
Explore the dynamics of language origins and diffusion, considering the migration of speakers as a key factor. Languages often originate in specific geographic locations and spread to other areas as populations migrate. This process of diffusion shapes linguistic diversity and distribution worldwide. Within this context, language hotspots emerge as regions with high linguistic diversity and cultural significance. Conversely, endangered language hotspots represent areas where languages are at risk of extinction due to factors such as globalization, cultural assimilation, and language shift. By examining the interplay between migration patterns and language vitality, we gain insights into the complex dynamics of linguistic evolution and preservation. Delve into the intricacies of language hotspots and endangered language hotspots, illuminating their significance in understanding cultural heritage and linguistic diversity.
Contents
Answer:
Introduction:
Language hotspots are regions characterized by high linguistic diversity and the presence of numerous native languages. On the other hand, endangered language hotspots are areas where many languages are at risk of extinction due to various socio-economic, political, and environmental factors.
Body:
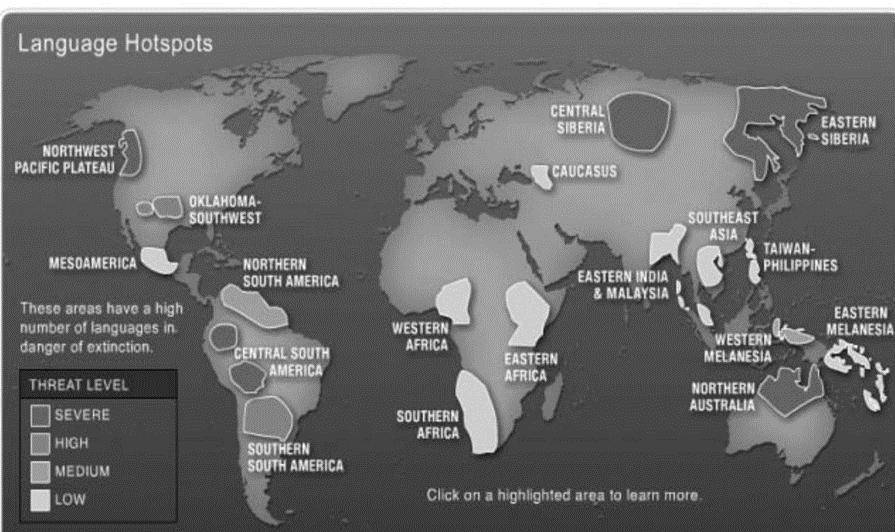
- The statement emphasizes the geographical aspect of language development, where languages originate in specific places and spread through the migration of speakers.
- Examples of language diffusion from language hotspots include the Bantu languages originating in West Africa and spreading across sub-Saharan Africa through migrations, leading to linguistic diversity.
- Similarly, the Austronesian language family, originating in Taiwan, diffused throughout Southeast Asia, the Pacific, and Madagascar via migrations and seafaring activities, contributing to linguistic diversity in these regions.
- In the context of endangered language hotspots, the statement reflects how external pressures lead to language endangerment as speakers shift to dominant languages. For instance, European colonization in North America led to the endangerment of indigenous languages due to forced migrations and assimilation policies.
- Endangered language hotspots like Oklahoma in the United States and Northeast India face challenges such as socio-economic changes, government policies, and rapid social shifts, contributing to language endangerment.
- Despite the challenges, efforts to revitalize and preserve endangered languages are underway, such as initiatives to preserve Navajo and Mohawk languages in North America.
- Language hotspots and endangered language hotspots provide insights into the factors shaping linguistic diversity and the urgent need for preservation efforts to maintain cultural heritage and linguistic richness.
- Understanding the dynamics of language diffusion and endangerment in these hotspots is crucial for devising effective strategies for language preservation and cultural sustainability.
Conclusion:
Language hotspots and endangered language hotspots serve as focal points for studying linguistic diversity and the challenges faced by endangered languages. Future efforts should prioritize linguistic preservation initiatives in these hotspots to safeguard cultural heritage and promote linguistic diversity globally.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here

