
Carbon farming hailed as a sustainable solution to combat climate change, has garnered significant attention in recent years. By sequestering carbon dioxide from the atmosphere into agricultural soils and vegetation, carbon farming practices offer a dual benefit: mitigating greenhouse gas emissions while enhancing soil fertility and agricultural productivity. However, the effectiveness of carbon farming hinges on various factors such as land management practices, soil types, and regional climate conditions. While its potential is promising, widespread adoption and scalability remain challenges. Adequate investment, policy support, and education are essential to unlock the full potential of carbon farming as a vital tool in the fight against climate change.
| Prelims: Carbon Farming. Mains: Significance and challenges of Carbon farming. |
Context:
- The objective of carbon farming is to alleviate climate change by diminishing the levels of carbon dioxide (CO2) and other greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.
Carbon farming:
- Carbon farming is an encompassing agricultural method targeting the sequestration of atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) into soil and vegetation, thereby mitigating climate change and improving soil health and agricultural productivity.
- It entails adopting regenerative agricultural practices like agroforestry, cover cropping, rotational grazing, conservation tillage, composting, and diversified crop rotations to enhance carbon sequestration.
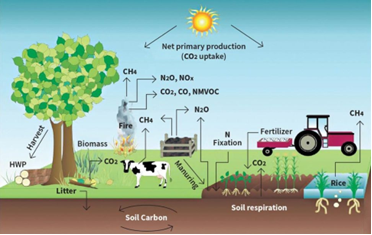
Significance of Carbon Farming:
- Mitigation of Climate Change: Carbon farming practices like rotational grazing, agroforestry, conservation agriculture, and integrated nutrient management aid in sequestering atmospheric carbon dioxide into soil and vegetation.
- Soil Health Improvement: Carbon farming improves soil health by elevating soil organic carbon levels, enhancing soil structure, fertility, water retention, and resilience to drought and extreme weather events. Methods such as zero tillage, cover cropping, and crop residue management minimise soil disturbance while augmenting organic content.
- Biodiversity Conservation: Agroforestry, agroecology, and land restoration practices within carbon farming foster biodiversity conservation. They achieve this by diversifying plant and animal species, furnishing habitats for wildlife, and rehabilitating degraded ecosystems.
- Sustainable Agriculture: Carbon farming advocates sustainable agricultural practices by curbing environmental impacts, conserving natural resources, and amplifying the long-term productivity and resilience of agricultural systems.
Challenges in Carbon Farming:
- Water Availability: Carbon farming faces challenges in hot, dry regions where limited water availability hampers plant growth and carbon sequestration potential, impacting practices like cover cropping.
- Plant Selection: Choosing plant species is critical, as not all species sequester carbon equally effectively. Fast-growing trees and deep-rooted perennial grasses excel in carbon sequestration, but suitability varies, especially in arid environments.
- Financial Resources: Small-scale farmers in developing countries often lack resources for investing in sustainable land management practices and environmental services.
- Policy Support: Adequate policy support is vital for widespread adoption of carbon farming. This entails incentives, subsidies, regulations, and technical assistance at local, national, and international levels to facilitate its implementation.
Carbon farming schemes worldwide:
- Voluntary Carbon Markets: Carbon trading in agriculture, notably in countries like the U.S., Australia, New Zealand, and Canada. Platforms like the Chicago Climate Exchange incentivize carbon mitigation activities in agriculture.
- Kenya’s Agricultural Carbon Project: Supported by the World Bank, this project exemplifies efforts in economically developing countries to address climate mitigation, adaptation, and food security challenges through carbon farming initiatives.
- ‘4 per 1000’ Initiative: Launched during the COP21 climate talks in Paris, this initiative emphasises carbon sinks’ role, including those from carbon farming, in mitigating greenhouse gas emissions. It advocates wise management of the global carbon budget.
The opportunities for carbon farming in India:
- Financial Benefits: Agro-ecological practices in India offer significant economic benefits, potentially generating $63 billion from around 170 million hectares of arable land. Farmers could receive ₹5,000-6,000 per acre annually for providing climate services through sustainable agricultural practices.
- Extensive Agricultural Land: Regions like the Indo-Gangetic plains and the Deccan Plateau, with extensive agricultural land, are ideal for adopting carbon farming. Coastal areas face challenges due to salinization and limited resources, hindering traditional farming practices.
- Carbon Credit System: Carbon credit systems incentivize farmers by offering additional income for environmental services, promoting carbon farming adoption.
- India’s Journey towards Carbon Neutrality: Studies suggest that agricultural soils in India can absorb 3-8 billion tonnes of CO2-equivalent annually over 20-30 years. This capacity can help bridge the gap between feasible emissions reductions and climate stabilisation, making carbon farming a sustainable strategy for mitigating climate change and enhancing food security.
Government Initiatives to Boost Carbon Farming
- Green Credit Scheme: It aims to promote and support sustainable practices, including those in agriculture.
- National Mission on Natural Farming (NMNF): Three main objectives: sustainably increasing agricultural productivity and incomes. adapting and building resilience to climate change. reducing greenhouses gas emissions wherever possible
Conclusion:
Hence, expanding carbon farming necessitates unified efforts to confront challenges like limited awareness, insufficient policy support, technological barriers, and the need for an enabling adoption environment. Promoting carbon farming aligns with India’s interests, serving to combat climate change, enhance soil health, preserve biodiversity, and offer economic opportunities for its practitioners.
Source: (TH)
FAQs
Q: What is carbon farming?
Carbon farming refers to agricultural practices aimed at sequestering carbon dioxide from the atmosphere into soil and vegetation. These practices include techniques like agroforestry, cover cropping, rotational grazing, and no-till farming, among others.
Q: How does carbon farming help combat climate change?
Carbon farming helps mitigate climate change by removing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and storing it in the soil and biomass. This process, known as carbon sequestration, reduces the amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, thus mitigating global warming and its associated impacts.
Q: What are the benefits of carbon farming?
Carbon farming offers numerous benefits, including improved soil health and fertility, enhanced agricultural productivity, increased water retention in soils, and biodiversity conservation. Additionally, it can provide economic opportunities for farmers through carbon credit markets and ecosystem service payments.
Q: What are some common carbon farming practices?
Common carbon farming practices include agroforestry, which involves integrating trees and shrubs into agricultural landscapes, cover cropping, where cover crops are planted to protect and enrich the soil between cash crop seasons, rotational grazing, which rotates livestock through different pastures to improve soil health, and no-till farming, which minimizes soil disturbance to preserve organic matter and carbon.
Q: What challenges does carbon farming face?
Despite its potential benefits, carbon farming faces challenges such as limited awareness and understanding among farmers, technical and financial barriers to adoption, variability in effectiveness based on local conditions, and the need for supportive policies and incentives to encourage widespread implementation. Overcoming these challenges will be crucial for realizing the full potential of carbon farming as a climate change mitigation strategy.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here

