
In recent years, the Agriculture Export Policy has emerged as a pivotal instrument in shaping the trajectory of a nation’s agricultural economy. This policy not only underscores a government’s commitment to bolstering agricultural exports but also serves as a strategic roadmap for harnessing the sector’s potential to contribute to economic growth, employment generation, and rural development. By fostering an enabling environment through measures such as trade facilitation, infrastructure development, and market access, the Agriculture Export Policy aims to empower farmers and agribusinesses to tap into global markets, thereby enhancing their competitiveness and income levels. However, the effectiveness of such policies hinges not only on their formulation but also on their implementation and periodic review to address emerging challenges and capitalize on evolving opportunities in the dynamic global trade landscape.
Tags: Economy- GS Paper – 3, Agricultural Marketing — Direct & Indirect Farm Subsidies – Buffer Stocks & Food Security — Government Policies & Interventions
For Prelims: Minimum Export Price (MEP), Agriculture Export Policy,Food Security, Food Inflation, Operation Greens, SAMPADA, E-NAM, APEDA, Organic Farming
For Mains: About Agricultural Export Policy, Need for an Agri Export Policy in India, Challenges in Agri Export policy in India, Steps Ahead for a Stable Agri Policy in India.
Contents
- 1 What is Agricultural Export Policy?
- 2 UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
- 3 FAQs
- 3.1 Q: What is the Agriculture Export Policy (AEP)?
- 3.2 Q: What are the objectives of the Agriculture Export Policy?
- 3.3 Q: How does the Agriculture Export Policy benefit farmers?
- 3.4 Q: What measures are included in the Agriculture Export Policy to support exporters?
- 3.5 Q: How does the Agriculture Export Policy address sustainability and environmental concerns?
- 4 In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
Context:
- India’s agricultural export policy must shift from being restrictive to becoming stable and competitive.
What is Agricultural Export Policy?
About:
- The Agricultural Export Policy, or agri export policy, comprises governmental regulations and incentives aimed at governing and boosting the export of agricultural products from a specific country.
- It involves measures like export subsidies, tariff reductions, quality standards, market access agreements, financial incentives, and trade promotion initiatives.
Vision:
- In December 2018, the Government introduced a comprehensive Agricultural Export Policy with the goal of leveraging India’s agricultural export potential to establish global agricultural dominance and increase farmers’ income.
Objective:
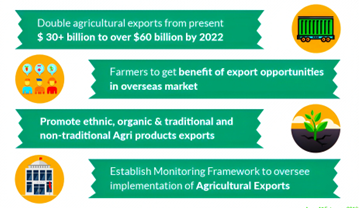
Elements:
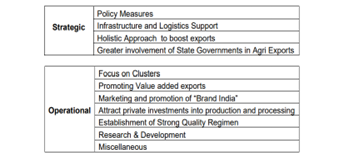
What is the Need for an Agri-Export Policy?
- Economic Impact: India’s agricultural export sector has been a significant contributor to total exports, with approximately USD 53 billion in agricultural and processed food products exported in fiscal year 2022-2023. However, India’s global share of agricultural exports was only 2.2% in 2016.
- Food Security: Despite supporting a substantial portion of the world’s population with limited resources, a well-planned export policy can generate additional revenue to reinvest in enhancing food security and increasing farmers’ income.
- Controlling Food Inflation: Agricultural exports can help stabilise domestic prices, benefiting both consumers and producers, especially during years of bumper harvests.
- Employment Generation: With around 45% of the workforce engaged in agriculture, promoting agricultural exports can create more job opportunities, particularly in rural areas where farming is predominant.
- Balance of Payments (BOP): Agricultural exports contribute significantly to India’s foreign exchange reserves, offsetting the trade deficit and maintaining currency stability.
- Crop Diversity: India’s production of various agricultural commodities presents substantial export potential, which can be harnessed through a well-structured export policy.
- Trade Relationships: Agricultural exports play a crucial role in building and strengthening trade relationships with countries like the United States, Saudi Arabia, and the United Arab Emirates.
- Structural Challenges: Addressing challenges such as low farm productivity, poor infrastructure, global price volatility, and market access can be tackled through the policy framework.
Challenges in India’s Agri Export Policy:
- Restrictive Export Policy: Policies favouring domestic consumers over farmers hinder meeting export targets. Like Basmati rice export restrictions, such as the MEP of USD 1,200, limit exports.
- Subsidy-Centric Schemes: Increased subsidies during election periods, like food and fertiliser subsidies, strain fiscal discipline. Populist measures like loan waivers and free power for farmers impact the financial health of the agricultural sector.
- Inadequate R&D Investment: Low investment in agriculture R&D, around 0.5% of agricultural GDP, hampers significant growth. Doubling or tripling R&D investment is crucial for India to excel in agricultural production and exports.
- Quality and Standards: Maintaining consistent quality and meeting international standards pose challenges. Variability in quality and compliance issues hinder exports, while meeting SPS Measures is difficult due to pests and diseases.
- Infrastructure: Inadequate infrastructure for storage, transportation, and processing results in post-harvest losses, diminishing export competitiveness.
- Environmental and Sustainability Concerns: Balancing increased exports with environmental sustainability is challenging. Over-exploitation of resources can lead to long-term consequences, necessitating careful management
Government Schemes to Promote Agri-Export in India:
- Operation Greens: Aims to stabilise supply and prices of essential agricultural commodities like fruits and vegetables. Reduces price volatility, ensures farmers receive fair prices, and fosters sustainable agri exports.Operation Greens received an allocation of INR 500 crores in the Union Budget 2023-2024.
- Market Access Initiative (MAI): Supports export promotion activities such as participation in trade fairs, capacity building, and market research. MAI has facilitated participation of Indian exporters in over 100 international trade fairs annually.
- Scheme for Agro-Marine Processing and Development of Agro-Processing Clusters (SAMPADA): Modernises infrastructure for agro-processing clusters, reducing post-harvest losses and increasing shelf life. SAMPADA received a budgetary allocation of INR 6,000 crores for the period 2020-2021 to 2024-2025.
- National Horticulture Mission (NHM): Promotes sustainable horticulture practices, including organic farming and precision farming. NHM has supported the establishment of over 100 Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs) for horticultural products and supports production of high-value horticultural products for export.
- E-NAM (National Agriculture Market): A pan-India electronic trading portal for agricultural commodities and enables farmers to sell directly to buyers, reducing intermediaries and ensuring fair prices. E-NAM has integrated 1,000 wholesale markets and 585 mandis across 18 states and 3 Union Territories.
- APEDA : Promotes export of scheduled products and provides guidelines for sustainability and quality. APEDA facilitated exports of agricultural products worth USD 22.17 billion during the financial year 2022-2023.
- Setting up of Agri Export Zones (AEZs): Provides infrastructure development and technology adoption for sustainable agri exports. AEZs have been established for commodities like mangoes, grapes, and spices, leading to increased export volumes.
- Promotion of Organic Farming: Initiatives to promote organic farming for environmental sustainability and increased export potential of organic products. The area under organic farming in India increased to 3.90 million hectares in 2022-2023, with exports of organic products totaling USD 1.04 billion.
Conclusion:
Hence, a stable agricultural export policy must exhibit dynamism, responsiveness, and adaptability to secure India’s continued growth in the global agricultural trade market. It should prioritise the long-term sustainability of agriculture, environmental responsibility, and the welfare of farmers while bolstering India’s position as a significant player in international agricultural trade.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q:1 In India, which of the following can be considered as public investment in agriculture? (2020)
- Fixing Minimum Support Price for agricultural produce of all crops
- Computerization of Primary Agricultural Credit Societies
- Social Capital development
- Free electricity supply to farmers
- Waiver of agricultural loans by the banking system
- Setting up of cold storage facilities by the governments
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 5 only
(b) 1, 3, and 4 and 5 only
(c) 2, 3 and 6 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6
Ans:C
Q:2 What is/are the advantages/advantages of implementing the ‘National Agriculture Market’ scheme? (2017)
- It is a pan-India electronic trading portal for agricultural commodities.
- It provides the farmers access to nationwide markets, with prices commensurate with the quality of their produce.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither1 nor 2
Ans: C
Mains
Q:1 What are the main constraints in transport and marketing of agricultural produce in India? (2020)
FAQs
Q: What is the Agriculture Export Policy (AEP)?
The Agriculture Export Policy (AEP) is a comprehensive framework established by governments to promote and facilitate the export of agricultural products. It encompasses various strategies and initiatives aimed at enhancing the competitiveness of farmers and agribusinesses in the global market.
Q: What are the objectives of the Agriculture Export Policy?
The primary objectives of the Agriculture Export Policy are to increase agricultural exports, diversify export destinations, promote value addition in agriculture, create employment opportunities in rural areas, and integrate farmers and agricultural producers into global value chains.
Q: How does the Agriculture Export Policy benefit farmers?
The Agriculture Export Policy benefits farmers by providing them with access to larger markets beyond domestic borders, thereby increasing demand for their produce and potentially leading to higher incomes. Additionally, it encourages value addition and quality improvement, enabling farmers to command better prices for their products.
Q: What measures are included in the Agriculture Export Policy to support exporters?
The Agriculture Export Policy typically includes measures such as trade facilitation, infrastructure development, financial assistance, market access initiatives, promotion of agricultural exports through branding and marketing, and policy reforms to reduce trade barriers and streamline export procedures.
Q: How does the Agriculture Export Policy address sustainability and environmental concerns?
Many Agriculture Export Policies incorporate provisions to promote sustainable agricultural practices, including organic farming, water conservation, soil health management, and biodiversity conservation. By encouraging sustainable production methods, these policies aim to ensure the long-term viability of agricultural exports while minimizing negative environmental impacts.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here

