India’s space economy is rapidly becoming a significant player on the global stage. With advancements in satellite technology, space exploration, and commercial space services, India is leveraging its expertise to drive economic growth and innovation. The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has been at the forefront, achieving remarkable feats like the Mars Orbiter Mission and numerous successful satellite launches. This booming sector not only supports national security and communication but also opens up new opportunities for businesses and startups. By investing in space technology, India aims to enhance its technological capabilities, create jobs, and foster international collaborations, positioning itself as a key contender in the global space economy.

Tags: GS- 3, Science & Technology- Space Technology- Achievements of Indians in Science & Technology
Contents
Why in the news?
- Recently, the Department of Space received an 18% increase in its budget for the fiscal year 2024-25, with a major portion allocated to advancing space technologies.

India’s Space Economy:
- Early Achievements:
- India’s space journey began with the launch of Aryabhata in 1975.
- Since then, ISRO has achieved significant milestones, including the Chandrayaan and Mangalyaan missions, which have greatly contributed to scientific research and practical applications.
- Current Valuation and Future Projections:
- Present Valuation:
- India’s space economy is valued at approximately ₹6,700 crore (about $8.4 billion), representing a modest 2% share in the global space economy.
- Future Outlook:
- The Indian National Space Promotion and Authorization Centre (IN-SPACe) projects that by 2033.
- India’s space economy could grow to ₹35,200 crore (approximately $44 billion), capturing around 8% of the global market share.
- Present Valuation:
- The goal is to achieve a 15% share by 2047.
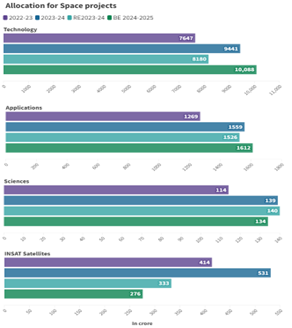
Budgetary Allocation:
- Union Budget 2024-25: The Central government allocated ₹13,042.75 crore for space-related initiatives.
- Venture Capital Fund (VCF):
- An additional ₹1,000 crore (about $134 million) has been earmarked as a Venture Capital Fund to boost the space sector.
- This funding aims to significantly increase the space economy over the next decade and promote innovation, private sector participation, and global competitiveness.
Decadal Vision and Strategy:
- Demand Generation: The focus is on creating a strong demand for space-related services and applications.
- Local Manufacturing: Encouraging the indigenous production of satellites, launch vehicles, and other space hardware.
- Infrastructure Development: Building necessary infrastructure to support space activities.
- Regulatory Framework: Establishing clear guidelines to facilitate the participation of non-governmental entities (NGEs) in the space sector.
Key Segments of the Space Ecosystem
- Space-for-Earth: Includes applications such as weather forecasting, communication, and remote sensing.
- Access-to-Space: Involves enabling satellite launches and transportation.
- Space-for-Space: Focuses on scientific research, exploration, and interplanetary missions.
Potential of the Space Sector:
- Export Potential and Investment:
- Current Export Market: India’s space-related services exports are valued at ₹2,400 crore (about $0.3 billion). The goal is to increase this to ₹88,000 crore ($11 billion).
- Investment Plans: An ambitious investment of ₹17,600 crore ($22 billion) is planned over the next decade.
- Space Tourism:
- Market Growth:
- In 2023, the space tourism market was valued at $848.28 million, with expectations to grow to $27,861.99 million by 2032.
- Key players include Virgin Galactic, Blue Origin, SpaceX, Boeing, Axiom Space, and Space Perspective.
- Market Growth:
Challenges in India’s Space Sector:
- Global Competition: Indian space companies need to compete effectively on the international stage by offering competitive services, advanced technology, and reliable launch capabilities.
- Private Sector Participation: There is a need for more substantial investment and long-term commitment from the private sector, with clear government policies to support collaboration.
- Technology Development: Significant investment is required for developing advanced technologies such as reusable launch vehicles, miniaturised satellites, and advanced propulsion systems.
- Regulatory Framework: Navigating complex licensing processes and export controls requires clarity and transparency in regulations.
- Infrastructure and Facilities: Developing and maintaining infrastructure demands substantial capital. Collaborations between ISRO and private entities can help address this.
- Talent and Skill Development: Attracting and retaining skilled professionals is crucial, requiring enhanced educational programs and industry-academia partnerships.
- Risk Management and Insurance: The private sector needs robust risk assessment and insurance options to mitigate financial risks from mission failures.
- Collaboration with ISRO: Balancing contributions from private companies while benefiting from ISRO’s expertise is essential to avoid dependency and ensure fair competition.
Major Reforms in the Space Sector:
- Indian Space Policy 2023: This policy outlines the roles and responsibilities of ISRO, New Space India Limited (NSIL), and private sector entities, aiming to boost participation from research, academia, startups, and industry.
- Strategic Proposals by SIA: The Space Industry Association – India (SIA-India) has proposed a significant increase in the space budget to support program expansion, private sector involvement, and technological advancements.
- Tax Incentives: Additional initiatives are needed for tax exemptions, holidays, or accelerated depreciation for companies involved in space sector activities.
FDI in the Space Sector:
- New Rules (2024):
- The Finance Ministry has introduced the Foreign Exchange Management (Non-debt Instruments) (Third Amendment) Rules, 2024.
- Which provides a liberalised entry route for Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) in satellites, launch vehicles, spaceports, and related manufacturing.
- This allows 100% FDI in these areas, with up to 74% through the automatic route and requiring government approval for investments beyond that.
Space-Related Start-Ups in India:
- Growth and Investment:
- Start-Up Surge: The number of space start-ups has risen from just 1 in 2014 to 189 in 2023, as per the DPIIT Start-Up India Portal.
- Investment: Investment in Indian space start-ups reached $124.7 million in 2023.
- Private Sector Involvement:
- The establishment of IN-SPACe in 2020 has been pivotal in promoting, authorising, and supervising space activities by non-governmental entities (NGEs), encouraging greater private sector participation.
Conclusion:
India’s space sector has seen impressive progress, from launching satellites for communication, navigation, and scientific research to successful missions to the Moon and Mars. With significant potential for growth, driven by innovation and collaboration, India is set to become a major player in the global space economy.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Mains:
Q.1 What is India’s plan to have its own space station and how will it benefit our space programme? (2019)
Q.2 Discuss India’s achievements in the field of Space Science and Technology. How the application of this technology helped India in its socio-economic development? (2016)
Source: TH
FAQs
Q: What is India’s space economy?
- Answer: India’s space economy includes all the activities related to space exploration, satellite launches, and the development and use of space technology. It involves government agencies like ISRO, private companies, and various industries that benefit from space-related advancements.
Q: Why is India’s space economy important?
- Answer: India’s space economy is important because it contributes to national security, scientific research, and economic growth. Satellite technology, for example, helps in communication, weather forecasting, disaster management, and navigation, making life better for people in many ways.
Q: How does India’s space economy benefit everyday people?
- Answer: The space economy benefits everyday people through improved communication networks, better weather forecasts, and enhanced navigation systems. It also supports agriculture with satellite imagery for monitoring crops and helps in disaster management by providing crucial data during natural calamities.
Q: What are some notable achievements of India’s space economy?
- Answer: Some notable achievements include the successful Mars Orbiter Mission (Mangalyaan), the Chandrayaan missions to the Moon, and the launch of numerous satellites for both domestic use and international clients. These missions have showcased India’s capabilities in space technology on the global stage.
Q: What is the future of India’s space economy?
- Answer: The future of India’s space economy looks promising with plans for more ambitious missions, including manned spaceflights and deeper space exploration. Increased collaboration with private companies and international space agencies is expected to drive further growth, innovation, and economic benefits.
To get free counseling/support on UPSC preparation from expert mentors please call 9773890604
- Join our Main Telegram Channel and access PYQs, Current Affairs and UPSC Guidance for free – Edukemy for IAS
- Learn Economy for free- Economy for UPSC
- Mains Answer Writing Practice-Mains Answer Writing
- For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here

