8. Assertion (A) A jet aircraft moving at Mach number equal to 1 travels faster at an altitude of 15km than while moving at Mach number equal to 1 near the sea level. Reason (R) The velocity of sound depends on the temperature of the surrounding medium. (2007)
- 9 In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
Q1. When the same note is played on a sitar and a flute, the sound produced can be distinguished from each other because of the difference in (1995)
(a) pitch, loudness and quality
(b) pitch and loudness
(c) quality only
(d) loudness only
Ans. (c)
The characteristic timbre of sound plays a significant role in distinguishing between the same note played on a sitar versus a flute. Timbre, or sound quality, allows us to discern between sounds of identical pitch and volume. Pitch refers to the attribute of sound that allows differentiation between sounds of equal volume, determined by the frequency of vibration. Meanwhile, loudness measures the amount of sound energy perceived by the ear per unit of time.
Q2. A girl is swinging on a swing in sitting position. When the same girl stands up, the period of swing will (1997)
(a) be shorter
(b) be longer
(c) depend on the height of the girl
(d) not change
Ans. (a)
When a girl transitions from sitting to standing while swinging on a swing, the swing’s period becomes shorter. Swings exemplify simple harmonic motion, a specific type of repetitive motion in which an object moves back and forth around an equilibrium point. This concept is also demonstrated by simple pendulums. The time period (T) of a swing is calculated as T = 2π√(l/g), where l represents the length of the swing and g denotes the acceleration due to gravity. The time period of a simple pendulum is directly linked to the square root of its effective length, denoted as T∝√l. When a girl sitting on a swing stands up, her center of gravity ascends, causing the effective length of the swing to decrease. Consequently, the swing’s time period decreases accordingly.
Q3. A noise level of 100 decibel would correspond to (2000)
(a) just audible sound
(b) ordinary conversation
(c) sound from a noisy street
(d) noise from a machine shop
Ans. (d)
A noise level reaching 100 decibels indicates the sound intensity akin to that found in a highly noisy machine shop. Sound loudness is quantified using the decibel (dB) scale, contingent upon the amplitude of vibration generated by the sound source. Amplitude denotes the maximum displacement of particles within the medium from their initial undisturbed position.
Q4. Consider the following statements. (2001)
A simple pendulum is set into oscillation, then
1. the acceleration is zero when the bob passes through the mean position.
2. in each cycle, the bob attains a given velocity twice.
3. both acceleration and velocity of the bob are zero when it reaches its extreme position during the oscillation.
4. the amplitude of oscillation of the simple pendulum decreases with time.
Which of these statements are correct?
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 3 and 4
(c) 1,2 and 4
(d) 2, 3 and 4
Ans. (c)
Statements (1), (2), and (4) are accurate.
In the case of a simple pendulum, the net acceleration becomes zero as the bob reaches the mean position.
In each cycle, the bob’s velocity increases from zero at the extreme position to a maximum at the mean position, indicating that the bob achieves a particular velocity twice.
The amplitude of oscillation of a simple pendulum diminishes over time due to air friction.
Statement (3) is incorrect since the acceleration of the bob is maximum at the extreme position.
Q5. Which one of the following statements is not correct? (2003)
(a) The velocity of sound in air increases with the increase of temperature.
(b) The velocity of sound in air is independent of pressure.
(c) The velocity of sound in air decreases as the humidity increases.
(d) The velocity of sound in air is not affected by the change in amplitude and frequency.
Ans. (c)
Statement (c) is incorrect because the velocity of sound in air actually decreases as humidity increases. The speed of sound is inversely proportional to the amount of moisture in the air because the presence of moisture increases the density of air. Therefore, the velocity of sound in humid air, represented by the formula
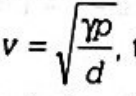
, will be less than in dry air.
Q6. In which one among the following is the speed of sound maximum? (2006)
(a) Air at 0°C
(b) Air at 100° C
(c) Water
(d) Wood
Ans. (d)
The speed of sound is at its maximum in solids, higher in liquids, and minimum in gases.
Q7. Consider the following statements. (2007)
1. A flute of smaller length produces waves of lower frequency.
2. Sound travels in rocks in the form of longitudinal elastic waves only.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) Only 1
(b) Only 2
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans. (d)
Neither statement (1) nor statement (2) is correct.
In a flute, the frequency of the produced wave is indeed inversely proportional to the length of the flute. Therefore, a shorter flute produces waves of higher frequency.
Sound travels through rocks in the form of compressional (longitudinal) waves and not transverse waves. Longitudinal waves involve the displacement of the medium in the same or opposite direction as the wave’s propagation. They create compressions and rarefactions as they move through a medium.
Q8. Assertion (A) A jet aircraft moving at Mach number equal to 1 travels faster at an altitude of 15km than while moving at Mach number equal to 1 near the sea level. Reason (R) The velocity of sound depends on the temperature of the surrounding medium. (2007)
Codes
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Ans. (d)
Statement A is false, but statement R is true.
The velocity of sound is indeed dependent on the temperature of the surrounding medium. With every 1°C increase in temperature, the speed of sound in the atmosphere increases by approximately 0.61 m/s.
Supersonic waves are often measured in terms of the Mach number, which represents the ratio of the speed of an object to the speed of sound in the surrounding medium.
As altitude increases from sea level, temperature generally decreases, resulting in a decrease in the speed of sound. Therefore, at an altitude of 15 km, Mach 1 implies that the speed of a jet aircraft is lower than that at sea level.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here

