The Forest Rights Act (FRA), enacted in 2006, stands as a pivotal legislation in India, aimed at recognizing and restoring the rights of local forest-dwelling communities. Its implementation has ushered in a transformative era for these communities, altering the dynamics of their relationship with the forests they inhabit. The FRA seeks to address historical injustices by granting legal recognition to the traditional rights and livelihoods of marginalized forest dwellers. This legislation not only marks a significant departure from earlier conservation-centric policies but also endeavors to strike a balance between ecological preservation and the socio-economic well-being of local communities. As we delve into the impact of the Forest Rights Act, it becomes evident that its implications are far-reaching, influencing the lives, cultures, and futures of the local forest communities across the diverse landscapes of India.
Contents
Answer
The Forest Rights Act (FRA) of 2006 is a landmark legislation aimed at addressing historical injustices and recognizing the rights of local forest communities. It has not only recognized the rights of these communities but has also influenced their relationship with forest resources and the environment.
The impact of the Forest Rights Act, on the local forest communities is as follows:
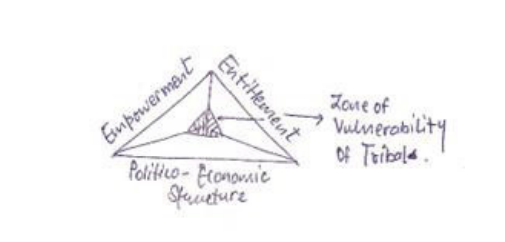
- Promoted “spatial justice”
- FRA shifted the power dynamics in favour of local forest communities by empowering Gram Sabhas to make decisions about forest management and land use -Promoted better forest governance.
- Helped in preserving Ecosystem services by Joint Forest Management (JFM)
- Local communities gained legal rights over forests, and become more committed to conservation efforts
- For e.g. The Kani tribal community in Kerala, played a significant role in protecting the biodiversity of the Agasthyamalai Biosphere Reserve after securing their rights under FRA.
- Promoted local growth foci (RP Mishra model) in the region
- FRA has enhanced the livelihoods of local communities by providing access to forest resources.
- Reduced their dependency on seasonal migration to urban areas thus promoting diffused and sustainable urbanisation
- For e.g. In the Mendha Lekha village in Maharashtra, the FRA rights recognition has led to improved income from the sale of non-timber forest produce and reduced out-migration.
- Reinforced the “place identity” (Yi-FuTuan)
- It focuses on the cultural and emotional connections people have with their surroundings.
- FRA has helped in preserving the cultural and spatial identities of forest communities.
- It recognizes the importance of forests in the cultural identity of these communities.
- For e.g. The Dongria Kondh tribe in the Niyamgiri Hills of Odisha continues to practice their cultural rituals and protect their sacred groves after securing forest rights.

However, there have been many challenges in FRA as well, such as:
- Implementation challenges include delays in processing claims, inadequate awareness among forest communities, and bureaucratic hurdles.
- Potential conflicts between forest rights and conservation goals, especially in protected areas.
- For e.g., Conflict between The Dongria Kondh tribe of the Niyamgiri Hills of Odisha and Vedanta resources.
- Mistrust from the Forest Department results in conflicts.
- Certain marginalized forest communities, such as nomadic and pastoralist groups, have not been effectively covered under the FRA.
Establishing a dedicated Forest Rights Commission to oversee the implementation of the FRA and to address the grievances of forest-dwelling communities, increasing the budget for the implementation of the FRA, and amending the FRA to address any loopholes that may be exploited by vested interests can be a good way forward.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here