

Biotechnology is “the integration of natural sciences and engineering sciences in order to achieve the application of organisms, cells, parts thereof and molecular analogs for products and services.” The term biotechnology was first used by Károly Ereky in 1919, meaning the production of products from raw materials with the aid of living organisms.
Contents
- 0.1 Concept of Biotechnology
- 0.2 Origin and Development
- 0.3 Principles Of Biotechnology
- 0.4 Types Of Biotechnology
- 0.5 Colour Classification of Branches of Biotechnology:
- 0.6 Biotechnology in India
- 0.7 Applications Of Biotechnology In Various Fields
- 0.8 Applications Of Biotechnology In Agriculture
- 0.9 Application Of Biotechnology In the Environment
- 1 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Concept of Biotechnology
It is an advanced technology that comprises techniques for utilizing living organisms or their body parts to create or develop new products. For instance, baking bread using yeast or making yogurt with the help of lactic acid bacteria comes under biotechnology.
These traditional methods utilize living organisms in their original or developed form. In contrast, modern biotechnology uses a more modified form of them. Moreover, it deals with biological and biopharmaceutical productions on an industrial scale.
Origin and Development
Modern biotechnology is a biotechnology practice developed with genetic manipulation technique, in which the transfer of genetic material(transfer of gene) from one living organism to the other occurs. Through this technique, humans can control production according to their desires. For example, the production of pest and disease-resistant plants, imperishable fruits, and cattle which can produce more milk.
In the genetic manipulation process, organisms whose bodies contain foreign genes are called transgenic organisms. They can be transgenic plants, transgenic animals, and transgenic bacteria.
- Biotechnology is a technology that utilizes biological systems, living organisms, or parts of these to develop or create different products.
- Brewing and baking bread are examples of processes that fall within the concept of biotechnology (use of yeast (= living organism) to produce the desired product).
- Such traditional processes usually utilize the living organisms in their natural form (or further developed by breeding), while the more modern form of biotechnology will generally involve a more advanced modification of the biological system or organism.
- With the development of genetic engineering in the 1970s, research in biotechnology (and other related areas such as medicine, biology, etc.) developed rapidly because of the new possibility to make changes in the organisms’ genetic material (DNA).
- Biotechnology deals with industrial-scale production of biopharmaceuticals and biologicals using genetically modified microbes, fungi, plants, and animals.
- The applications of biotechnology include therapeutics, diagnostics, genetically modified crops for agriculture, processed food, bioremediation, waste treatment, and energy production.
Principles Of Biotechnology
Biotechnology deals with large-scale production and marketing of products and processes using live organisms, cells, or enzymes. Modern biotechnology using genetically modified organisms was made possible only when man learned to alter the chemistry of DNA and construct recombinant DNA.
1. Genetic Engineering:
The principle of genetic engineering is to manipulate and modify the genetic material of an organism to incorporate desirable traits. Recombinant DNA technology is the main pillar of genetic engineering.
Recombinant DNA Technology is a technique to alter the genes of an organism. The desired gene is inserted into the host using recombinant DNA technology. The host shows the desired trait phenotypically, which is governed by the inserted gene.
The recombinant DNA technology involves the following main steps:
- Selection of the desired gene
- Selection of vector for the transfer of the gene known as a cloning vector, e.g. plasmid
- Insertion of recombinant DNA into the host
- Maintaining the introduced DNA in the host so that it is passed on to the next generation
Recombinant DNA Technology requires various tools like vectors, hosts, and enzymes such as restriction enzymes, ligases, polymerases, etc.
Process
- Restriction enzymes are known as molecular scissors that cut the desired sequence of DNA.
- This DNA is then ligated into the vector with the help of ligases before inserting it into the host organism.
- The DNA-vector combination is known as the Recombinant DNA which is then transformed into the host.
- This recombinant DNA along with the foreign DNA gets multiplied within the host.
- It is then provided with optimum conditions to induce the expression of the target protein. This protein is known as the recombinant protein.
- Many genetically modified crops are produced using this technology, e.g. Bt cotton, a pest-resistant variety of cotton.
It technique to alter the chemistry of genetic material to introduce it into the host organism and thus change the phenotype of an organism
(NOTE: The genotype is a set of genes in DNA responsible for unique traits or characteristics while the phenotype is the physical appearance or characteristic of an organism.)
2. Bioprocess Engineering:
Maintenance of sterile (microbial contamination-free) ambiance in chemical engineering processes to enable the growth of only the desired microbe/eukaryotic cell in large quantities for the manufacture of biotechnological products like antibiotics, vaccines, enzymes, etc.
Modern biotechnology is responsible for the advancement of the pharmaceutical industry. It helped in the production and storage of products like antibiotics, enzymes, vaccines, etc. on a large scale.
A large amount of culture can be obtained by carrying out the multiplication of organisms in the bioreactors under sterile and optimum conditions. We get a higher yield of the required product using bioprocess engineering.
Process
- The host organism containing the rDNA is cultured in a sterile bioreactor by providing suitable growth conditions. The products formed are either released in the growth medium or accumulated inside the cells
- The obtained products are subjected to a series of processes before being marketed.
- The products are purified by a process called downstream processing and formulated by various processes.
- The product undergoes a strict quality check before it is subjected to further trials.
The modern processes in biotechnology are used for human welfare and have a significant impact on our lives. The products have greatly enhanced various medicines and food production. Extensive research is going on in this field to combat various diseases and improve quality of life.
Types Of Biotechnology
Biotechnology is the use of biological systems found in organisms or the use of the living organisms themselves to make technological advances and adapt those technologies to various fields.
Colour Classification of Branches of Biotechnology:
The concept of “color classification” in biotechnology is not a standard or widely recognized term within the field. Biotechnology is a broad interdisciplinary field that utilizes biological processes, organisms, or systems to develop or create products and technologies that benefit various sectors, including medicine, agriculture, the environment, and industry.
However, if you are referring to the classification of biotechnology based on color-coded areas of application or research focus, it is essential to note that such a classification does not exist in any formal scientific context. Biotechnology is commonly classified based on its applications and techniques rather than color-coding.
Typically, biotechnology can be categorized into several areas based on its applications:
- Medical Biotechnology: This area involves the use of biotechnological techniques to develop pharmaceuticals, diagnostics, gene therapy, and medical devices for improving human health and treating diseases.
- Agricultural Biotechnology: Agricultural biotechnology applies biotechnological methods to enhance crop production, develop genetically modified organisms (GMOs), and improve food security and agricultural sustainability.
- Industrial Biotechnology: Industrial biotechnology focuses on using biological processes to produce chemicals, enzymes, biofuels, and other industrial products in an environmentally friendly and sustainable manner.
- Environmental Biotechnology: Environmental biotechnology deals with using biological processes to remediate polluted environments, treat wastewater, and address other environmental challenges.
- Marine Biotechnology: This area explores the use of marine organisms and resources for various applications, including medicine, food, and biotechnology.
- Bioinformatics: Bioinformatics combines biology, computer science, and mathematics to analyze and interpret biological data, such as genomics and proteomics.
- Synthetic Biology: Synthetic biology involves designing and constructing new biological systems and organisms for specific purposes using genetic engineering and other techniques.
- Nanobiotechnology: Nanobiotechnology combines nanotechnology with biotechnology to develop novel materials and devices for medical, environmental, and industrial applications.
These classifications are not color-coded but represent the diverse range of applications and research areas within the field of biotechnology. Remember that the field of biotechnology is continually evolving, and new subfields and interdisciplinary approaches emerge as technology advances and scientific knowledge expands.
Gold Biotechnology
- Bioinformatics: Computational Biology à addresses biological problems using computational techniques.
Red Biotechnology:
- Biopharma à relates to medicine and veterinary products.
White Biotechnology:
- Industrial Biotech à to design more energy-efficient, low-resource-consuming products.
Yellow Biotechnology:
- Biotech in the Food Industry.
Grey Biotechnology:
- Environmental applications to maintain Biodiversity.
Green Biotechnology:
- Emphasizes Agriculture interests.
Blue Biotechnology:
- based on the use of marine resources.
Violet Biotechnology:
- deals with law, ethical, and philosophical issues of biotechnology.
Dark Biotechnology:
- associated with bioterrorism and biological weapons.
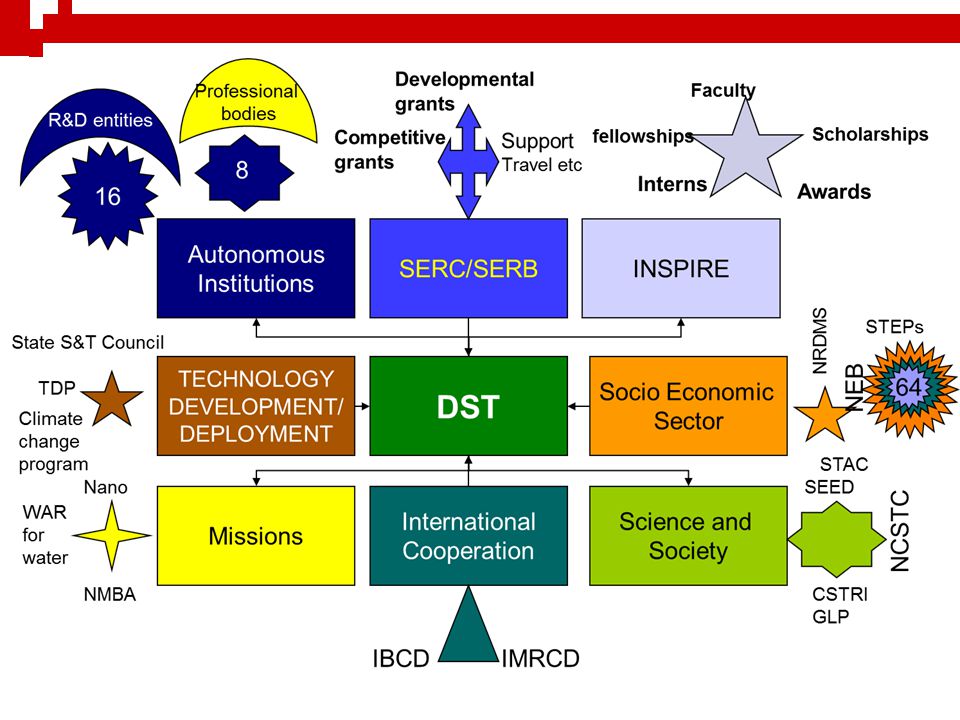
Biotechnology in India
The Department of Biotechnology under the Ministry of Science and Technology administers most programs of the biotechnology sector in India. Its objectives are as follows:
- Provide resources, infrastructure, and services in research areas.
- Implement biosafety guidelines for recombinant DNA products and genetically tweaked organisms.
- Conduct programs based on biotechnology to benefit society.
- Build an information network in the national and international scientific community for India’s Bioinformatics mission.
Besides, India’s Genetic Engineering Appraisal Committee (GEAC) works under India’s Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEF&CC). It is responsible for administering activities regarding dangerous recombinants and microorganisms in industrial production and research centers.
Department of Biotechnology (DBT)
The remarkable march of India into the world of biosciences and technological advances began in 1986, when a separate Department for Biotechnology, within the Ministry of Science and Technology, Government of India was created.
The first autonomous institute, the National Institute of Immunology which was set up in 1981 was brought under the wings of DBT. Soon after, it was joined by the National Facility for Animal Tissue and Cell Culture of Pune formed in 1986 which was later christened the National Centre for Cell Science. The late 1990s and early 2000 saw many other institutes like The National Institute for Plant Genome Research (NIPGR), the National Brain Research Centre (NBRC), the Centre for DNA Fingerprinting & Diagnostics, the Institute of Bioresources and Sustainable Development and the Institute of Life Sciences take shape. Subsequently, several other prominent institutes like the Translational Health Science and Technology Institute (THISTI), Institute for Stem Cell Biology and Regenerative Medicine (INstem), National Agri-Food Biotechnology Institute (NABI) at Mohali, and the National Institute of Biomedical Genomics (NIBMG) at Kalyani in West Bengal were established.
National Biotechnology Development Strategy
In the year 2015, DBT announced, “The National Biotechnology Development Strategy-2015-2020” (hereinafter referred to as ‘Strategy-II’), which was framed after wider consultation with stakeholders. Strategy II was seamlessly built on the earlier Strategy to accelerate the pace of growth of the biotechnology sector at par with global requirements.
Major Initiatives of the National Biotechnology Development Strategy 2015-2020
- Launch four major missions in healthcare, food and nutrition, clean energy, and education
- Create a technology development and translation network across India with global partnership, including 5 new clusters, 40 biotech incubators, 150 TTOs, and 20 bio-connect centers
- Ensure strategic and focused investment in building human capital by setting up a Life Sciences and Biotechnology Education Council
Applications Of Biotechnology In Various Fields
Biotechnology has made significant contributions in various fields, revolutionizing industries and improving our lives. Here are some applications of biotechnology in different sectors:
Forensics and Biometrics:
- DNA Profiling: Biotechnology-based techniques like DNA fingerprinting are employed in forensic investigations for identifying individuals, resolving paternity disputes, and criminal justice purposes.
- Biometric Identification: Biotechnology plays a role in biometric identification systems, such as fingerprint recognition, iris scanning, and facial recognition, used for security and access control.
Applications Of Biotechnology In Medicine
Medicine and Healthcare:
- Biotechnology techniques are used in medicine for the diagnosis and treatment of different diseases. It gives opportunities for people to protect themselves from dangerous diseases.
- In the field of Biotechnology, genetic engineering has introduced techniques like gene therapy, recombinant DNA technology, and polymerase chain reaction which use genes and DNA molecules to diagnose diseases and insert new and healthy genes in the body which replace the damaged cells
- Genetic modification in mosquitoes can solve the problems of epidemic diseases such as dengue and malaria
- Artificial insemination is the artificial introduction of semen into the reproductive tract of a female animal. It is used extensively in breeding animals, such as sheep and cattle
- Medical researchers believe that stem cell therapy has the potential to dramatically change the treatment of human diseases. Several adult stem cell therapies already exist, particularly bone marrow transplants that are used to treat leukemia.
- Stem cell transplantation was first used in the treatment of blood disorders and it was a breakthrough. Conventionally known as bone marrow transplantation, the stem cells responsible for the production of the blood cells reside in the bone marrow
Pharmaceutical Production:
- Biotechnology plays a crucial role in the development and production of therapeutic drugs, including biologics such as vaccines, antibodies, and recombinant proteins.
Gene Therapy:
- Biotechnology enables the modification or replacement of faulty genes in individuals, potentially treating genetic disorders and diseases.
Diagnostic Tools:
- Biotechnological advancements have led to the development of highly sensitive and specific diagnostic tests, such as DNA sequencing and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assays.
Tissue Engineering:
- Biotechnology allows the creation of artificial organs and tissues for transplantation, promoting advancements in regenerative medicine.
Applications Of Biotechnology In Agriculture
Agriculture and Food Production:
- Biotechnology has played a major role in agriculture by altering genes, studying and cloning various crops to provide better quality products of foods ultimately improving our lives.
- Hybrid Seeds, Artificial Seeds, Photosynthesis improvers, Stress-resistant crops and plants, Biofertilizers, and Bio-pesticides are some of the potential applications.
- Potential advantages that biotechnology can confer across a wide range of agricultural applications are in areas such as livestock management, storage of agricultural products, and sustaining current crop yields while reducing the use of fertilizers, herbicides, and pesticides.
- Biotechnology offers a very promising alternative to synthetic foods and an improvement on conventional plant-breeding technologies. Combined with other advanced agricultural technologies, it offers an exciting and environmentally responsible way to meet consumer demand for sustainable agriculture.
Genetically Modified Crops:
- Biotechnology helps in the development of genetically modified (GM) crops with enhanced traits, such as increased resistance to pests, diseases, or environmental stresses, leading to improved yields and reduced pesticide usage.
Crop Improvement:
- Biotechnology facilitates the breeding of plants with desirable traits through methods like marker-assisted selection, which accelerates the development of new crop varieties.
Food Processing:
- Enzymes produced through biotechnology are used in food processing to enhance flavors, improve nutritional value, and increase shelf life.
Industrial Applications:
Enzyme Production:
- Biotechnology allows the large-scale production of enzymes for various industrial applications, including detergent manufacturing, textiles, and biofuels.
Bioplastics:
- Biotechnology enables the development of biodegradable and renewable plastics as alternatives to traditional petroleum-based plastics, reducing environmental impact.
Industrial Fermentation:
- Biotechnological processes like fermentation are used to produce a wide range of products, such as bio-based chemicals, vitamins, amino acids, and enzymes.
Applications Of Biotechnology In Animal Husbandry
- The application of biotechnology in this area, in increasing production efficiency through manipulation and control of physiological systems and improving the health and well-being of animals, assumes great significance.
- Embryo transplantation, used with cattle, goats, pigs, and sheep, aims to increase the number of offspring from a quality female.
- Cloning embryos to artificially produce genetic duplicates of an animal has also become possible.
- Direct manipulation and alteration of an animal’s genetic material— genetic engineering—has the potential to produce even more drastic changes in animal breeding. It is believed that genetically altered pigs may one day be able to provide compatible organs for emergency transplantation (xenotransplantation) into humans.
Application Of Biotechnology In Food Processing
- Biotechnology has a major application in the food sector.
- Bread, cheese, wine, beer, yogurt, and vinegar are all made by culturing microorganisms and are the oldest products of biotechnology.
- It helps in improving the edibility, texture, and storage of the food; and in preventing the attack of the food, mainly dairy, by the virus-like bacteriophage.
- Biotechnologists are also developing tests that will allow the detection of food-contaminating microorganisms and the toxins they produce, which may be present only in minute quantities.
- Biotechnology also has applications in the detection of mutagens (substances that cause genetic mutations) in individual food products.
- GM crops that have been approved for use in food items in select countries include corn, maize, soya, tomato, potato, and papaya.
- Latest innovations in biotechnology that fortify major staples with micronutrients like vitamin A, zinc, and iron can be game changers for the hunger problem in India.
Application Of Biotechnology In the Environment
Environmental Conservation:
Bioremediation:
Biotechnology offers solutions for cleaning up environmental contaminants using living organisms or their products to degrade or remove pollutants from soil, water, and air.
Biofuels:
Biotechnology enables the production of biofuels, such as ethanol and biodiesel, from renewable sources like crops and algae, offering a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels.
Waste Management:
Biotechnological processes can be employed to treat and convert waste materials into useful products, such as composting organic waste or generating biogas from anaerobic digestion.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What is biotechnology, and how does it contribute to various sectors?
Answer: Biotechnology is a multidisciplinary field that involves the use of living organisms, cells, and biological systems to develop products and technologies that benefit various sectors. It encompasses areas such as genetic engineering, molecular biology, bioinformatics, and more. Biotechnology contributes significantly to agriculture (through genetically modified crops), medicine (gene therapy, vaccines), industry (enzyme production, biofuels), and environmental management.
Q: Explain the significance of CRISPR-Cas9 technology in biotechnology.
Answer: CRISPR-Cas9 is a revolutionary gene-editing tool that allows precise modification of DNA in living organisms. The technology has significant implications in biotechnology, offering precise and targeted gene editing capabilities. Its applications include gene therapy to treat genetic disorders, creating genetically modified organisms, and studying gene function. CRISPR-Cas9 has opened up new possibilities for advancements in healthcare, agriculture, and various other fields.
Q: Discuss the ethical concerns associated with biotechnological advancements.
Answer: Biotechnological advancements raise ethical concerns related to issues such as genetic engineering, cloning, and gene editing. The ability to modify genes in humans, animals, and plants raises questions about the potential for unintended consequences, ethical use of technology, and the impact on biodiversity. Striking a balance between the benefits of biotechnology and its ethical implications is crucial. Regulatory frameworks and guidelines are necessary to ensure responsible and ethical practices in the field of biotechnology.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here
Visit our YouTube Channel – here

