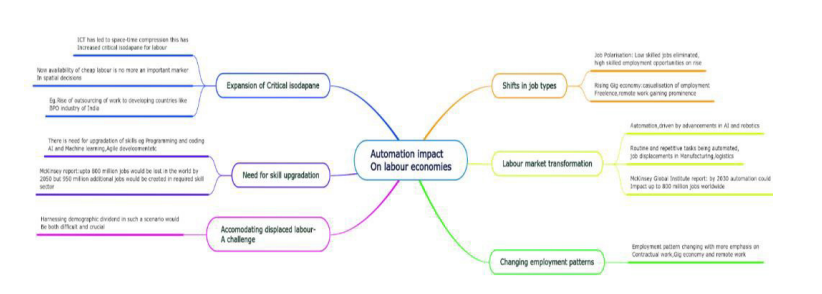
In the contemporary landscape of global economies, the swift advancement of automation is ushering in a transformative era, reshaping the dynamics of labor and exerting profound influence on trade patterns. As technology continues to evolve at an unprecedented pace, industries are increasingly integrating automated systems and artificial intelligence to streamline processes and enhance efficiency. This inexorable march toward automation not only alters the traditional landscape of human labor but also promises far-reaching implications for global trade. The profound impact of automation on economies is not merely a localized phenomenon; rather, it stands as a formidable force poised to redefine the very nature of work and trade relationships on a global scale. Understanding the multifaceted effects of automation is crucial for policymakers, businesses, and individuals alike as they navigate the complex terrain of this paradigm shift.
Contents
Answer
While automation boosts economic growth, creates jobs, and improves living standards, it can also present serious challenges for the labor market and will also have a profound impact on global trade patterns.
Reshoring and Nearshoring
- Due to the reduced need for low-wage labor, companies are bringing manufacturing processes closer to home or “restoring”, impacting global supply chains and trade routes.
- For eg. The United States has nearshored a significant amount of its manufacturing production to Mexico in recent years. This has led to a decrease in US imports of manufactured goods from China and an increase in US imports of manufactured goods from Mexico.

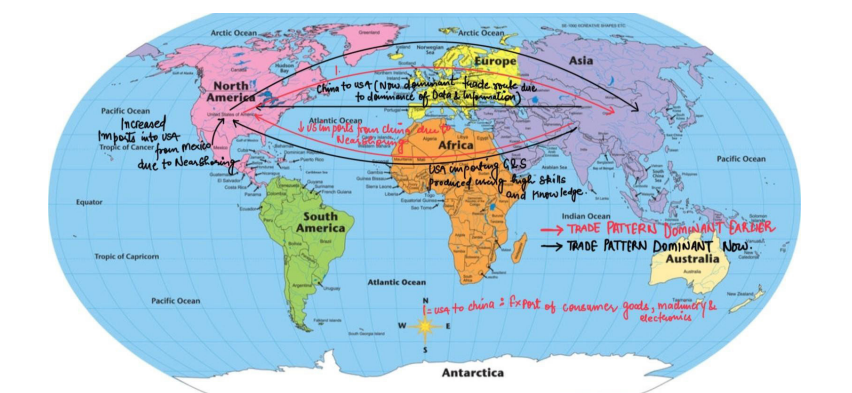
Shifts in Trade Patterns Towards Data and Information
- Trade patterns move from being consumer goods oriented to more data and information oriented eg. From{United States to China(Earlier Dominant)}: Consumer goods, electronics, machinery to {China to the United States(Now Dominant): Data and information}.
Skills-Based Trade Impacting Trade Pattern
- Trade patterns may increasingly align with skills-based and knowledge-based industries, where countries with highly educated and skilled workforce are better positioned to compete.
- For eg. The United States is increasingly importing goods and services that are produced using high levels of skill and knowledge from countries such as India and China.
E-commerce and Changes in Global Trade patterns
- E-commerce giants like Amazon, and Alibaba are increasingly shaping the direction of global trade patterns
- For eg. China, the world’s largest exporter of e-commerce goods, and also a major importer of e-commerce goods and services, growth of e-commerce led to an increase in Chinese imports of goods from the United States, as US e-commerce companies have become increasingly popular among Chinese consumers.
Therefore, automation is not only changing how work is done but also influencing the structure of economies and trade patterns. It has the potential to disrupt traditional industries, create new economic opportunities, and reshape global trade dynamics.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here