Today’s daily current affairs briefing for UPSC aspirants explores the latest developments relevant to the upcoming civil services examination. Our focus today includes a critical analysis of recent policy changes, international affairs, and national developments, all of which play a pivotal role in shaping India’s socio-political and economic landscape. Stay informed and stay ahead in your UPSC preparations with our daily current affairs updates, as we provide you with concise, well-researched insights to help you connect the dots between contemporary events and the broader canvas of the civil services syllabus.

Contents
- 1 The Great Stupa of Sanchi
- 2 Restatement of Values of Judicial Life
- 3 Commission for Scientific and Technical Terminology (CSTT)
- 4 Neuromorphic Computing
- 5 UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
- 6 AL NAJAH V Military Exercise
- 7 Rangeen Machhli App
- 8 State Finance Commission
- 9 Salt Pans
- 10 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 10.1 Q: What are daily current affairs?
- 10.2 Q: Why is it important to stay updated with daily current affairs?
- 10.3 Q: Where can I access daily current affairs information?
- 10.4 Q: How can I effectively incorporate daily current affairs into my routine?
- 10.5 Q: What are some tips for critical analysis of daily current affairs?
- 11 To get free counseling/support on UPSC preparation from expert mentors please call 9773890604
The Great Stupa of Sanchi
Tags:GS-1, History- Architecture
Why in the news?
- Recent visit to Germany, the External Affairs MinisterShri. Jayshankar of India paid a visit to the replica of Sanchi’s Great Stupa’s EastGate standing in front of Humboldt Forum Museum in Berlin.
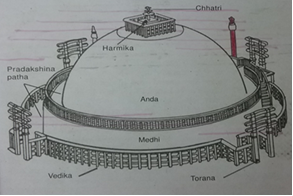

What is a Stupa?
- Meaning:
- A stupa in Buddhism is a dome-shaped structure that contains relics, typically those of Buddha or revered monks, and serves as a place of meditation.
- Origin:
- Stupas were originally pre-Buddhist burial mounds in ancient India, which later gained religious significance in Buddhism.
- Development:
- Expansion under Ashoka (250 BCE): Emperor Ashoka, a patron of Buddhism, is said to have built 84,000 stupas to distribute Buddha’s relics across India.
- Decorated Stupas (125 BCE): By the 2nd century BCE, stupas like those in Bharhut, Bodh Gaya, and Sanchi began to be adorned with sculptural reliefs.
- Gandhara Development (3rd century BCE – 5th century CE): In Gandhara, the stupa design evolved significantly, influencing Buddhist architecture in Central Asia, China, Korea, and Japan.
The Great Stupa of Sanchi
- About:
- Built in the 3rd century BCE by Ashoka, the Great Stupa of Sanchi is India’s oldest stone structure.
- It contains the relics of Buddha and his disciples Sariputra and Maudgalyayan.
- Rediscovered in 1818 by British General Henry Taylor, it was restored in the early 20th century by John Marshall with funding from Bhopal’s begums.
- Declared a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1989, it is located in Sanchi Town, Madhya Pradesh.
- Significance:
- The Stupa is a key site for understanding the evolution of Buddhist art and architecture in India.
The Gateways (Toranas) of the Great Stupa
- About:
- The original stupa was plain, but the four ornate gateways were added in the 1st century BCE during the Satavahana reign.
- These toranas face the four cardinal directions and depict scenes from Buddha’s life and the Jataka tales through exquisite sculptures.
- East Gate of Sanchi Stupa:
- Upper architrave: Depicts the seven Manushi Buddhas.
- Middle architrave: Shows the Great Departure of Siddhartha.
- Lower architrave: Illustrates Ashoka visiting the Bodhi tree.
- Cultural Significance in Europe: The East Gate’s replica, made in the 1860s by Lieutenant Henry Hardy Cole for the Victoria and Albert Museum, has been displayed in several European museums, contributing to its fame in the West.
Source: IE
Restatement of Values of Judicial Life
Tags: GS-4 –Ethics
Why in the news?
- The Restatement of Values of Judicial Life is a code of judicial ethics adopted by the Supreme Court of India in 1997 and It outlines the ethical conduct expected from judges to preserve the integrity, impartiality, and independence of the judiciary.
Key Guidelines (16 Points of the Code):
- Impartiality and Public Confidence: Judges must avoid any actions that could erode public confidence in the impartiality of the judiciary. Justice must be seen to be done.
- Credibility and Perception: Any official or personal act by a judge that might undermine the public’s trust in the judiciary’s credibility should be avoided.
- Non-Involvement in Elections: Judges should not contest elections to any office of clubs, societies, or associations, except those related to law.
- Professional Boundaries with Lawyers: Close personal associations with members of the Bar, especially those practicing in the same court, must be avoided.
- Family in Legal Practice: Judges must not allow immediate family members who are part of the Bar to appear before them or be involved in cases they handle.
- Residence for Professional Work: Judges’ residences or facilities must not be used by family members for professional purposes.
- Dignified Aloofness: Judges should maintain a level of distance and dignity appropriate to their office.
- Disqualification in Certain Cases: Judges should not hear cases involving close family, friends, or companies in which they hold shares unless full disclosure is made, and no objections are raised.
- Non-Participation in Public Debates: Judges should refrain from public debates or expressing political views, especially on matters likely to come before the court.
- Media Interaction: Judges should allow their judgments to speak for themselves and avoid media interviews.
- No Gifts or Hospitality: Judges should not accept gifts or hospitality, except from family and close friends.
- Disclosure of Interests: If a judge holds shares in a company involved in a case, they must disclose this interest before hearing the case.
- Restrictions on Stock Market Activity: Judges should not speculate in shares or stocks.
- Non-Engagement in Trade or Business: Judges must not engage in trade or business, except for publishing legal work or hobbies.
- Fundraising: Judges should not solicit or engage in fundraising activities.
- Avoidance of Perquisites: Judges should not seek financial benefits or privileges beyond what is clearly available through their office.
Major Concerns About Judicial Integrity in India:
- Political Ambitions of Judges: Judges entering politics soon after resignation or retirement and accepting government roles post-retirement, especially after rulings benefiting the ruling party, suggests potential quid pro quo arrangements.
- Transparency Issues: Lack of transparency in handling sensitive cases erodes public trust in the judiciary. Opaque processes in case allocation and decision-making undermine confidence in judicial fairness.
- Conflict of Interest: Judges must avoid conflicts of interest. Involvement in political activities or delivering rulings with political impacts while still serving raises doubts about impartiality.
- Public Trust and Confidence: Actions or rulings by judges that suggest bias weaken public trust. The judiciary’s legitimacy depends on maintaining a perception of integrity and fairness.
Way Forward:
- Strengthen Judicial Ethics Training: Reinforce adherence to the Restatement of Values of Judicial Life and the Bangalore Principles of Judicial Conduct through mandatory ethics training and refresher courses for judges.
- Establish Independent Oversight: Create independent bodies to audit and review judicial conduct periodically, ensuring that ethical standards are maintained.
- Leverage Global Networks: Engage with the Global Judicial Integrity Network, which assists in strengthening judicial integrity and preventing corruption, aligned with the United Nations Convention against Corruption.
- Public Engagement Initiatives: Foster public engagement by organizing forums or discussions where citizens can interact with the judiciary, enhancing transparency and trust in judicial processes.
- Cooling-off Period for Judges Entering Politics: Introduce strict cooling-off periods for judges entering politics and mandate disclosure of any judicial decisions that could raise conflicts of interest.
- Post-Retirement Roles: Establish clear guidelines for post-retirement roles, ensuring that these positions do not compromise the integrity of judicial decisions or give the appearance of political favoritism.
Terms
Commission for Scientific and Technical Terminology (CSTT)
Tags: GS-2, Polity & Governance- Govt. Incentive & Schemes
Why in the news?
- Recently, The Government of India under NEP 2020 is promoting education in the Indian language especially in technical fields like engineering, medicine.
- A special programme, the “AICTE Technical Book Writing and Translation” project, provides textbooks in 12 planned Indian languages.
Council on Scientific and Technical Terminology (CSTT):
- About:
- It was established in 1961 to standardize scientific and technical terminology in the Indian language.
- It also publishes dictionaries, glossaries, and bilingual, trilingual, and multilingual monographs.
- It publishes quarterly magazines like Vigyan Garima Sindhu and Gyan Garima Sindhu.
- It cooperates with textbook courses and textbook boards for university textbooks.
- Creates terminology used by government departments, research agencies and state agencies.
- ‘Shabd’ Glossary Platform:
- CSTT’s online platform Shabd (https://shabd.education.gov.in) acts as a repository of technical and scientific terms in the Indian language.
- Includes dictionaries compiled by CSTT and external organizations, allowing users to search by language, topic, or genre.
- Launched in March 2024, it has 322 words covering 21,84,050 topic words in headlines.
- Standardization Process:
- Expert advisory committees composed of subject matter experts and linguists are fixed terms.
- These terms are recognized by organizations like NCERT, NTA, AICTE, Text Book Boards and others.
- The platform is highly accessible and has more than 136,968 hits worldwide.
- Terms & Disciplines Covered:
- The Shabd portal spans over 60 subjects including Humanities, Social Sciences, Medical Sciences, Engineering, and Agricultural Sciences.
- Disciplines include Journalism, Chemistry, Botany, Psychology, Civil and Electrical Engineering, Ayurveda, Agriculture, and more.
- Future Plans:
- CSTT aims to incorporate Artificial Intelligence (AI) and digital technologies to enhance terminology development, ensuring Indian languages keep pace with educational and technological advancements.
Source: TH
Neuromorphic Computing
Tags: GS-3, Science & Technology- IT & Computers
Why in the news?
- The researchers at the Indian Institute of Science (IISc) have recently developed a neuromorphic or brain-inspired analog computing that stores and processes data in 16,500 states using molecular film.
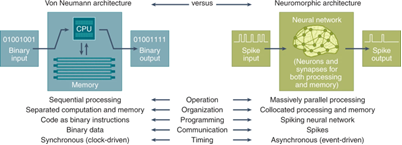
What is Neuromorphic Computing?
- About:
- Neuromorphic computing is designed to mimic the brain’s structure and functions, using artificial neurons and synapses.
- It shifts from binary computing to systems capable of learning from the environment.
- Working Mechanism:
- It employs Artificial Neural Networks (ANN) composed of artificial neurons that communicate via electric spikes, replicating brain-like processing through Spiking Neural Networks (SNN).
- This enables efficient tasks like visual recognition and data interpretation.
- Key Features:
- Brain-Inspired Design: Modeled after the neocortex for cognitive functions.
- Spiking Neural Networks: Utilizes electrical signals resembling biological neuron behavior.
- Memory-Processing Integration: Merges memory and computation for improved efficiency, unlike von Neumann architecture.
- Advantages:
- Enhances problem-solving, pattern recognition, and decision-making.
- Revolutionizes AI hardware, enabling advanced AI tasks on personal devices, bypassing data center limitations.
- Integration with Molecular Film:
- Molecular films improve performance by simulating brain-like parallel processing, storing data efficiently with 16,500 states, far surpassing binary systems.
- Differences from Traditional Computing:
- Parallel Processing: Processes multiple streams simultaneously.
- Energy Efficiency: Uses power only when needed, making it ideal for real-time data tasks.
- Analog vs. Binary: While binary operates with two states (0 or 1), neuromorphic systems behave like a dimmer switch, with a range of values.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q:1 With the present state of development, Artificial Intelligence can effectively do which of the following? (2020)
- Bring down electricity consumption in industrial units
- Create meaningful short stories and songs
- Disease diagnosis
- Text-to-Speech Conversion
- Wireless transmission of electrical energy
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1, 2, 3 and 5 only
- 1, 3 and 4 only
- 2, 4 and 5 only
- 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Ans: (b)
AL NAJAH V Military Exercise
Tags: GS-3, Science & Technology- Defence technology
Why in the news?
- Recently, the Indian Army contingent departed for the 5th edition of the India-Oman Joint Military Exercise AL NAJAH, to be held at Rabkoot Training Area in Salalah, Oman.
- About:
- The contingent comprises 60 personnel from a Mechanised Infantry Regiment and other support units.
- It is a biennial exercise alternating between India and Oman since 2015.
- Objective:
- To enhance the joint military capability of both sides in conducting counter-terrorism operations under Chapter VII of the UN Charter.
- The exercise will specifically concentrate on operations in desert environments.
- Other exercises between India and Oman:
- Navy exercise: Naseem-Al-Bahr
- Air Force: Eastern Bridge
Source: PIB
Rangeen Machhli App
Tags: GS-3, Economy- Growth & Development- Industry
Why in the news?
- Recently, the Union Minister for Fisheries, Animal Husbandry and Dairying has launched ‘Rangeen Machhli’ App.
- About App: ICAR-Central Institute of Freshwater Aquaculture Supported by the Prime Minister’s Fisheries Resource Programme.
- Purpose: Provides multilingual content on a popular topic Varieties of ornamental fish in eight Indian languages.
- Features: Hide nearby aquarium shops, and promote community To connect businesses and users with reliable resources decorating fish.
- Ornamental Fishing in India: They fish in bright colors, maintained in a limited water system.
- Native ornamental fishes: loaches, eels, barbs, catfish, and gobies, clownfish.
Source: PIB
State Finance Commission
Tags: GS-2, Polity & Governance- SFC
Why in the news?
- Recently, Kerala Cabinet cleared a proposal to constitute the seventh State Finance Commission.
About the State Finance Commission (SFC):
- Article 243I of the Constitution empowers the Governor of a State to establish a Finance Council every five years.
- Article 243I was introduced by the 73rd Constitution Amendment Act 1992 .
- It reviews the financial position of the Panchayats.
- Recommends principles of governance:
- Distribution between state and panchayats of net proceeds of state taxes
- Determination of taxes, duties, tolls and fees which may be assigned to Panchayats
- Grants-in-aid to Panchayats from State Consolidated Fund.
- Article 243Y provides that the SFC will do the same Recommendations for cities.
Source: TH
Salt Pans
Tags: GS-2, Economy- Growth & Development
Why in the news?
- Recently, The Centre approved transferring 256 acres of Mumbai’s salt pan land to Dharavi Redevelopment Project Pvt Ltd (DRPPL) for building rental houses for slum dwellers.
About Salt Pan land:
- About: These are low-lying areas where seawater flows in at specific times and leaves behind salts and other minerals.
- Regulation: According to the 2011 Coastal Regulation Zone (CRZ) report, environmentally sensitive desalination falls under the CRZ-1B category, which does not allow any economic activities except desalination and creation of air required
- Scale: In all, 5,378 acres of land in Mumbai have been designated as salt pan lands.
- Usage: They can be used for water collection and salt production. They can also support huge biodiversity.
- States: Andhra Pradesh (20,716 acres) has the highest such area, followed by Tamil Nadu (17,095 acres) and Maharashtra (12,662 acres).
- Environmental importance: Salt marsh along with mangroves prevents flooding and the city is home to a variety of birds and insects.
- Coastal Regulation Areas: Coastal land up to 500 meters above high tide level (HTL) and stage up to 100 meters along marine, estuaries, backwaters and river banks.
Source: IE
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are daily current affairs?
A: Daily current affairs refer to the most recent and relevant events, developments, and news stories that are happening around the world on a day-to-day basis. These can encompass a wide range of topics, including politics, economics, science, technology, sports, and more.
Q: Why is it important to stay updated with daily current affairs?
A: Staying updated with daily current affairs is crucial because it helps individuals make informed decisions in their personal and professional lives. It enables people to understand the world around them, stay aware of significant events, and engage in informed discussions about important issues.
Q: Where can I access daily current affairs information?
A: There are various sources for daily current affairs, including newspapers, news websites, television news broadcasts, radio programs, and dedicated apps or newsletters. Social media platforms are also widely used to share and access current affairs information.
Q: How can I effectively incorporate daily current affairs into my routine?
A: To incorporate daily current affairs into your routine, consider setting aside specific times each day to read or watch news updates. You can also subscribe to newsletters or follow news apps to receive curated content. Engaging in discussions with peers or participating in online forums can further enhance your understanding of current events.
Q: What are some tips for critical analysis of daily current affairs?
A: When analyzing daily current affairs, it’s essential to cross-reference information from multiple sources to ensure accuracy. Additionally, consider the source’s credibility and bias, if any. Develop the ability to identify the main points and implications of news stories, and critically evaluate the significance and impact of the events reported.
To get free counseling/support on UPSC preparation from expert mentors please call 9773890604
- Join our Main Telegram Channel and access PYQs, Current Affairs and UPSC Guidance for free – Edukemy for IAS
- Learn Economy for free- Economy for UPSC
- Learn CSAT – CSAT for UPSC
- Mains Answer Writing Practice-Mains Answer Writing
- For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here

