Today’s daily current affairs briefing for UPSC aspirants explores the latest developments relevant to the upcoming civil services examination. Our focus today includes a critical analysis of recent policy changes, international affairs, and national developments, all of which play a pivotal role in shaping India’s socio-political and economic landscape. Stay informed and stay ahead in your UPSC preparations with our daily current affairs updates, as we provide you with concise, well-researched insights to help you connect the dots between contemporary events and the broader canvas of the civil services syllabus.

Contents
- 1 Supreme Court extends interim stay on Kanwar Yatra order
- 2 Using Children’s Personal Data Legally and Securely
- 2.1 Why in the news?
- 2.2 Key Functions of Unified District Information System for Education Plus (UDISE+):
- 2.3 Linkage of UDISE+ and the National Education Policy 2020:
- 2.4 Concerns Surrounding UDISE:
- 2.5 Solution: Adherence to the Supreme Court’s Puttaswamy Judgment
- 2.6 Need for Specific Protocols to Handle Children’s Data:
- 2.7 Conclusion
- 3 Are Enough Formal Jobs Being Created
- 4 The budget push for infrastructure
- 5 UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
- 6 ADCs Raise Demand to Pass 125th Constitutional Amendment Bill
- 7 UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
- 8 GROWTH-India Telescope
- 9 Climate Finance Action Fund
- 10 Steel Import Monitoring System’ 2.0 Portal
- 11 Cultural Property Agreement
- 12 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 12.1 Q: What are daily current affairs?
- 12.2 Q: Why is it important to stay updated with daily current affairs?
- 12.3 Q: Where can I access daily current affairs information?
- 12.4 Q: How can I effectively incorporate daily current affairs into my routine?
- 12.5 Q: What are some tips for critical analysis of daily current affairs?
- 13 To get free counseling/support on UPSC preparation from expert mentors please call 9773890604
Supreme Court extends interim stay on Kanwar Yatra order
Tags: GS-2 , Polity & Governance- Judiciary – SC Judgements
Why in the news?
- The Supreme Court has extended the interim order staying the directives from the Uttar Pradesh and Uttarakhand governments which required eateries along the Kanwariya pilgrim route to display the names of their owners and staff.
- This stay order will remain effective until August 5, the next hearing date.

Background of the Case:
- Directive Issued by Muzaffarnagar District Police
- Date: July 17, 2023
- Content: Hotels, dhabas, and shops on the Kanwar Yatra route were directed to display the names of their owners and employees.
- Objective: To avoid “religious discrimination” and prevent “law-and-order situations” due to confusion about shop names among Kanwariyas, who follow a strictly vegetarian diet.
- Kanwar Yatra Duration: July 22 to August 19, 2023.
- Challenge in Apex Court
- Petitioners’ Argument: The directive targets Muslim-owned businesses by forcing them to disclose their religious identity, potentially leading to economic consequences and targeting.
- Relief Sought: Public withdrawal of the directive.
- Stay Order by the Supreme Court
- Decision: Prohibited the enforcement of the public notice until further hearing.
Key Takeaways from the Hearing:
- No Government Order
- Observation: No government order empowered the police to issue such directions.
- Alternative Acts: Suggested directives could be issued under the Food Safety and Standards Act, 2006, or the Street Vendors Act, 2014, to ensure strictly vegetarian food for Kanwar Yatris.
- Limits to Police Action
- Observation: Police cannot usurp the powers of the competent authority under these Acts without a legal foundation.
- Voluntary Display: The police directions asked shops to “voluntarily display” the names of their owners and employees.
- Legal Authority: Penal actions against food business operators indicated the police might have overstepped their legal authority.
- Question of Discrimination
- Constitutional Arguments: The petitioners argued that the directions violated Article 15(1) by discriminating based on religion and supporting untouchability, banned under Article 17.
- Economic Boycott: Led to an economic boycott of establishments hiring Muslims and Dalits.
Legal Basis for the Directions Issued by Police:
- No Specific Law Cited
- Police Directions: Muzaffarnagar Police did not cite any specific law.
- Section 144 IPC: Typically used in urgent situations involving “nuisance or apprehended danger,” mirrored in Section 163 of the Bharatiya Nagarik Suraksha Sanhita, 2023.
- Magistrate’s Authority: Allows a Magistrate, empowered by the state government, to direct individuals to refrain from certain acts to prevent public disturbances or danger to life and safety.
- SC Guidelines for Exercising Power under Section 144
- Case: ‘In Re: Ramlila Maidan Incident’ (2012)
- Grounds: Actions by public authorities must be tested on:
- Legal authority conferred by law.
- Reasonableness.
- Current Case Onus: Determine whether any law grants the police and state government the power to issue directions to shopkeepers and if those directions were reasonable.
Police Directives and Shopkeepers’ Right to Privacy:
- Right to Privacy under Article 21:
- Judgement: ‘Justice K S Puttaswamy v. Union of India’ (2017)
- Scope: Recognized the fundamental right to privacy, including the “privacy of the mind” covering religious faith and the freedom to express or withhold such choices.
- Three-Fold Test for Restrictions:
- Existing law allows such restrictions.
- Legitimate state aim.
- Proportionality to the government’s objective.
- Evaluation in Kanwar Yatra Case
- Consideration: Whether the police directions restrict the right to privacy.
- Supporting Law: If found, the Court will evaluate if avoiding a “law and order situation” is a legitimate aim and if the measure is proportionate.
Police Directions and the Issue of Discrimination:
- Article 15(1) of the Constitution: The State shall not discriminate against any citizen on grounds only of religion, race, caste, sex, place of birth or any of them.”
- Assessment: Whether the requirement to disclose names, revealing religious and caste identities, constitutes discrimination, particularly targeting Muslim-owned businesses.
- Police Justification: Intended to provide convenience to devotees abstaining from certain food items.
- Petitioners’ Argument: Directions are based on discriminatory assumptions about who can prepare and serve satvik or pure veg food.
- Article 19(1)(g): Right to “practise any profession, or to carry on any occupation, trade or business.”
- Claim: Directions led to an economic boycott of Muslim minorities
Source: IE
Using Children’s Personal Data Legally and Securely
Tags: GS Paper – 2, Governance- Government Policies & Interventions- Children
Why in the news?
- India’s school education system is among the largest and most intricate globally, comprising around 15 lakh schools, 97 lakh teachers, and nearly 26.5 crore students from pre-primary to higher secondary levels.
- The importance of adhering to data privacy and minimization principles given the sensitivity of children’s personal data.

Key Functions of Unified District Information System for Education Plus (UDISE+):
- Data Collection, Management, and Real-Time Updates
- Comprehensive Data Collection: UDISE+ gathers detailed information on school infrastructure, teacher demographics, student enrolment, and academic performance.
- Centralised System: Integrates data into a centralised system, offering a holistic view of the education landscape.
- Real-Time Updates: Enables quick reflection of changes in school infrastructure, staffing, or student enrolment, providing policymakers with the most current information.
- Resource Allocation, Monitoring, and Evaluation
- Effective Resource Allocation: Facilitates accurate distribution of resources such as textbooks and teacher deployment based on up-to-date data.
- Continuous Monitoring: Allows for ongoing assessment of educational programs and policies, helping the Ministry of Education adjust initiatives as needed.
- Educational Trends Mapping and Policy Formulation
- Trend Mapping: Tracks enrolment rates, dropout rates, gender parity, and academic achievements to identify gaps and areas needing intervention.
- Policy Formulation: Provides data-driven insights for developing and implementing evidence-based policies tailored to regional and demographic needs.
Linkage of UDISE+ and the National Education Policy 2020:
- UDISE+ and the National Education Policy 2020
- APAAR Integration: Incorporates the Automated Permanent Academic Account Registry (APAAR), a unique identifier for each student, consolidating academic credentials and demographic information.
- Seamless Transitions: Ensures accurate tracking of students’ educational journeys, facilitating smoother transitions between education levels.
- Enhancing Ease of Schooling
- Automated Admissions: Reduces dropout rates during transitions (e.g., primary to secondary education) and improves accessibility to continuing education.
- Ed-Tech Collaborations: Partners with ed-tech companies and entities like DigiLocker to provide secure digital infrastructure for academic records.
Concerns Surrounding UDISE:
- Privacy Risks:
- UDISE+ enhances data management and policy formulation but raises significant data privacy and security concerns.
- Potential issues include inadequate guidance on what constitutes verifiable parental consent for minors’ data under the UDISE+/APAAR system.
- Compliance Issues:
- The Data Protection and Privacy (DPDP) Act requires that personal data be collected only for specified legitimate purposes.
- Using children’s data under UDISE+ for purposes beyond the authorised scope could breach this requirement.
- Data Exposure:
- The integration of various data sources raises concerns about the security of student information, with risks of exposure to multiple actors within the educational ecosystem.
- Sensitive Information:
- The reliance on personal data, including Aadhaar information, necessitates stringent protective measures to safeguard against data theft and cyber breaches.
Solution: Adherence to the Supreme Court’s Puttaswamy Judgment
- Puttaswamy Judgment Overview: The Supreme Court’s Justice K.S. Puttaswamy (Retd.) v. The Union of India (2018) case recognized the right to privacy as a fundamental right.
- It established a three-part test for assessing the impact of state actions on privacy:
- Legitimate State Interest: The restriction must serve a legitimate state interest.
- Necessity and Proportionality: The restriction must be necessary and proportionate to achieve the stated interest.
- Legal Framework: The restriction must be imposed by law.
- Aadhaar Compliance:
- Integration of Aadhaar in APAAR/UDISE+ must align with these principles to ensure data privacy.
- Adequate measures should be in place to prevent unauthorised access, data theft, and cyber breaches.
Need for Specific Protocols to Handle Children’s Data:
- Lack of Specific Mechanisms
- Unclear Roles: Uncertainty exists about roles and responsibilities regarding data sharing, including data fiduciaries, processors, and principals.
- Privacy Policy Gaps: APAAR’s privacy policy lacks specific protocols for sharing children’s data for unspecified purposes.
- No Clarity on Legal Responsibilities
- Legal Uncertainty: The Ministry’s non-responsibility for data accuracy and disclosure under UDISE+ raises concerns about the adequacy of the grievance handling system and legal accountability.
- Recommendations
- Develop Protocols: Establish standard operating procedures and a comprehensive governance framework to ensure data accuracy, legal compliance, and effective handling of complaints.
- Strengthen Governance: Implement technical and legal protocols to safeguard children’s personal data and ensure lawful and secure use.
Conclusion
The vast and diverse Indian school education system requires robust mechanisms to manage and protect student data. Developing and implementing comprehensive technical and legal protocols within a strong governance framework is crucial to ensure lawful, secure, and effective handling of children’s personal data.
Source: TH
Are Enough Formal Jobs Being Created
Tags: GS Paper – 3, Economy- Industrial Policy – Employment
Why in the News?
- The Union Budget for 2024-25 underscored job creation as a top government priority, with the finance minister emphasising it 23 times during the budget speech.
- Amid concerns about rising unemployment, Prime Minister Modi has endorsed a package of employment-focused schemes.

Current State of Employment in India:
- Workforce Distribution (2022-23):
- Agriculture: 45%
- Manufacturing: 11.4%
- Services: 28.9%
- Construction: 13%
- Unemployment and Underemployment:
- Official Unemployment Rate: 3.2%
- Urban Unemployment (March 2024): 6.7%
- Youth Unemployment (2022-23): 10%
- Underemployment: Many job seekers are engaged in informal or casual labour, with nearly one in five workers, primarily women, being unpaid in household enterprises.
- Formal Employment Trends:
- The proportion of regular salaried workers declined from 22.8% in 2017-18 to 20.9% in 2022-23.
- A significant number of salaried workers lack formal contracts or social security benefits.
Employment Schemes Announced in the Budget:
- First-Time Employee Subsidy:
- Details: ₹15,000 wage subsidy for hiring first-time employees.
- Target: One crore individuals.
- Manufacturing Sector Subsidy:
- Details: Wage subsidies up to 24% of a ₹25,000 monthly wage for first-time employees, applicable for four years.
- New Worker Incentive:
- Details: Reimbursement of up to ₹3,000 of the employer’s monthly EPFO contribution for new hires.
- Industrial Training Institutes (ITI) Upgrade:
- Details: Enhancement of ITI facilities to benefit 20 lakh students.
- Internship Program:
- Details: On-the-job training for one crore youth with internships, offering a ₹5,000 monthly allowance for one year.
Challenges in Implementation
- Subsidy Obstacles:
- First-Time Employee Subsidy: Payment in three instalments, with the second requiring completion of an online financial literacy course, which may be impractical across sectors.
- Employer Refund Risk: Employers must refund the subsidy if the employee leaves within 12 months, creating financial risk for small businesses.
- Manufacturing Sector Scheme:
- Hiring Requirement: Companies must hire at least 50 people or 25% of the existing workforce, which is burdensome for small firms.
Effectiveness of the Schemes:
- Cost of Hiring vs. Other Constraints:
- Primary Constraint: Economists argue that wage costs are not the main barrier. The real issues are insufficient demand, low consumption, and lack of private investment.
- Skilling: While important, skilling is not the central barrier to hiring.
- Additional Measures Needed
- Focus on MSME Sector: Support labour-intensive industries, especially in small towns, and infuse capital into MSMEs to stimulate economic growth.
- Wage Enhancements: Increase wages under MGNREGA and create a similar scheme for urban workers to boost consumption and demand.
Conclusion
The government’s employment schemes represent a positive step, but addressing fundamental issues such as low demand, underinvestment, and the need for formal job creation in labour-intensive sectors is essential for achieving sustainable employment growth in India.
Source: TH
The budget push for infrastructure
Tags: GS-3, Economy- Growth & Development- Infrastructure
Why in the news?
- In the 2024-25 Budget, Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman allocated ₹11 lakh crore for capital expenditure, representing 3.4% of GDP.
- An additional ₹1.5 lakh crore will be provided to states as long-term interest-free loans to encourage infrastructure investment.

Key Highlights of Target:
- Overall Expenditure: Infrastructure spending remains steady at 13.9% of the total budget, slightly down from 14.3% in FY2024.
- Transport Sector: The largest portion of infrastructure spending, constituting 11.29% of the budget, though this share has decreased by 0.4 percentage points from the previous year.
- Power Sector: Slight increase in allocation.
- Roads, Transport, and Highways: Allocated ₹2.78 lakh crore for 2024-25.
- Railways: Record allocation of over ₹2.55 lakh crore, with increased funding for signalling, telecom, and the KAVACH automatic train protection system.
- Civil Aviation: Allocation decreased by 20% to ₹2,357 crore.
- Shipping: Allocation remains unchanged at ₹2,377 crore.
- Regional Connectivity Scheme: Receives ₹502 crore.
Performance on Road, Railways, Shipping, and Airports:
- Road:
- National highways have grown 1.6 times from 2014 to 2024.
- Bharatmala Pariyojana expanded high-speed corridors 12 times and 4-lane roads 2.6 times.
- Development of 11 industrial corridor projects is underway.
- The Ministry of Road Transport and Highways revised Build-Operate-Transfer agreements to attract private investment, including construction support.
- The focus needs to shift from asset creation to asset management, maintenance, and safety.
- Experts recommend standard operating procedures for constructing bridges and tunnels to avoid incidents like the Silkyara tunnel collapse.
- Railways:
- Capital expenditure has risen by 77% over five years, reaching ₹2.62 lakh crore in FY24, with funds allocated to new lines, gauge conversion, and doubling.
- Challenges persist, including the need to shift freight movement from roads to rail, where long-haul road freight is 25-30% more costly for distances under 500 km.
- Issues include uncertain rake supply, infrastructure delays, and the shared use of tracks by passenger and freight trains.
- Enhancing the efficiency of freight vehicle entry and exit is crucial for better loading and unloading operations.
- Shipping and Airports:
- Sagarmala program initiated 839 projects worth ₹5.8 lakh crore since 2015; 262 projects worth ₹1.4 lakh crore are completed.
- Over 230 maritime ports exist, but 40% of cargo passes through just two ports (JNPT and Mundra), necessitating a development plan for other ports.
- Under the 2019 privatisation phase, six AAI airports were privatised, with plans for 25 more
Attracting Private Investments:
- Investment Breakdown (FY 2019-2023): Central Government contributed 49%, state governments 29%, and the private sector was expected to contribute the remainder.
- Private Sector Hesitation: Market risks and project delays affect returns, necessitating the identification of more monetizable assets.
- Policy Recommendations: Implement recommendations from the Kelkar Committee report (2015) to address policy and regulatory challenges.
Conclusion
The Budget 2024-25 emphasises significant capital expenditure on infrastructure with a focus on transport, roads, railways, and power. Despite progress, challenges like private investment hesitancy, project delays, and the need for better asset management and development plans for ports and airports persist. Targeted policy measures and infrastructure strategies are crucial for maintaining growth and efficiency.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q1. With reference to ‘National Investment and Infrastructure Fund’, which of the following statements is/are correct? (2017)
- It is an organ of NITI Aayog.
- It has a corpus of `4,00,000 crore at present.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (d)
Q: 2. In India, the term “Public Key Infrastructure” is used in the context of (2020)
- Digital security infrastructure
- Food security infrastructure
- Health care and education infrastructure
- Telecommunication and transportation infrastructure
Ans: (a)
Mains
Q:1 “Investment in infrastructure is essential for more rapid and inclusive economic growth.” Discuss in the light of India’s experience. (2021)
Source: TH
ADCs Raise Demand to Pass 125th Constitutional Amendment Bill
Tags: GS – 2, Polity & Governance- Federalism- Constitutional Amendments– Centre-State Relations– Constitutional Bodies
Why in the news?
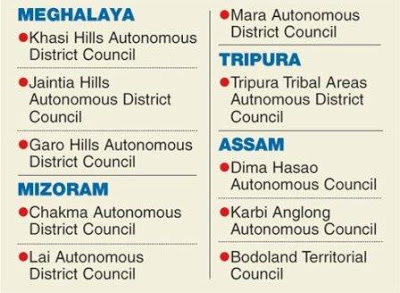
- Recently, Chief Executive Magistrates (CEMs) from 10 Autonomous District Councils (ADCs) across Assam, Meghalaya, Mizoram, and Tripura met with the Union Home Minister to advocate for the passing of the 125th Constitutional Amendment Bill.
- In response, the Union government has decided to form a committee, led by the Minister of State for Home Affairs, to address the issues associated with the Bill.
What are the Proposed Amendments in the 125th Constitutional Amendment Bill?
- Enhanced Powers for Tribal Councils: The Bill seeks to increase financial, executive, and administrative powers for tribal autonomous councils under the Sixth Schedule of the Constitution.
- Village and Municipal Councils:
- Creation of Councils: The proposal includes establishing Village and Municipal Councils in addition to the existing District and Regional Councils.
- Function: Village Councils will cater to individual villages or clusters in rural areas, while Municipal Councils will be set up in urban areas within each district.
- Authority: District Councils will have the power to legislate on the composition, delimitation, and functions of Village and Municipal Councils.
- Rules for Devolution of Powers:
- Governor’s Authority: The Governor will be empowered to create rules for delegating powers to Village and Municipal Councils, covering aspects like economic planning, land reforms, urban planning, and land use.
- Disqualification: Rules may also address the disqualification of council members due to defection.
- State Finance Commission:
- Appointment: A Finance Commission will be established to evaluate the financial status of District, Village, and Municipal Councils.
- Recommendations: The Commission will recommend tax distribution, grants-in-aid, and other financial matters.
- Elections to Councils:
- Oversight: The State Election Commission, appointed by the Governor, will oversee elections for District, Regional, Village, and Municipal Councils.
Current Status of the Bill:
- Legislative Progress:
- The Constitution (125th Amendment) Bill 2019 was introduced in the Rajya Sabha and referred to the Departmental-Related Standing Committee on Home Affairs.
- Pending Issues: The committee raised concerns in its 2020 report, and the Bill has remained pending since.
Sixth Schedule of the Constitution:
- Scope:
- Provides governance for tribal areas in Assam, Meghalaya, Tripura, and Mizoram to protect tribal rights and ensure self-administration.
- Constitutional Basis:
- Article 244 (2): Specifies that the provisions of the Sixth Schedule apply to the administration of tribal areas in Assam, Meghalaya, Tripura, and Mizoram.
- Article 275 (1): Guarantees grants-in-aid from the Consolidated Fund of India to these states for the administration of tribal areas.
- Autonomy:
- Establishes Autonomous District Councils (ADCs) which have the authority to legislate on matters such as land, forests, cultivation, inheritance, customs, and taxes.
- Governance:
- ADCs function as miniature states with legislative, executive, and judicial powers, enabling self-governance and local administration
What are Autonomous District Councils (ADCs)?
- Purpose and Structure:
- About: ADCs are constitutional entities under the Sixth Schedule (Article 244) aimed at preserving tribal cultures and resources in Northeast India.
- Governor’s Authority: The Governor can organise, reorganise, and modify the autonomous districts, including their areas and boundaries.
- Tribal Distribution: In districts with multiple tribes, autonomous regions may be created.
- Composition and Administration:
- District Council: Each district has a council of 30 members (26 elected and 4 nominated), serving a five-year term.
- Regional Council: Each autonomous region has its own council.
- Management: Councils manage their jurisdictions and may set up village councils or courts for tribal disputes, with appeals handled as per the Governor’s directives.
- Current ADCs:
- There are 10 autonomous councils: three each in Assam, Meghalaya, and Mizoram, and one in Tripura.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q:1 Under which Schedule of the Constitution of India can the transfer of tribal land to private parties for mining be declared null and void? (2019)
(a) Third Schedule
(b) Fifth Schedule
(c) Ninth Schedule
(d) Twelfth Schedule
Ans: (b)
GROWTH-India Telescope
Tags: GS-3, Science & Technology- Achievements of Indians in Science & Technology– Scientific Innovations & Discoveries
Why in the news?
- Recently, the GROWTH-India Telescope captured a 116-meter, building-sized asteroid during its closest approach to Earth.

About GROWTH-India Telescope:
- Key Features:
- India’s First Robotic Telescope: Fully automated optical research telescope.
- Primary Mission: Observing explosive transients, variable sources, and near-Earth asteroids.
- Location: Indian Astronomical Observatory, Hanle, Ladakh, at 4500 meters above sea level.
- Significance: One of the highest observatory sites globally, renowned for its excellent observational conditions.
- Other Telescopes at Hanle: Himalayan Chandra Telescope (HCT), gamma-ray array telescope (HAGAR), and imaging Cherenkov telescope (MACE).
- Construction and Partnerships:
- Institutions Involved: Indian Institute of Astrophysics (IIA) and Indian Institute of Technology Bombay (IITB).
- Support: Department of Science and Technology (DST) and Indo-US Science and Technology Forum.
- Global Collaboration:
- GROWTH-India Project: Part of the Global Relay of Observatories Watching Transients Happen (GROWTH).
- Objective: Continuous monitoring of significant celestial events.
- Collaborative Network: Ensures uninterrupted observations by mitigating the impact of daylight, thus allowing for comprehensive data collection.
Source: TOI
Climate Finance Action Fund
Tags: GS-3 , Ecology & Environment- Climate Finance
Why in the news?
- Recently, Azerbaijan hosted the 29th Conference of Parties (COP29) to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change, announcement of the ‘Climate Finance Action Fund’.

About Climate Finance Action Fund:
- Key Features:
- Capitalisation: Contributions from fossil fuel-producing countries and companies across oil, gas, and coal sectors, with Azerbaijan as a founding contributor.
- Launch Context: Part of a package of 14 initiatives under the framework of COP29 thematic days.
- Nature of Fund: Catalytic public-private partnership aiming to mobilise the private sector and de-risk investments.
- Operational Details:
- Special Facilities: Includes concessional and grant-based support to address natural disasters in developing countries.
- Initial Fundraising: Seeks to raise $1 billion with commitments from at least 10 contributing countries to become operational.
- Allocation of Funds:
- Developing Countries: 50% of capital for climate projects focusing on mitigation, adaptation, and R&D.
- Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs): 50% for helping member countries meet the next generation of NDCs, aiming to maintain the 1.5°C temperature target.
- Rapid Response Funding Facility (2R2F): 20% of revenues generated from investments will support this facility, providing highly concessional and grant-based assistance.
- Headquarters:
- Location: Baku, Azerbaijan.
Source: DTE
Steel Import Monitoring System’ 2.0 Portal
Tags: GS-3, Economy- Industry- Steel Monitoring System
Why in the news?
- Recently, the Union Minister of Steel and Heavy Industries introduced SIMS 2.0, an upgraded version of the Steel Import Monitoring System.

About Steel Import Monitoring System 2.0 Portal:
- Key Features:
- API Integration: Connects with multiple government portals, enhancing quality control and streamlining processes for improved efficiency and effectiveness.
- Data Entry System: Ensures consistent and authentic data, promoting transparency and accountability.
- Database Integration: Helps stakeholders identify risk areas for better risk management.
- Functionality:
- If an import consignment declares a source not licensed by the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS), the Ministry can recommend against its import.
- This detailed data assists Customs in better analysing and managing risks associated with steel imports.
- Background:
- Initial Introduction: SIMS was launched in 2019 and has been instrumental in providing detailed steel import data to the domestic industry.
- Upgradation: Based on industry feedback, the Ministry has revamped the portal to create SIMS 2.0, enhancing its effectiveness in monitoring steel imports and supporting the growth of the domestic steel industry.
- Significance:
- Policy Input: The availability of detailed data aids in policy-making.
- Industry Growth: Signals areas for production and growth to the domestic steel industry, fostering development.
Conclusion
SIMS 2.0 represents a significant advancement in monitoring steel imports, integrating modern technology and industry feedback to promote transparency, accountability, and the growth of the domestic steel sector.
Source: PIB
Cultural Property Agreement
Tags: GS-1, Art & Culture- Cultural Agreement
Why in the news?
- The Government of India and the Government of the United States of America signed their first-ever ‘Cultural Property Agreement’ on the sidelines of the 46th World Heritage Committee at Bharat Mandapam, New Delhi.

About Cultural Property Agreement:
- Objective:
- To prevent and curb the illicit trafficking of antiquities from India to the USA.
- Alignment:
- The agreement is in line with the 1970 UNESCO Convention on the Means of Prohibiting and Preventing the Illicit Import, Export, and Transfer of Ownership of Cultural Property, to which both countries are States Party.
- Scope:
- Import Restrictions: The agreement restricts the importation into the USA of specific archaeological material dating from 1.7 million years ago to 1770 CE and certain ethnological materials.
- These include civic, religious, and royal architectural materials, religious and ceremonial items, and manuscripts dating from the 2nd century BCE to 1947 CE.
- Return of Artefacts:
- The USA will offer to return any object or material on the Designate List forfeited to the US Government to India.
- Precedents:
- The USA has already executed similar agreements with other countries, including Algeria, Belize, Bolivia, Bulgaria, Cambodia, Chile, China, Colombia, Costa Rica, Cyprus, Ecuador, Egypt, El Salvador, Greece, Guatemala, Honduras, Italy, Jordan, Mali, Morocco, Peru, and Turkey.
- Significance:
- The agreement facilitates the quick seizure of Indian antiquities at US Customs and their repatriation back to India.
Conclusion
The Cultural Property Agreement marks a significant step in protecting India’s cultural heritage by preventing the illicit trafficking of antiquities and ensuring their return from the USA, aligning with international conventions and fostering bilateral cooperation.
Source: PIB
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are daily current affairs?
A: Daily current affairs refer to the most recent and relevant events, developments, and news stories that are happening around the world on a day-to-day basis. These can encompass a wide range of topics, including politics, economics, science, technology, sports, and more.
Q: Why is it important to stay updated with daily current affairs?
A: Staying updated with daily current affairs is crucial because it helps individuals make informed decisions in their personal and professional lives. It enables people to understand the world around them, stay aware of significant events, and engage in informed discussions about important issues.
Q: Where can I access daily current affairs information?
A: There are various sources for daily current affairs, including newspapers, news websites, television news broadcasts, radio programs, and dedicated apps or newsletters. Social media platforms are also widely used to share and access current affairs information.
Q: How can I effectively incorporate daily current affairs into my routine?
A: To incorporate daily current affairs into your routine, consider setting aside specific times each day to read or watch news updates. You can also subscribe to newsletters or follow news apps to receive curated content. Engaging in discussions with peers or participating in online forums can further enhance your understanding of current events.
Q: What are some tips for critical analysis of daily current affairs?
A: When analyzing daily current affairs, it’s essential to cross-reference information from multiple sources to ensure accuracy. Additionally, consider the source’s credibility and bias, if any. Develop the ability to identify the main points and implications of news stories, and critically evaluate the significance and impact of the events reported.
To get free counseling/support on UPSC preparation from expert mentors please call 9773890604
- Join our Main Telegram Channel and access PYQs, Current Affairs and UPSC Guidance for free – Edukemy for IAS
- Learn Economy for free- Economy for UPSC
- Mains Answer Writing Practice-Mains Answer Writing
- For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here

