Welcome to our monthly current affairs update for August 2023. In this ever-changing world, staying informed about the latest events, trends, and developments is crucial. This month, we’ll take you on a journey through the most significant and noteworthy happenings across the globe. From politics to technology, from culture to the environment, we’ll cover it all. Join us as we explore the stories shaping our world and the issues that demand our attention. Our goal is to provide you with a concise and insightful overview of the events that are shaping our times, enabling you to engage in informed conversations and make well-informed decisions. So, without further ado, let’s dive into the whirlwind of current affairs for this month.
Contents
- 1 Rural India shift to sugars and processed foods
- 2 Advisory Board on Banking and Financial Frauds
- 3 Concerns Over Consuming Ultra-Processed Food
- 4 Future of Work Report- AI at Work
- 5 First ABDM Microsite
- 6 Scientific Authenticity of Nano Liquid Urea
- 7 India’s Ageing Workforce
- 8 20th ASEAN-India Economic Ministers’ Meeting
- 9 Rail-Sea-Rail (RSR) Initiative
- 10 Advisory board on bank frauds
- 11 Market Coupling
- 12 RBI’s Public Tech Platform for Frictionless Credit
- 13 Reforms for Secure Digital Connectivity
- 14 Bharat New Car Assessment Programme (Bharat NCAP)
- 15 Infrastructure Debt Fund-NBFCs (IDF-NBFCs)
- 16 Amitabh Kant Committee recommendation on stalled housing projects
- 17 India has started manufacturing 38 APIs
- 18 RBI’s State of the Economy report
- 19 Indian Pharmacopoeia Recognition in Suriname
- 20 Remittances to India
- 21 Investor Education and Protection Fund Authority (IEPFA)
- 22 New Soil Health Card Scheme
- 23 IMF Quota Review
- 24 RBI launches new features for UPI
- 25 Deflation
- 26 CAG Report on Railway Finance
- 27 National Policy on Official Statistics
- 28 Fertilizer Availability and Local Production
- 29 Mission Indradhanush
- 30 Tidal energy potential
- 31 Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB-PMJAY)
- 32 Excess cane payments
- 33 India’s Strategic Petroleum Reserves
- 34 Bharat Net Project
- 35 Revised Good Manufacturing Practices Standards
- 36 Bhu-Vision
- 37 Rajmargyatra
- 38 G20 Principles for Financing Cities of Tomorrow
- 39 Gross Fixed Capital Formation (GFCF)
- 40 Schemes for Farmers’ Welfare
- 41 Gross Fixed Capital Formation
- 42 MSME CARD
- 43 Akhil Bharatiya Shiksha Samagam and ULLAS Initiative
- 44 Self-Reliant India Fund for MSMEs
- 45 Barrier to Women’s Labor Force Participation
- 46 Corporate Debt Market Development Fund
- 47 RBI’s Digital Payments Index (RBI-DPI)
- 48 Resource Efficiency Circular Economy Industry Coalition
- 49 Vivad se Vishwas 2.0
- 50 Maharatna and Navratna category
- 51 Restrictions on the import of electronic devices
- 52 GOBARdhan Initiative
- 53 Odisha Millets Mission (OMM)
- 54 Mahila Samman Savings Certificate Scheme (MSSC)
- 55 Urea Gold
- 56 FAQs on Monthly Current Affairs – August 2023
- 56.1 Q1: What are monthly current affairs?
- 56.2 Q2: Why are monthly current affairs important?
- 56.3 Q3: What are the key events and developments related to polity and governance that I should be aware of this month?
- 56.4 Q4: How can I better understand the implications of monthly political developments on governance and policy?
- 57 In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
Rural India shift to sugars and processed foods
In News:
ICRISAT deliberates on challenges in accessing Nutrient-Rich Foods and promotion of Processed Foods
About Rural India shift to sugars and processed foods
- The International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics (ICRISAT) has recently conducted research highlighting the shift in dietary preferences among rural Indian families.
- The study reveals that carbohydrates and sugary processed foods are being favoured over protein and micronutrient-rich options.
- In this regard, the ICRISAT report aims to present more solutions to address these dietary shifts and promote better nutrition outcomes in rural India.
Key highlights:
- Traditional food systems in rural India are undergoing changes due to accessibility issues and limited availability of protein and micronutrient-rich foods.
- Rural households are increasingly favouring carbohydrates and sugary processed foods over protein and nutrient-rich options.
- Limited access to protein and micronutrient-rich foods is driving this shift, as these options are becoming harder to source.
- Traditional food systems are evolving due to difficulties in accessing nutritious foods and the declining availability of wild fruits and forest-sourced foods.
- People migrating from rural to urban areas are exposed to packaged and processed foods due to widespread promotions, leading to changes in dietary choices.
- The shift towards sugars and processed foods is linked to rising concerns about malnutrition and obesity in rural regions.
- Policy measures are needed to strengthen nutrition-sensitive food supply chains with the food processing industry to make nutritious products more appealing and accessible.
- The study highlights the role of traditional farming practices and local markets in providing access to healthier food options.
- The study’s findings are particularly relevant due to regional imbalances in nutritional health, with higher rates of stunting observed in rural areas.
- Balancing regional nutritional disparities remains a critical endeavour for India’s overall health and well-being.
- Overall, ICRISAT research highlights the need for policy measures needed to prioritize nutrition-sensitive food supply chains and promote awareness about healthy dietary choices in rural India.
Advisory Board on Banking and Financial Frauds
In News:
Central Vigilance Commission reconstitutes Advisory board on Bank Frauds
About Advisory Board on Banking and Financial Frauds
- The Central Vigilance Commission (CVC) has recently reconstituted the advisory board on Banking and Financial Frauds (ABBFF) to examine bank frauds before involving investigative agencies.
- It will be a five membered board headquartered in New Delhi with Suresh N Patel, the former Central Vigilance Commissioner as Chairman and four other members including:
- Ravikant (retired IAS officer), Rajnikant Mishra (former Director General, BSF), David Rasquinha (former MD of Exim Bank), Partha Pratim Sengupta (former MD & CEO of Indian Overseas Bank).
- Each member will have a tenure of Two years from joining date in accordance with the Central Vigilance Commission order.
- The board will examine officials’ role in public sector banks, insurance companies, and financial institutions for frauds of ₹3 crore and above.
- Institutions will have to refer such fraud cases to ABBFF before initiating criminal investigation and its advice on officials’ involvement in criminality/malafide will be considered by competent authority.
- ABBFF will be authorised to analyse financial system frauds and provide inputs for fraud-related policy formulation to RBI and CVC within a month of initial reference.
- However, CVC can reject Indian Banks Association’s proposal for a sunset clause, preventing action against bankers for credit decisions after a set period.
- It is aimed at strengthening fraud risk management mechanisms by collaborative effort of Government, RBI, and public sector banks.
- It will also help address recovery actions for loan frauds including legal actions, debt recovery tribunals, SARFAESI law, insolvency cases, and settlements.
- Overall, the CVC’s reconstituted ABBFF will go a long way to enhance scrutiny of bank fraud cases and provide expert advice to prevent and address fraudulent activities in the financial sector.
Enforcement Directorate (ED) Data:
- ED has recorded 757 bank fraud cases under PMLA in the past decade, including 36 cases in the current year.
- Nearly 10 cases involved individuals fleeing the country, 6 declared as fugitive economic offenders while 7 as proclaimed offenders.
- ED has confiscated assets worth ₹15,805.91 crore and restituted ₹15,113 crore to Public Sector Banks(PSBs).
Concerns Over Consuming Ultra-Processed Food
In News:
According to a recent WHO report India’s ultra-processed food sector grew at a compound annual growth rate of 13.37 percent in retail sales value from 2011 to 2021, a report by the World Health Organization.
About Ultra Processed Food
- Processed foods often contain additional salt, sugar, and fats, and when a food product undergoes considerable alteration by incorporating five or more supplementary ingredients, it falls into the category of ultra-processed foods.
- These extra components generally consist of enhancers for flavor and taste, emulsifiers, and various colors, all intended to extend shelf life, enhance taste, or increase the convenience of consumption.
- For example, raw atta represents an unprocessed state. When salt and sugar are introduced to make Dalia, it becomes a processed food. However, when cookies are made using atta as a base and combined with other ingredients, the outcome qualifies as ultra-processed.
- Nutritional Concerns and Health Impact: Ultra-processed foods often contain excessive amounts of added sugars, unhealthy fats, and high levels of sodium. These components can contribute to a diet that is high in calories and lacking in essential nutrients, leading to various health issues such as obesity, diabetes, and heart disease. Any imbalance in gut health can lead to a host of problems, from neurological issues and stress to mood swings and obesity.
- Disruption of Eating Patterns: The convenience and palatability of ultra-processed foods can lead to overconsumption and disrupted eating patterns. These foods are often designed to be addictive, making it difficult for individuals to control their portion sizes and cravings.
- Lack of Fiber and Nutrients: Ultra-processed foods are typically stripped of natural fiber, vitamins, and minerals present in whole foods. This deficiency can lead to digestive problems, compromised gut health, and deficiencies in essential nutrients.
- Impact on Children’s Health: Children are particularly vulnerable to the negative effects of ultra-processed foods due to their developing dietary habits. Regular consumption can establish a preference for overly sweet or salty flavors and may contribute to childhood obesity and related health issues.
- Sustainability Challenges: The reliance on ultra-processed foods in diets can exacerbate issues related to food sustainability. Their production often requires intensive agricultural practices, contributing to soil depletion and deforestation.
- Misleading Advertising: Packaging and advertising of ultra-processed foods may promote them as healthier options than they actually are. Claims such as “low-fat,” “natural flavors,” or “fortified” can create a false perception of nutritional value.
- Cultural and Culinary Erosion: The prevalence of ultra-processed foods can contribute to declining traditional and cultural dietary practices. These foods often lack the diversity and richness of whole, locally sourced ingredients that are a part of many culinary traditions.
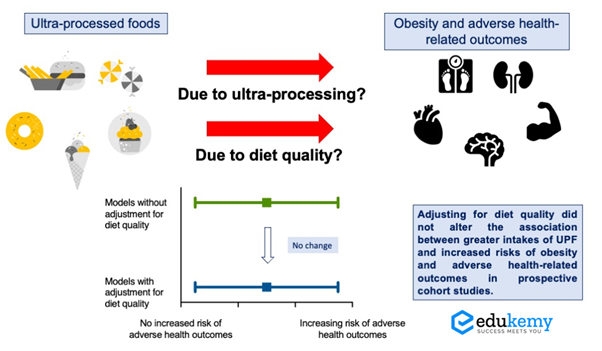
Way Forward
- Enhanced Regulations on Advertising and Marketing: More rigorous regulations on advertising and marketing practices, especially for products like sweet biscuits that are popular among children.
- Clear Definition of High Fat Sugar Salt (HFSS) Foods: Collaboration between the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) and relevant stakeholders is highlighted in the report to establish a precise and unambiguous definition of High Fat Sugar Salt (HFSS) foods.
- Linking Tax Structure to HFSS Definition: To promote healthier choices and encourage reformulated options, a connection between the tax structure and the HFSS foods definition. This can be achieved by implementing higher taxes on products that surpass recommended levels of fat, sugar, and salt through the GST Council.
- Comprehensive National Nutrition Policy: Nutrition policy should be formulated through extensive consultations with stakeholders and should encompass clearly defined objectives and targets. It also highlights the need for broader coverage of overnutrition and diet-related diseases, as existing policies like Saksham Anganwadi and Poshan 2.0 lack this comprehensive approach.
Future of Work Report- AI at Work
In News:
According to the new data released by LinkedIn, it is visible how AI is shaping the world of work and how professionals and companies are adapting to this emerging technology.
About the Report:
- The Future of Work Report uncovers the latest real-time trends around how AI is ushering in a new era of work, based on insights from over 950 million professionals worldwide.
- This report is designed to help both professionals and business leaders in understanding the changing landscape of the job market.
Key Highlights of the Report:
- The intersection of AI and the world of work
- The report shows increased focus on AI at work in a variety of ways, including in the job listings, skills employees are adding to their profiles, and in everyday conversations.
- Employers will need to focus on up skilling & reskilling professionals to boost AI literacy
- Increased emphasis is being laid on hiring for skills
- Acceleration of AI skills across industries and geographies:
- AI Skills Index of LinkedIn provides an insight into how AI skills are being adopted across geographies and industries.
- According to the AI Skills Index Singapore, Finland, Ireland, India, and Canada are experiencing the fastest rate of AI skills diffusion.
- The adoption of AI skills extend beyond tech to a range of industries, including retail, education, financial services, and many others.
- Executive and employee sentiment:
- US executives have a positive outlook of the impact of AI on their overall business and its ability to drive profit and invest in future growth, despite lingering uncertainty around the macro environment.
- Employees are worried as seen with any technological change, but a large number of employees (70%) would delegate as much work as possible to AI to lessen their workloads.
- GAI is starting to change the way we work:
- Generative AI will reduce the time spent on some tasks such as writing or data analysis. It will also drive up demand for other skills, especially people and specialised skills.
- People skills are becoming more critical than ever. Since the launch of ChatGPT, some of the fastest-growing skills in job postings in the US are people skills, such as flexibility and ethics.
First ABDM Microsite
Tags: GS –2, GS– 3 Health, Government Policies & Interventions, Central Sector Schemes
In News:
Recently, The National Health Authority (NHA) had announced 100 Microsites project for accelerated adoption of Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM) across the country.
About:
- Mizoram has achieved a remarkable feat by becoming the first state to operationalize an ABDM Microsite in its capital city, Aizawl.
- Under this, all healthcare facilities including the private clinics, small hospitals and labs in the region shall be made ABDM-enabled and will offer digital health services to the patients.
ABDM Microsites:
- The ABDM Microsites are defined geographical regions where focused outreach efforts would be made to onboard small and medium scale private healthcare providers.
- These Microsites are primarily managed by State Mission Directors of ABDM, with NHA providing financial resources and guidance.
- Patients can link their health records generated at these facilities with their Ayushman Bharat Health Accounts and access and share these records through ABDM-enabled Personal Health Record applications.
- Besides Mizoram, other states including Andhra Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh, Maharashtra and Chhattisgarh have also made significant progress regarding implementation of ABDM Microsites.
| Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission |
| The Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM) is a national initiative that aims to develop the digital health infrastructure of the country. It was launched in September 2021. Ayushman Bharat is a flagship scheme of India which was launched as recommended by the National Health Policy 2017, to achieve the vision of Universal Health Coverage (UHC). |
Scientific Authenticity of Nano Liquid Urea
In News:
An opinion paper for critical examination scrutinizing IFFCO’s claims on Nano Liquid Urea
About scientific authenticity of Nano urea:
- Scientists from Europe have recently released an opinion paper titled “Is India’s largest fertilizer manufacturer misleading farmers and society using dubious plant and soil science?”
- The paper has questioned the IFFCO’s claims about nano liquid urea regarding its scientific basis and efficacy of the fertilizer.
- Concerns have also been raised about its potential negative impacts on crop yield, food security besides efficacy in enhancing crop productivity.
- Nano Liquid Urea were introduced by Indian Farmers and Fertiliser Cooperative (IFFCO) as an alternative to traditional urea.
- Major findings:
- Field Performance of Nano Liquid Urea has shown increased input costs for farmers with minimal results.
- Quality and properties based on existing scientific evidence shows no evidence supporting dramatic crop yield improvements.
- IFFCO’s yield improvement claims have been criticized for lack of clear reference points to support yield improvement claims.
- Doubts about the effect of nano urea raise concerns about product pricing as nano liquid urea price seems excessive given scientific uncertainties.
- Government and IFFCO are planning to open 10 new factories for nano urea production with an aim to increase annual production capacity to 440 million by 2025.
- Government has also planned to export liquid nano urea to 25 countries, mainly in Asia, Africa, and South America.
- Previously, IFFCO has claimed that nano zinc, nano copper, and nano di-ammonium-phosphate having positive impacts on crop yield and environmental sustainability.
- However, lack of scientific claims about positive environmental effects of nano urea my release excess nitrogen causing environmental issues like climate change and species loss.
- Overall, there is need to further study the Nano fertiliser’s behavior, its impact and scientific validation in evaluating new agricultural technologies before advocating their widespread adoption.
India’s Ageing Workforce
In News:
India’s population despite being youthful sees a shift in demographics impacting employment and productivity dynamics.
About India’s ageing Population:
- Economic Think-tank Centre for Monitoring Indian Economy (CMIE) has recently released “Economic Outlook data” report highlighting India’s demographic paradox with its workforce.
- The report suggests that despite a youthful population, India’s workforce is experiencing an ageing trend with share of older workers (above 45) in the workforce is increasing steadily.
- Factors such as longer life expectancy, delayed retirement due to financial concerns and changing social norms are contributing to ageing workforce.
- Key findings:
- Share of young workers decreasing from 25% in 2016-17 to 17% (2022-23) while middle age group also experiencing share decline from 38% to 33%.
- Rise of older workforce with oldest age category’s share growing from 37% to 49% in just seven years while young workers aged under 30 dropped from 10.34 crore to 7.1 crore.
- Decline in Youth Participation with total employed individuals dropping from 41.27 crore to 40.58 crore which is the sharpest fall among all categories.
- Youth Employment Rate (ER) falls from 29% to 19% with employed youth decline by 3.24 crore despite an increase in Youth population.
- Shortage of skilled workers besides lack of sufficient new job opportunities for young people makes experienced older employees more valuable.
- Skills gap between older and newer generations due to changing technology puts potential strain on social welfare systems as ageing workers retire.
- However, the report raises apprehensions that older workers might face age-related discrimination in hiring and promotion besides health issues and reduced physical abilities affecting productivity.
- Overall, addressing the challenges of an ageing workforce is crucial for India’s economic sustainability and the policies should focus on promoting inclusivity, skills development, and intergenerational collaboration.
20th ASEAN-India Economic Ministers’ Meeting
In News:
20th ASEAN-India Economic Ministers’ meeting was held on 21st August 2023 in Semarang, Indonesia and co-chaired by India and Indonesia.
About ASEAN
- ASEAN is a regional grouping established in 1967 at Bangkok through the signing of the Bangkok Declaration.
- It promotes economic, political, and security cooperation among the member nations.
- India and ASEAN concluded a Free Trade Agreement in 2010, after which the bilateral trade which was $ 57 billion in 2010-11, rose to $131.5 billion in 2022-23.
- The 10 member nations of ASEAN are Brunei, Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, the Philippines, Singapore, Thailand and Vietnam.
Highlights of the Meeting:
- Review of bilateral trade and Investment:
- The Ministers reviewed the bilateral trade and investment relations between India and ASEAN and expressed their commitment to strengthen and enhance the economic partnership.
- The leaders resolved to ensure that the ASEAN-India Comprehensive Strategic Partnership delivers meaningful benefits for both sides, particularly in the post-pandemic era.
- Interaction with ASEAN-India Business Council (AIBC):
- The Ministers interacted with the AIBC and took note of the activities undertaken by AIBC in 2023.
- Non-Tariff Barriers flagged by the businesses were noted and exchange of information and concerns between the stakeholders from both sides was appreciated.
- Regional and Global challenges
- Views were exchanged on the regional and global challenges, such as the multidimensional impact of the COVID-19 pandemic, climate change, heightened volatility in the global financial market, inflationary pressures, and geopolitical tensions.
- Both sides identified resilient supply chains, food security, energy security, health and financial stability as priority areas of cooperation.
- ASEAN-India Trade in Goods Agreement (AITIGA)
- Timely review of AITIGA, signed in 2009, was the main agenda of this year’s meeting.
- AITIGA Joint Committee meeting deliberated the roadmap for the review and finalised the Term of Reference and the Work Plan of the AITIGA Review Negotiations.
- The review of AITIGA was a long-standing demand of Indian businesses and early commencement of review would help in making FTA facilitative & mutually beneficial.
- The review of AITIGA is expected to enhance and diversify trade while addressing the current asymmetry in the bilateral trade.
Rail-Sea-Rail (RSR) Initiative
In News:
Government launches steps for integration of transportation for efficient coal Transportation
About Rail-Sea-Rail (RSR) Initiative
- The Rail-Sea-Rail (RSR) Initiative is a strategic approach introduced by the Ministry of Coal to optimize the movement of coal across various stages of transportation.
- This innovative approach involves seamlessly integrating rail and sea routes for efficient coal evacuation.
- It aims to address the increasing demand for coal and focusing on establishing a well-organized and efficient coal evacuation system.
- Key features:
- RSR involves a combination of rail and sea transportation modes, creating a holistic and efficient coal evacuation process.
- Coal is transported from mines to ports via railways, ensuring a smooth flow of raw material from the production centers.
- From ports, coal is further transported via sea routes to reach end-users and powerhouses, reducing transit times and costs.
- By providing an alternative route for coal evacuation, RSR helps alleviate congestion on all-rail routes, ensuring uninterrupted supply.
- RSR enhances the overall logistic efficiency by minimizing delays and bottlenecks in the coal transportation process.
- The integration of rail and sea transportation modes leads to cost savings, optimization of infrastructure for future coal exports, opening up additional revenue streams.
- Compared to an all-rail route, RSR has a lower carbon footprint, contributing to more sustainable coal transportation.
- However, the implementation of RSR requires careful planning and collaboration between government agencies, railways, and port authorities.
- The RSR Initiative is expected to increase coal transportation capacity significantly, reaching 112 MT by 2030, up from the existing 40 MT.
- The strategy will not only improve coal evacuation but also strengthens India’s position in the global coal market.
- By reducing transportation bottlenecks and costs, RSR will help support the energy sector’s sustainability and reliability.
- Overall, the Rail-Sea-Rail (RSR) Initiative aligns with the government’s focus on enhancing infrastructure and logistics all of which are critical for India’s energy and economic growth.
Advisory board on bank frauds
In News:
Recently, the Central Vigilance Commission (CVC) has reconstituted the advisory board on Banking and Financial Frauds (ABBFF).
About:
- It conducts the first level examination of bank frauds before recommendations or references are made to investigative agencies such as the Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI).
- Composition: It consists of the Chairman and four other members, and the tenure of the Chairman/ Members would be for two years.
- Functions of the board:
- The ABBFF’s authority encompasses examining the roles of officials and whole-time directors in public sector banks, insurance companies, and financial institutions when frauds amounting to ₹3 crores and above occur.
- The ABBFF is also authorized to conduct periodic fraud analysis within the financial system, providing inputs for fraud-related policy formulation to the RBI and CVC.
- CVC or CBI may also refer any case/technical matter to the ABBFF for its advice.
- The ABBFF, headquartered in New Delhi, is mandated to provide advice within a month of receiving initial references from the Ministry, Department, CVC, or investigative agencies.
More Information:
- Notably, the suggestion from the Indian Banks Association (IBA) for introducing a “sunset clause” to limit actions against bankers for credit decisions after a specific period hasn’t been accepted by the CVC.
Market Coupling
In News:
Recently, the Central Electricity Regulatory Commission (CERC) has released a staff paper on implementing market coupling in India’s power sector.
About:
- Market coupling is a process in the energy sector where bids from various power exchanges are matched to determine a uniform market clearing price for electricity trading.
- It aims to optimize transmission infrastructure use, maximize economic surplus, and create simultaneous benefits for both buyers and sellers.
- This process helps in efficient price discovery and integration of different electricity markets or geographies, promoting transparency and competition in the energy trading sector.
- The CERC (Central Electricity Regulatory Commission) has introduced provisions for market coupling among power exchanges in the country under its CERC Power Market Regulations (PRC) 2021.
- However, these provisions are yet to be officially implemented.
India has three power exchanges:
- Indian Energy Exchange (IEX) is the oldest and largest power exchange in India, with a market share of over 98% of the traded volume in power.
- Power Exchange India Limited (PXIL) is the second-largest power exchange, with a market share of about 1.5%.
- Hindustan Power Exchange (HPX) is the newest power exchange.
RBI’s Public Tech Platform for Frictionless Credit
In News:
RBI has announced a pilot programme for ‘Public Tech Platform for Frictionless Credit’ which would strive to deliver frictionless credit by “facilitating seamless flow of required digital information to lenders.”
About the Public Tech Platform for Frictionless Credit:
- Digital delivery of credit is preceded by a process of scrutiny known as credit appraisal, which involves evaluation and prediction of the prospective borrowers’ ability for repay the credit/loan.
- This pre-disbursal process is important for banks since it would in turn determine their interest income and impact their balance sheet.
- RBI observed that the data required for the process rests with different entities like central and state governments, account aggregators, banks, credit information companies etc. which creates hindrances in frictionless and timely delivery of rule-based lending.
- The new platform developed by its wholly owned subsidiary, the Reserve Bank Innovation Hub (RBIH) brings all the data together in a single place.
- The platform’s scope encompasses digital loans beyond KCC (Kisan Credit Card), including dairy loans, MSME loans without collateral, personal loans, and home loans.
Benefits from the Platform:
- Improved credit risk and overall credit portfolio management: The platform’s data consolidation would improve risk assessment and lead to better credit portfolio management.
- Fact-based and quick credit assessments: It ensures that credit or other financial instruments are extended to a larger set of borrowers with good credit history.
- Lower cost of accessing capital: The borrowers would benefit by the resulting lower cost of accessing capital, which would translate into productive investment spending.
- The lending platform would bring about reduction of costs, quicker disbursement and scalability.
Reforms for Secure Digital Connectivity
In News:
Government of India launches Mobile User Protection Reforms to create a safer online environment for users and promote secure digital transformation.
About Reforms for Secure Digital Connectivity
- Ministry of Communications has recently launched reforms for safer digital ecosystem in the aftermath of increased digitalization and growth in users of mobile services for online activities.
- The step has been done with an objective to ensure secure digital connectivity, enhance security and build trust in the digital ecosystem.
- Key features:
- Strengthened KYC (Know Your Customer) process for telecom services and scanning of QR code of printed Aadhaar for accurate demographic details.
- Non-allocation of disconnected mobile numbers for 90 days with mandate of complete KYC for SIM replacement, with temporary SMS restrictions.
- Addition of facial biometric authentication to existing methods and mandatory registration of Franchisee, Agents, and Distributors (POS) by Licensees.
- Written agreement between POS and Licensees for indisputable verification of POS by Licensee to eliminate rogue actors.
- While existing POS will be required to be registered within 12 months, there will also be provision of penalty of termination and blacklisting of rogue POS for 3 years.
- Launching of Sanchar Saathi portal to empower mobile users for protection with ability to identify registered connections, report fraud, and block lost/stolen mobiles.
- However, there is need to emphasise on fostering a secure digital environment besides combining cutting-edge technology with vigilant oversight.
- Overall, ensuring the highest level of safety and trust in telecommunications will help providing a secure and reliable communication environment for all users.
Bharat New Car Assessment Programme (Bharat NCAP)
In News:
The Union Minister of Road Transport and Highways will be launching the Bharat New Car Assessment Programme (Bharat NCAP).
About:
- The programme aims to provide a tool to car customers to make a comparative assessment of crash safety of motor vehicles available in the market.
- Under this programme, car manufacturers can voluntarily offer their cars tested as per Automotive Industry Standard (AIS) 197.
- Based on the performance of the car in the tests, car will be awarded star ratings for Adult Occupants (AOP) and Child Occupants (COP).
- Significance:
- It is expected that the demand for safer cars will increase, encouraging car manufacturers to comply with customer needs.
- This programme is a significant step forward in the Government’s commitment to improving road safety by raising the safety standards of motor vehicles up to 3.5 tonnes in India.
Infrastructure Debt Fund-NBFCs (IDF-NBFCs)
In News:
Recently, The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has issued revised guidelines for Infrastructure Debt Fund-NBFCs (IDF-NBFCs) with the aim of enhancing their role in financing the infrastructure sector.
About:
- Infrastructure Debt Fund-Non-Banking Financial Companies (IDF-NBFCs) are specialized financial entities registered as NBFCs to facilitate the flow of long-term debt into infrastructure projects.
- IDF-NBFCs come under the regulation of RBI.
- It raises resources through the issue of rupee or dollar-denominated bonds of minimum 5-year maturity.
- Only Infrastructure Finance Companies (IFC) can sponsor IDF-NBFCs.
- NBFC is permitted to refinance infrastructure projects that have completed at least one year of commercial operations.
- NBFC is also permitted to finance Toll-Operate-Transfer (TOT) projects as a direct lender.
About the revised guidelines:
- IDF-NBFCs must have a minimum net owned fund (NOF) of Rs 300 crore, and a capital-to-risk weighted assets ratio (CRAR) of at least 15%, with a minimum Tier 1 capital of 10%.
- IDF-NBFC shall raise funds through the issue of either rupee or dollar-denominated bonds of minimum five-year maturity.
- The requirement for a sponsor for IDF-NBFCs has been removed, and shareholders will now undergo scrutiny similar to other NBFCs.
- Under the earlier guidelines, an IDF-NBFC was required to be sponsored by a bank or an NBFC-Infrastructure Finance Company (NBFC-IFC).
- All NBFCs would be eligible to sponsor IDF-MFs with prior approval of RBI.
Need:
- These changes are intended to facilitate a greater flow of long-term debt into infrastructure projects and harmonize financing regulations in the infrastructure sector.
Amitabh Kant Committee recommendation on stalled housing projects
In News:
Recently, the committee headed by former NITI Aayog CEO Amitabh Kant suggested reviving stalled real estate projects by requiring all stakeholders, including developers, financiers, and land authorities, to accept “haircuts” to make the projects financially viable.
Haircut:
- A haircut refers to the lower-than-market value placed on an asset being used as collateral for a loan.
- It refers to the acceptance of reduced amounts or losses by stakeholders, such as developers and financiers, to make financially troubled projects viable.
Housing Projects in India:
- The Indian Banks’ Association (IBA) has estimated that over 4 lakh stressed dwelling units involving over Rs 4 lakh crore are impacted in these stalled real estate projects.
- The committee reported that 44% of stalled projects are in the National Capital Region and 21% in the Mumbai Metropolitan.
Other Recommendations of the Committee:
- A “Zero Period” from April 1, 2020, to March 31, 2022, should be established where interest and penalties would be suspended due to Covid-19 and court orders putting a stay on construction within 10 km of the Okhla Bird Sanctuary.
- State governments should create rehabilitation packages, and developers should commit to a three-year completion timeline.
- It recommended allowing “co-developers” to help developers complete projects.
- A partial surrender policy should be designed in which developers can surrender unused land against their outstanding dues.
- Plan approvals should be extended by three years without payment to the Authority.
- Homebuyers of projects under the state government’s package should not be charged penalties or extra interest.
- The use of the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code should be a last resort.
- The Real Estate (Regulation and Development) Act, 2016, a provision for registering projects with the respective Real Estate Regulatory Authority (RERA), must be enforced.
- RERAs should identify mostly complete projects facing administrative hurdles and provide a resolution within 30 days.
India has started manufacturing 38 APIs
In News:
India has started manufacturing 38 active pharmaceutical ingredients, or APIs, in the past 1.5 years.
About:
- This achievement has been facilitated through the production-linked incentive (PLI) scheme for the pharmaceutical sector.
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs):
- APIs are the active components in a pharmaceutical drug that produces the required effect on the body to treat a condition.
- APIs are produced by processing chemical compounds.
- In a biologic drug, the active ingredient is known as a bulk process intermediate (BPI).
- In the context of drug development and manufacturing, APIs are the key active components that interact with specific receptors or target molecules in the body to bring about the desired physiological or therapeutic response.
- All drugs are made up of two core components:
- Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient (API), which is the central ingredient, and Excipients.
- They are substances other than the drug that helps deliver the medication to your system.
- Excipients are chemically inactive substances, such as lactose or mineral oil.
- Example: For instance, if you have a headache, acetaminophen is the API, while the liquid in the gel-capsule or the bulk of a pill is the excipient.
More Information:
- India’s dependence on a single country for the import of 95% of these APIs was reevaluated after the 2017 border standoff with China at Doklam.
- The move towards self-reliance in producing active pharmaceutical components is seen as a strategic shift to reduce dependency on a single source for critical medical supplies.
RBI’s State of the Economy report
In News:
Recently, RBI released the State Of The Economy report, which suggests that the economic momentum (on a quarter-on-quarter basis) is likely to remain healthy even as the global recovery is slowing down.
About the State of the Economy Report:
- The State of the Economy report is released by the RBI which summarises the economic status of the country and provides a record of economic progress.
- The report discusses inflation, employment status, economic growth and the central bank’s plan for managing money.
- RBI uses the key highlights of the reports to make decisions about interest rates and other economic policies, and it also assists economists, investors, and regular citizens understand the economy and make smart choices.
Key Highlights of the Report:
- Decline in merchandize exports: Merchandise exports declined by around 16% in July, falling to a nine month low $32.25 billion.
- Growth in private consumption and investment: Although the contraction in exports will drag down growth, increase in private consumption and investment activity is expected to offset that.
- Healthy signs by high-frequency indicators: Several high-frequency indicators of both demand and supply show healthy signs.
- E-way bill volumes have registered robust growth.
- FMCG sales have also improved sequentially.
- Cargo at major ports as well as railway freight traffic has picked up in July.
- Both steel and cement consumption have registered healthy growth.
- Positive investment intentions: Investment intentions closely track actual investments and serve as a useful indicator of gauging the private investment cycle. In 2022-23, investment plans were made for 982 projects with a capital outlay of Rs 3.5 lakh crore as compared to 791 projects worth Rs 1.96 lakh crore in 2021-22
- Increase in investment in infrastructure projects: Around 60% of these 982 projects financed by banks and financial institutions are in the infrastructure sector i.e. power, roads and bridges, SEZs, industrial biotech and IT park.
- Improved capex cycle: Stronger bank and corporate sector balance sheets, improving demand conditions and rising capacity utilisation rates, will bode well for the capex cycle.
Concerns highlighted by the Report:
- Weak Automobile sales: Automotive sector, with the exception of three-wheelers, remains weak.
- Increased MNREGA demands: Demand for work by households/individuals under MGNREGA is higher than last year.
- Weak domestic demands: Non-oil imports are lower than last year which indicates weak domestic demand.
- Materialisation of investments: Despite rise in investment intentions, materialisation of the investments remains a big concern.
Indian Pharmacopoeia Recognition in Suriname
In News:
Recently, the Cabinet approves the signing of an MoU between India and Suriname in the field of the regulation of medicines
About
- India and Suriname signed MoU exemplifies the mutual commitment to collaborate closely in the realm of medicine regulation.
- It aims to recognize the importance of adhering to respective laws and regulations while ensuring the quality of medicines in both countries.

About MoU
- Indian Pharmacopoeia (IP) Acceptance: The MoU solidifies the acceptance of the IP as a comprehensive book of standards for medicines in Suriname.
- Quality Control: The requirement for duplicate testing of medicines within Suriname is eliminated through the acceptance of the Certificate of Analysis issued by Indian Manufacturers adhering to the IP standards.
- Cost-effective Standards: The MoU facilitates access to IP Reference Substances (IPRS) and Impurity standards from the IPC at reasonable costs.
Significance of the MoU between India and Suriname
- Accessible Medications: Acknowledging intellectual property (IP) paves the way for the production of generic medicines in Suriname. This results in a higher availability of affordable drugs for the people of Suriname, aligning with the objective of improving public health.
- Economic Benefits: For India, recognizing the Indian Pharmacopoeia in Suriname marks a stride towards an ‘Atmanirbhar Bharat’ (self-reliant India). This acknowledgment facilitates the export of Indian medical products, generating foreign exchange earnings, and fortifying India’s pharmaceutical industry on the world stage.
- Enhancing Indian Pharmaceutical Exports: The acceptance of IP by Suriname eliminates the need for redundant testing and checks, providing Indian pharmaceutical exporters with a competitive advantage. The reduction in regulatory aaobstacles leads to more profitable trade for the Indian pharmaceutical sector.
- Broader International Validation: The official recognition of the Indian Pharmacopoeia has already extended to countries such as Afghanistan, Ghana, Nepal, Mauritius, and now, Suriname. This expansion underscores India’s endeavors to bolster its influence and collaboration in the global pharmaceutical arena.
Remittances to India
In News:
Ministry of Finance data indicates trend of sustained and fast-paced increase in “personal transfers” to India
About Remittances to India:
- Remittances to India surge to $112.5 Billion in FY23 highlighting continued growth in India’s Global Appeal.
- It is a remarkable increase of 26% reinforcing India’s status as the leading recipient of global remittances.
- Key highlights:
- Non-resident Indians contribute significantly to the surge in remittances fuelled by the pandemic-induced demand for Indian professionals globally.
- While FY21 witnessed a disruption due to the pandemic, but the trend has rebounded and strengthened.
- Remittances to India stood at $89.1 billion in FY22 which has sustained and rapid growth in “personal transfers” seen in recent years.
- USA holds the leading position, accounting for 23.4% of total remittances followed by UAE (18%), UK (6.8%), besides Singapore and Saudi Arabia contributing 5.7% and 5.1% respectively.
- Private remittances play a crucial role in India’s current account stability as the deficit in merchandise trade is balanced by remittance flows which maintains a favourable balance of payments.
- The surge in remittances is however contrasted with the slowing flow of Foreign Direct Investment (FDI).
- India’s efforts, including 14 production-linked incentive schemes, attract $70.97 billion FDI in FY23, down from $84.8 billion in FY22.
- Thus, remittances serve as a steady source of economic support, especially in comparison to the fluctuating nature of FDI.
- Overall, the consistent surge in remittances reflects India’s strong connections with its global diaspora besides helps in reaping benefits from its enduring presence in the global economy.
Investor Education and Protection Fund Authority (IEPFA)
In News:
Investor Education and Protection Fund Authority (IEPFA) and Common Service Centre (CSC) launch “Niveshak Sarathi” Vans for Delhi-NCR.
About
- IEPFA was established in 2016 under the Companies Act, of 2013.
- The Authority is entrusted with the responsibility of administration of the Investor Education Protection Fund (IEPF) and making refunds of shares, unclaimed dividends, matured deposits/debentures etc to investors and promote awareness among investors.
- IEPF is under the control of the Ministry of Corporate Affairs
Investor Education Protection Fund (IEPF).
It has been established under Section 205C of the Companies Act, 1956 by way of the Companies (Amendment) Act, 1999.
The following amounts that remained unpaid and unclaimed for a period of seven years from the date they became due for payment are credited to the Fund:
- Amounts in the unpaid dividend accounts of the companies
- The application money received by companies for allotment of any securities and due for refund
- Matured deposits with companies
- Matured debentures with companies
- Grants and donations are given to the fund by the Central Government, State Governments, companies or any other institutions for the purposes of the Fund
- The interest or other income received out of the investments made from the fund
New Soil Health Card Scheme
In News:
Union minister of Agriculture and Farmers’ Welfare deliberates on new Soil Health Card Scheme in Rajya Sabha
About New Soil Health Card Scheme
- Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers Welfare has recently introduced new soil health card scheme aimed at enhancing soil health and fertility for farmers across India.
- The Soil Health Card Scheme was first introduced in 2014-15 to provide soil health cards to all farmers in India.
- The Soil Health Card scheme is now a component of the Rashtriya Krishi Vikas Yojana (RKVY) cafeteria scheme under “Soil Health & Fertility” since 2022-23.
- Important features:
- The Soil Health Card portal has been integrated with a Geographic Information System (GIS) to map test results.
- Mobile application improvements include restricted sample collection regions, automated latitude and longitude selection, and QR code generation.
- It sets guidelines for setting up Village Level Soil Testing Labs (VLSTLs) besides training sessions for states to familiarize them with the new system.
- These VLSTLs can be established by rural youth, Self Help Groups (SHGs), schools, and agriculture universities.
- Entrepreneurs submitting applications for VLSTLs need to be aged between 18 and 27 years and provide necessary qualifications.
- The testing labs will receive training on soil sampling, testing, generation of soil health cards, and educating farmers on fertilizer and crop recommendations.
- Detailed soil mapping at 1:10000 scale will be conducted using satellite data and field surveys by Soil & Land Use Survey of India.
- This Soil Resource Information is distinct from Soil Health Cards and is generated separately.
- Overall, the new scheme will help enhance implementation, monitoring and information on soil nutrient status and appropriate nutrient dosages to improve soil health and fertility.
IMF Quota Review
In news:
RBI Governor’s Call for IMF Quota Review: Enhancing Assistance and Accessibility at a G20 Finance Track seminar on the global economy in Mumbai.
About IMF Quota Review
- Reserve Bank of India (RBI) governor has recently emphasized the importance of review of quotas at the IMF to enhance the IMF’s capabilities and reduce perceived stigma and limited access.
- Major highlights:
- The review’s completion can enhance the IMF’s ability to provide effective assistance to distressed countries.
- The IMF’s support is tied to member countries’ quota sizes which forces poor countries to seek help from other sources beyond the IMF due to stigma or access issues.
- The IMF and World Bank play a central role in addressing global debt vulnerabilities and are integral to the international monetary system.
- There is need for financing mechanisms that are timely, non-stigmatizing, and easily accessible to countries in need.
- Present limitations of IMF funding mechanisms, including precautionary lending lines and stand-by arrangements calls for both IMF and World Bank to do more for countries in debt distress.
- Overall, completing quota reforms will enhance the legitimacy of the IMF in overseeing the international monetary and financial system besides not letting the burden of debt hinder global economic growth.
RBI launches new features for UPI
In News:
Recently, The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) announced a clutch of measures aimed at deepening the scope of digital payments.
About:
- A unified payment system (UPI) powers multiple bank accounts into a single mobile application, merging several banking features like Instant transfer of funds, bill-sharing facility, etc.
- It has been developed by: National Payments Corporation of India.
New features for UPI:
- Conversational Payments with AI: The RBI is launching “conversational payments” (audio interaction with AI bots) on UPI, enabling users to interact with an AI-powered system to initiate and complete transactions safely.
- This innovative mode aims to enhance ease of use and expand UPI’s reach.
- Transaction Limit Increase for Small-Value Payments: The transaction limit for small-value offline digital payments will be increased to ₹500.
- Offline Transactions with Near Field Communication (NFC): The RBI proposes enabling offline transactions using NFC technology.
- This approach supports digital payments in scenarios with weak or no internet connectivity, enhancing speed and accessibility.
- Expansion of UPI-Lite: The UPI-Lite wallet introduced by RBI, aimed at optimizing processing resources for banks, now processes over 10 million transactions a month, enhancing transaction reliability.
- UPI-Lite is an on-device wallet service that enables low-value transactions without utilizing a Remitter bank’s core banking systems in real-time.
- Digital Public Tech Platform: The Reserve Bank Innovation Hub is developing a digital platform for frictionless credit delivery with open architecture and APIs, allowing seamless connectivity for all financial sector players.
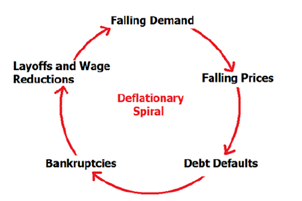
Deflation
In News:
Recently, China has officially slipped into deflation for the first time in two years as the country struggles with post-pandemic recovery.
About:
- Deflation is the economic term used to describe the drop in prices for goods and services.
- It normally takes place during times of economic uncertainty when the demand for goods and services is lower, along with higher levels of unemployment.
- Deflation slows down economic growth by causing businesses to cut jobs, freeze hiring, and offer discounts to maintain sales.
- It is the opposite of inflation, where prices tend to rise over time.
Reasons for deflation in China:
- China’s post-COVID-recovery momentum has faltered as domestic demand weakens.
- Government intervention in IT, Real state industries
- Geopolitical tensions leading to the trade war with the USA.
- Crackdown on polluting industries
- Rising wages in China
- Consumer Price Index (CPI) Dropped in China
- Product Price Index (PPI) Decline: The product price index, a measure of wholesale prices, continued its downward trajectory.
CAG Report on Railway Finance
In News:
According to a new Comptroller Auditor General (CAG) report, the Indian Railways’ finances have slipped into a “concern zone”, with the railways spending ₹107 to earn ₹100 during 2021-22.
About the CAG Report Findings:
- The report said that the Operating Ratio (OR) of the Railways was 107.39% in 2021-22 as against 97.45% in 2020-21.
- Operating Ratio is a measure to calculate the ratio of working expenses to earnings. Higher ratio indicates lower ability to generate a surplus.
- Indian Railways could not generate a net surplus during 2021-22 as it had done in 2020-21.
- The report also found that the total expenditure (revenue and capital heads) of the ministry of railways was ₹3,96,658.66 crore (35.19% more than the previous year), which was comprised of ₹1,90,267.07 crore (22.61% more than the previous year) of capital and 2,06,391.59 crore (49.31% more than the previous year) of revenue expenditure.
- The railways incurred around 75.47% of the total working expenses on staff costs, pension payments and lease hire charges on rolling stock.
- The report found that the Railways was not able to follow the guidelines for digital payment/limited cash transactions and made cash transactions of Rs 2,395.52 crore from 2017-18 to 2021-22.
Reasons for lower surplus generation:
- Inadequate generation of internal resources resulted in greater dependence on Gross Budgetary Support (GBS) and Extra Budgetary Resources (EBR).
- Cross subsidising of passenger fares through profits generated on freight operations. This cross-subsidisation continues to be a concern, as railways has not been able to raise fares in the sleeper class.
- Higher appropriation to pension funds in the FY 2021-2022 led to decline in profits,
The overall loss decreased over the previous year but the entire profit of ₹36,196 crore from freight traffic was utilised to cross-subsidise and compensate the loss on operation of passenger and other coach services.
National Policy on Official Statistics
In News:
The Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI) unveiled the revised draft national policy on official statistics, which focused on creating an overarching framework for the creation and release of statistics in the country using big data analytics, artificial intelligence and machine learning.
About the draft National Policy on Official Statistics (NPOS):

- The revised NPOS is introduced five years after the government released its draft policy based on suggestions from the National Statistical Commission and United Nations Fundamental Principles of Official Statistics.
- This policy will provide an overarching framework for providing reliable, timely and credible social and economic statistics to assist decision-making within and outside the Government.
- The Indian Official Statistical system is required to reorient their strategies with the emerging technologies including AI/ ML dovetailed with commensurate instruments of data collection, compilation processing, storage, integration, analysis and dissemination.
- Besides its focus on technology, the new policy envisages the creation of an integrated data system, optimisation of administrative statistics, innovation in surveys to reduce the burden on respondents and continuous augmentation quality of official statistics.
- National Statistical Commission (NSC) and central ministries have prepared a list of core statistics in eight domains: “National Income, Production & Services sectors, Budgetary Transactions, Money and Banking, Capital Market, Indices and other short-term indicators, External Sector, and Demography, Social and Environment Sectors.
Different Plans suggested by NPOS:
- Short Term Plan: Guidelines for designation of statistical advisers and finalisation of core statistics are its short-term plan to be completed within 1-2 years.
- Medium Term Plans: Integrated data systems, the creation of the National Data Sheet for a uniform format of data on a system, and the innovation of surveys are medium-term projects.
- Long term Plans: Coordination with sub-national governments and training form part of the long-term plan.
Fertilizer Availability and Local Production
In News:
Recently, the Standing Committee on Chemicals and Fertilizers has presented its reports highlighting concerns about fertilizer availability, subsidies, and GST rates on fertilizer components.
Fertilizers used in India:
- A fertiliser is a natural or artificial substance containing chemical elements (such as Nitrogen (N), Phosphorus (P) and Potassium (K)) that improve the growth and productiveness of plants.
- There are 3 basic fertilisers in India – Urea, DAP and Muriate of Potash (MOP).
- In India, urea is the most produced, imported, consumed and physically regulated fertiliser of all. It is subsidised only for agricultural uses.
- The price of non-urea fertilisers is fixed by the companies. All Non-Urea based fertilisers (such as DAP and MOP) are regulated under the Nutrient Based Subsidy (NBS) Scheme.
Concerns raised by the Committee:
- India heavily depends on imported fertilizers like urea, DAP, MOP, NPK, etc. (30% of urea, 100% muriate of potash, 60% Diammonium phosphate imported)
- Irregularities in fertilizers sale such as diversion, black marketing, hoarding, sub-standard quality etc.
- Current NBS policy excludes urea from subsidies. This creates price control for urea, unlike other fertilizers.
- GST rate for fertilizers: 5%; GST rate for raw materials (sulphuric acid, ammonia): 18%; This highlights the inconsistency in GST rates between fertilizers and their raw materials.
Recommendations from the Committee:
- Increase local fertilizers production (especially urea) by facilitating investments for public, cooperative and private fertilizers manufacturers.
- Creating a separate tariff code for urea used for non-agricultural purposes. Develop a central monitoring mechanism to conduct random checks.
- Review NBS policy to remove disincentives for using other fertilizers and promote balanced use.
- Lower GST on raw materials to support fertilizer manufacturing and farmers.
- Implement purchase policy reforms. Advocated for long-term import contracts for fertilizers and raw materials.
Mission Indradhanush
In News:
As per Health Management Information System (HMIS) 2022-23, 6 States/UTs have achieved 100% full immunization Coverage (FIC) whereas 17 States have achieved FIC of more than 90%
About:
- Mission Indradhanush was launched in 2014 as a special drive to expand full immunization coverage in India.
- The Mission Indradhanush (MI) initiative, operating under the Universal Immunization Program (UIP), focuses on low-immunization areas to vaccinate children and pregnant women who missed Routine Immunization.
- Ministry: Ministry of Health and Family Welfare (MOHFW).
- In 2022, the Intensified Mission Indradhanush (IMI) 4.0 was executed in 416 high-priority districts across India.
Universal Immunization Programme (UIP):
- India’s Universal Immunization Programme (UIP) provides free vaccines against 12 life threatening diseases.
- It provides life-saving vaccines to all children across the country free of cost to protect them against Tuberculosis, Diphtheria, Pertussis, Tetanus, Polio, Hepatitis B, Pneumonia and Meningitis due to Haemophilus Influenzae type b (Hib), Measles, Rubella, Japanese Encephalitis (JE) and Rotavirus diarrhea. (Rubella, JE and Rotavirus vaccine in select states and districts)
Tidal energy potential
In News:
Standing Committee submits inquiry report on Tidal Energy Potential assessment in India
About Tidal energy potential:
- The Standing Committee on Energy has recently released a report which focuses on assessing tidal, wave, and thermal energy potential in India.
- Tidal energy is generated from the gravitational forces between Earth, Moon, and Sun affecting ocean tides.
- These are of two types viz., Tidal stream systems (kinetic energy of moving water) and tidal range systems (potential energy from water level differences).
- Major highlights:
- The theoretical estimated potential of India is 12,455 MW for tidal power and 41,300 MW for wave power with the global energy potential estimated at 800 TWh/year.
- In India, coastal regions have potential for strong tidal currents such as Gulf of Kutch, Gulf of Cambay, Sundarbans Delta.
- These are predictable and reliable as tides follow lunar cycles, providing consistent energy generation and tidal currents being denser than air, allows efficient power extraction.
- As there is no greenhouse gas emissions or pollution during energy production, these are environmentally friendly with minimal visual impact.
- However, tidal energy faces a range of challenges including high infrastructure costs, limited suitable locations, environmental impact, technological complexity etc,
- Overall, Tidal energy holds significant promise as a clean and renewable energy source and will go a long way to help fight global warming threat.
Major Tidal Energy projects:
- Gulf of Kutch, India: Proposed demonstration tidal power project.
- Durgaduani Creek, West Bengal: Tidal Energy Research and Demonstration Project.
- La Rance, France: One of the world’s first tidal power plants, operational since 1966.
- MeyGen, Scotland: Large-scale tidal stream array generating power since 2016.
Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB-PMJAY)
In News:
Recently, “Ayushman Bharat – Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana” completes five years of its implementation.
About
Ayushman Bharat, a prominent initiative by the Government of India, was introduced following the recommendations of the National Health Policy 2017. The primary objective was to realize the vision of Universal Health Coverage (UHC) through two interconnected components: Health and Wellness Centres (HWCs) and Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (PM-JAY).
Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (PM-JAY):
- PM-JAY is the world’s largest government-funded health insurance scheme. Launched in February 2018, it offers a comprehensive coverage of up to Rs. 5 lakhs per family for both secondary care (non-super specialist) and tertiary care (super specialist) medical services.
- Beneficiaries of PM-JAY receive seamless access to cashless and paperless healthcare services directly at the hospital.
- The scheme encompasses various Health Benefits Packages, covering medical procedures, surgeries, daycare treatments, medication expenses, and diagnostic services.
- These packages are designed with all-inclusive rates, ensuring that beneficiaries are not charged separately for individual components. Once these rates are set, hospitals are not allowed to charge beneficiaries any additional amount.
Beneficiaries:
- PM-JAY operates on an entitlement-based approach, targeting individuals identified in the latest Socio-Economic Caste Census (SECC) data.
- Upon inclusion in the SECC database, beneficiaries become insured and can avail themselves of healthcare services at any empaneled hospital.
Funding:
- The funding structure for PM-JAY is shared between the central government and states/Union Territories (UTs).
- The distribution ratio is 60:40 for states/UTs with their own legislatures, 90:10 for Northeast states, Jammu and Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, and Uttarakhand, and 100% central funding for UTs without legislatures.
Nodal Agency:
- To ensure the effective implementation of PM-JAY in collaboration with state governments, the National Health Authority (NHA) was established as an independent entity under the Society Registration Act, 1860.
- State Health Agency (SHA), serves as the apex body within each state and is responsible for overseeing the execution of AB PM-JAY at the state level.
Impact of the Scheme:
- Reduced Out-of-Pocket Expenditure: Ayushman Bharat-Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB-PMJAY) has provided vital support to more than 12 crore families, with the ambitious goal of covering 50% of India’s population. This substantial coverage has effectively curtailed out-of-pocket healthcare expenses and resulted in savings of over Rs. 1 lakh crore in medical treatment costs.
- Promotion of Gender Equality: The scheme has actively contributed to promoting gender equality in healthcare. Notably, 48% of the beneficiaries receiving treatments are women, demonstrating a commitment to ensuring unbiased access to healthcare services.
- Advancement towards Universal Health Coverage: AB-PMJAY aligns seamlessly with Sustainable Development Goal 3.8, which aims to achieve universal health coverage. By guaranteeing quality healthcare services irrespective of economic status, the scheme has moved India closer to fulfilling this global objective.
- Enhanced Accessibility: With a network of over 27,000 hospitals that honor the Ayushman Card for free medical treatment, AB-PMJAY has facilitated easy access to healthcare for patients across the country. This accessibility is particularly beneficial for migrants who may need medical assistance while in different states.
- Efficient Fraud Prevention: To ensure the integrity of the scheme, AB-PMJAY has implemented robust fraud prevention measures. This includes the establishment of the National Anti-Fraud Unit (NAFU) and state-level units, as well as the integration of Aadhaar-based authentication and cutting-edge technologies like Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) to detect and deter fraudulent activities. The scheme has taken action against over 210 hospitals found in violation, resulting in their removal from the empanelled list.
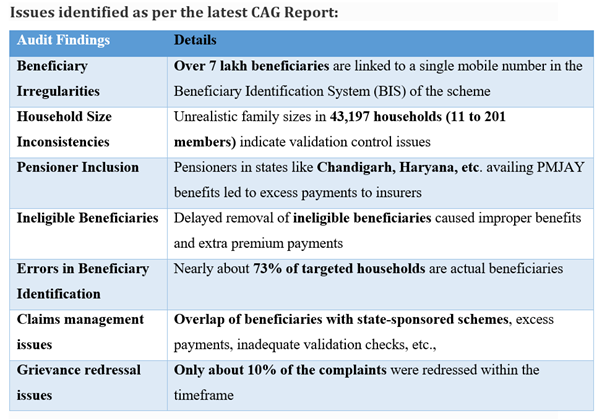
- Establishment of Feedback Mechanism: AB-PMJAY has implemented a systematic feedback mechanism wherein patients receive follow-up calls after their treatments. This practice not only helps evaluate the quality of services provided but also enhances accountability within the healthcare system, ultimately leading to improvements in service delivery.
Source: Indian Express
Excess cane payments
In News:
Centre allows relief to sugar cooperatives over excess cane payments made to farmers.
About the excess cane payments:

- The Centre fixes a fair and remunerative price (FRP) for sugarcane every year, which is the minimum amount that sugar mills have to pay to farmers for procuring their cane.
- Cooperative factories, particularly in Maharashtra, usually pay farmers a final cane price that is more than the Centre’s fair and remunerative price or FRP.
- Issue: This extra price paid has resulted in tax litigation, with mills claiming the excess payment as business expenditure.
- The Income Tax Department, has disallowed this and treats the excess price paid for sugarcane over and above the SMP as appropriation/distribution of profits, and thus not allowable as deduction.
Government’s efforts to resolve the issue:
- The 2015-16 Union Budget had introduced an amendment to the Finance Act.
- It provided for excess cane price payments made by cooperative sugar mills to be allowed as deduction for computing their business income.
- However, such deduction was made applicable only prospectively from 2016-17 assessment year.
- It did not end demands and litigation regarding previous assessment years.
- The Finance Ministry’s 2023-24 Budget sought to conclude the matter and to extend the benefit of deduction to all financial years prior to 2015-16.
- This was done by amending Section 155 of Income Tax Act.
- The Finance Ministry has notified the rules enabling cooperative sugar mills to claim past cane price payments made to farmers, in excess of the government’s statutory minimum price (SMP), as “business expenditure”.
- The move is expected to provide mills a relief of almost Rs 10,000 crore, against pending tax demands and litigation in respect of payments made before 2015-16 financial year.
India’s Strategic Petroleum Reserves
In News:
Ministry of Petroleum & Natural Gas deliberates on India’s Strategic Petroleum Reserves
About Strategic Petroleum Reserve Programme
- India’s Strategic Petroleum Reserve (SPR) Programme is a government initiative aimed at enhancing the country’s energy security by creating a strategic stockpile of crude oil.
- The program involves the establishment of underground storage to store crude oil that can be utilized during emergencies, supply disruptions, or fluctuations in global oil prices.
- Key features:
- India has an underground storage site with a total capacity of over 5.33 million Metric Tonnes (MMT) of crude oil.
- These are located in: Vishakhapatnam, Andhra Pradesh (1.33 MMT), Mangaluru, Karnataka (1.5 MMT) and Padur, Karnataka (2.5 MMT)
- Government has also approved establishment of additional facilities with total storage capacity to be expanded to 6.5 MMT.
- New locations include Chandikhol, Odisha (4 MMT) and Padur, Karnataka (2.5 MMT).
- These storages provides energy security and a buffer against supply disruptions during crises and strengthens India’s ability to manage energy needs effectively.
- Overall, Strategic Petroleum Reserves will play a crucial role in safeguarding the nation’s energy security and mitigating risks arising from global energy dynamics.
Bharat Net Project
In News:
Recently, the Union Cabinet has approved Rs 1.39 lakh crore for the Modernization of the BharatNet project.
BharatNet Project:
- National Optical Fibre Network (NOFN) was launched in October 2011 and was renamed as Bharat Net Project in 2015.
- It is the world’s largest rural broadband connectivity programme using Optical Fiber. And also, a flagship mission implemented by Bharat Broadband Network Ltd. (BBNL). BBNL is a Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV) set up by the Government of India under the Companies Act, 1956.
- Partnering with Village Level Entrepreneurs (Udyamis), who will play a pivotal role in providing fiber connections to the last mile.
- Government aims to expedite the process of connecting all 640,000 villages across India within the next 2.5 years. This acceleration aligns with the goal of enhancing digital connectivity and bridging the urban-rural digital divide.
- The government will cover the expenses related to bringing the necessary infrastructure to the households, such as laying down the fiber connections and related hardware.
Challenges to the BharatNet Project:
- The project has faced significant delays in implementation, with the pace of progress being slower than anticipated. Despite the government’s efforts to connect villages, only about 194,000 out of the targeted 640,000 villages have been connected so far.
- The challenging terrain, lack of proper roads, and logistical difficulties have all contributed to delays in connecting villages.
- Technical challenges such as signal quality, bandwidth limitations, and network downtime have affected the overall user experience.
- The presence of private telecom operators like Jio and Airtel in some rural areas poses a challenge for BharatNet.
Way Forward:
- Addressing technical, financial, operational, and awareness related challenges is essential for the project’s success in achieving its goal.
- Efforts should be made to expedite the implementation process by addressing bottlenecks and streamlining the deployment of infrastructure.
- Clear financial planning, allocation, and management are necessary to support the project’s expansion and maintenance activities.
- Focusing on improving the quality of service is vital to attract and retain users.
Revised Good Manufacturing Practices Standards
In News:
Recently, the government of India has directed all pharmaceutical companies to implement the Revised Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP), bringing their processes at par with Global Standards.
Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) standards:
- GMP standards are guidelines and regulations that ensure the quality, safety, and consistency of pharmaceutical products.
- It is designed to minimize the risks involved in any pharmaceutical production that cannot be eliminated through testing the final product.
- WHO (World Health Organization) has established detailed guidelines for GMP. Many countries have formulated their own requirements for GMP based on WHO GMP.
- GMP system was first incorporated in India in 1988 in Schedule M of Drugs and Cosmetics Rules, 1945. It was revised in 2018, bringing them on par with WHO standards.
- At present, only 2,000 of 10,500 manufacturing units in the country were found to be compliant with WHO-GMP standards.
Revised GMP Guidelines:
- The new guidelines introduce a pharmaceutical quality system, which emphasizes the establishment of a comprehensive quality management system throughout the manufacturing process.
- Companies are now required to implement quality risk management practices to identify potential risks to the quality of their products and take appropriate preventive measures.
- Companies are now required to conduct stability studies based on climate conditions.
- The new guidelines emphasize the use of computerized systems to manage GMP-related processes.
- Companies with over Rs 250 crore turnover must adopt the revised GMP within six months, while smaller enterprises having a turnover of less than 250 crore have a year.
- The new schedule also lists out the requirements for additional types of products, including biological products, agents with radioactive ingredients, or plant-derived products.
Significance of Revised GMP guidelines:
- Implementation of the new norms will bring the Indian industry on par with global standards.
- There has been a string of incidents where other countries have reported alleged contamination in India-manufactured syrups, eye-drops, and eye ointments.
- The improved standards will ensure that pharmaceutical companies follow standard processes, quality control measures, and do not cut corners, improving the quality of medicines available in India as well as sold in the global market.
- It will improve the quality of drugs in the domestic markets.
Source: Indian Express
Bhu-Vision
In News:
Recently, a revolutionary IoT-based automated soil testing and agronomy advisory platform, Bhu-Vision (also known as KRISHI-RASTAA Soil Testing System), has been officially launched at AICRP (ICAR-IIRR), Hyderabad.

About:
- Developed by ICAR-Indian Institute of Rice Research (ICAR-IIRR), Hyderabad.
- This system seamlessly conducts 12 key soil parameter tests in just 30 minutes, providing quick, accurate results directly to farmers and stakeholders through a soil health card on their mobile devices.
- These parameters include pH, electrical conductivity, organic carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium, sulfur, iron, zinc, and boron.
- It signifies a promising future for agricultural technology in India, contributing to a more comprehensive understanding of the nation’s soil health and agricultural landscape.
- This platform will play a vital role in completing the nation’s soil health map.
Rajmargyatra
In News:
Recently, National Highway Authority of India (NHAI) has launched a new app called ‘Rajmargyatra’ in a bid to improve user experience on highways and create a ‘citizen-centric unified mobile application’.
About:
- Rajmargyatra is a user-friendly app that will help provide travellers with comprehensive information about India’s highways and also offer them an efficient grievance redressal mechanism.
- This application is currently available in Hindi and English and can be downloaded via the Google Play Store and iOS App Store.
- Features
- Comprehensive Highway Information:
- It serves as a one-stop repository of essential information for National Highway users.
- The app will allow users to get real-time weather conditions, details of nearby toll plazas, petrol pumps, hospitals, hotels and other essential services and timely traffic alerts.
- Hassle-Free Complaint Redressal:
- The app comes equipped with an inbuilt complaint redressal and escalation mechanism.
- The registered complaints will be handled in a time-bound manner, with system-generated escalations to higher authorities in case of any delays.
- FASTag services:
- NHAI’s new app has integrated its services with various banking portals to make it convenient for users to recharge their FASTags, avail monthly passes and get other FASTag related services on a single platform.
- Safe driving features:
- The Rajmargyatra app comes with over-speeding notifications and a built-in voice assistant to encourage safe driving behavior.
- Comprehensive Highway Information:
G20 Principles for Financing Cities of Tomorrow
In News:
The G-20 members have come out with a report “Financing Cities of Tomorrow” after the third G20 Infrastructure Working Group meeting at Rishikesh. They endorsed the “Principles for Financing Cities of Tomorrow: Inclusive, Resilient and Sustainable”
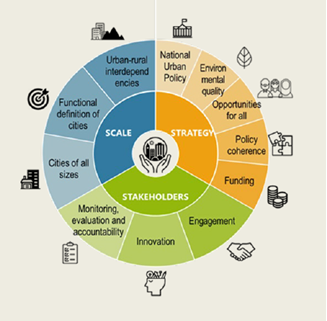
Key Highlights of the Report:
- Delivering quality urban infrastructure is one of the most pressing challenges for cities in a rapidly urbanising and changing world.
- The ‘G20 Principles on Financing Cities of Tomorrow’ and the “Financing Cities of Tomorrow” report provide guidance and evidence to accelerate quality infrastructure investment in cities.
- Cities have strong potential to better meet current and future urban infrastructure challenges and enhance investment.
- Better urban planning improves the likelihood of raising private capital for inclusive, resilient and sustainable urban investments. Financing of urban infrastructure cannot be achieved without cities leveraging private investment.
- City Governments have a key role in the planning and provision of urban infrastructure, with subnational governments responsible for almost 60% of total public investments in G20 countries. City governments can mobilise funds through:
- Municipal bonds: Ex. Municipal Bond in Vadodara
- Green, social and sustainable bonds: Ex. Green Bond in Mexico City
- Green, social and sustainable loans: Ex. Green and Social Loans from La Banque Postale (France)
- Sustainability-linked bonds: Ex. Sustainability-Linked Bond in the City of Helsingborg (Sweden)
- Catastrophe bonds: Catastrophe Bond in Los Angeles (US)
- Improving City Governments’ access to sustainable finance for quality infrastructure investments can help create more inclusive, resilient and sustainable cities.
- Create an enabling environment for City Governments to access affordable and sustainable finance, in line with national institutional contexts and ensuring fiscal responsibility.
- Ensure that cities have access to sufficient and predictable sources of funding.
- Enhance the use of sustainable financing instruments for infrastructure investments made by City Governments
Gross Fixed Capital Formation (GFCF)
In News:
Recently, The Minister stated that this is indicated by Gross Fixed Capital Formation (GFCF) in the Indian economy which has increased from Rs. 32.78 lakh crore (constant 2011-12 prices) in 2014-15 to Rs. 54.35 lakh crore in 2022-23 (Provisional Estimates).
About:
- Gross Fixed Capital Formation (GFCF) refers to the total amount of investment made in the production of physical assets, such as buildings, machinery, equipment, and infrastructure, within a country during a specific period.
- It does not account for the consumption (depreciation) of fixed capital.
- It indicates the increase in the nation’s capital stock and productive capacity.
- Generally, the higher the capital formation of an economy, the faster an economy can grow its aggregate income.
- As per RBI, Gross capital formation refers to the ‘aggregate of gross additions to fixed assets (that is fixed capital formation) plus change in stocks during the counting period.’
- It is a component of expenditure approach to calculating Gross Domestic Product (GDP).
- GFCF is not a measure of total investment, because only the value of net additions to fixed assets is measured, and all kinds of financial assets, as well as stocks of inventories and other operating costs are excluded.
Schemes for Farmers’ Welfare
In News:
The Ministry of Agriculture and Farmer Welfare, informed the Lok Sabha about the five major schemes launched by the Government during the last four years, to address various aspects of agriculture and benefit farmers including small and marginal farmers.
About the Schemes:
- Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samman Nidhi (PM-KISAN)
- The scheme is being implemented to provide income support to all landholding Farmers’ families to enable them to take care of expenses related to agriculture and allied activities as well as domestic needs.
- The Scheme aims to provide a payment of Rs.6000/- per year, released in three 4-quarterly instalments of Rs.2000/ for the farmers’ families with cultivable land holding, subject to certain exclusions. Payment is done through DBT.
- Formation and Promotion of 10,000 Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs)
- Government has launched the Central Sector Scheme (CSS) in 2020.
- Formation & promotion of FPOs are to be done through Implementing Agencies (IAs), which further engage Cluster Based Business Organizations (CBBOs) to form & provide professional handholding support to FPOs for a period of 5 years.
- It includes preparation and execution of business plans for the concerned FPOs for better marketing opportunities & market linkages on a sustainable basis.
- Agriculture Infrastructure Fund (AIF)
- To address the existing infrastructure gaps and mobilise investment in agriculture infrastructure, Rs 1 lakh crore Agri Infra Fund was launched under Aatmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyan.
- The AIF is a medium – long term debt financing facility for investment in viable projects for post-harvest management infrastructure and community farming assets through interest subvention and credit guarantee support.
- National Mission on Edible Oil-Oil Palm (NMEO-OP)
- A Centrally Sponsored Scheme namely, NMEO-OP was launched by GOI to promote oil palm cultivation for making the country AtmaNirbhar in edible oils with special focus on North-Eastern States and A&N Islands.
- The Mission will bring additional area of 6.5 lakh ha under Oil Palm plantation in next 5 years from 2021-22 to 2025-26.
- National Beekeeping & Honey Mission (NBHM)
- A new Central Sector Scheme entitled NBHM was launched in 2020 under AtmaNirbhar Bharat Abhiyan for overall promotion and development of scientific beekeeping & to achieve the goal of “Sweet Revolution”.
Gross Fixed Capital Formation
In News:
Gross Fixed Capital Formation (GFCF) in Indian economy increases from Rs. 32.78 lakh crore (constant 2011-12 prices) in 2014-15 to Rs. 54.35 lakh crore in 2022-23 (Provisional Estimates).
About India’s GFCF:
- GFCF consists of resident producers’ investments, deducting disposals, in fixed assets during a given period.
- It also includes certain additions to the value of non-produced assets realised by producers or institutional units.
- Fixed assets are tangible or intangible assets produced as outputs from production processes that are used repeatedly, or continuously, for more than one year.
- The Government and private sector together invest in the economy.
- This is indicated by Gross Fixed Capital Formation (GFCF) in the Indian economy which has increased from Rs. 32.78 lakh crore (constant 2011-12 prices) in 2014-15 to Rs. 54.35 lakh crore in 2022-23 (Provisional Estimates).
- The government is implementing
- Scheme for Special Assistance to States for Capital Expenditure (2020-21 & 2021-22), and
- Scheme for Special Assistance to States for Capital Investment (2022-23 & 2023-24).
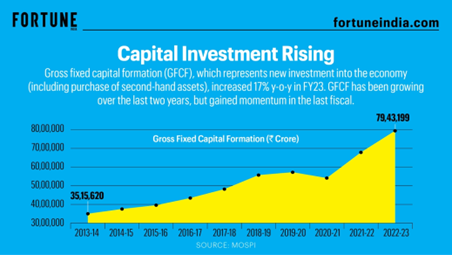
- Government approved and released special assistance (loan) in the form of 50-years interest free loan for capital expenditure on capital projects including capital projects pertaining to sectors like health, education. irrigation. power. etc for capital expenditure for different States.
MSME CARD
In News:
Recently, the Ministry of Micro Small and Medium Enterprises, (MSME) in association with National Payment Corporation of India (NPCI) had launched the MSME RuPay Credit Card on pilot basis, pan-India for Udyam registered MSMEs.
About:
- The MSME RuPay Credit Card provides a simplified payment mechanism to MSMEs to meet their business-related operational expenses like digital payments, utility bills payments, tax/statutory payments etc.
- MSME borrowers also takes benefit of interest-free credit period on their business spends as per the bank’s policy.
National Payment Corporation of India (NPCI)
- NPCI is an umbrella organization for operating retail payments and settlement systems in India.
- It is an initiative of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and Indian Banks’ Association (IBA) under the provisions of the Payment and Settlement Systems Act, 2007, for creating a robust Payment & Settlement Infrastructure in India.
Akhil Bharatiya Shiksha Samagam and ULLAS Initiative
In News:
Union government launches multiple initiatives on 3rd Anniversary of New Education Policy 2020 at Bharat Mandapam, New Delhi.
Akhil Bharatiya Shiksha Samagam and ULLAS Initiative
- Ministry of Education has recently launched the mobile application of ULLAS: Nav Bharat Saksharta Karyakram at the Akhil Bharatiya Shiksha Samagam 2023.
- Important features:
- ULLAS initiative aims to revolutionize education and literacy in India by creating a learning ecosystem that reaches every individual and bridges the gaps in basic literacy and critical life skills.
- The program imparts basic education, digital and financial literacy, and critical life skills to citizens aged 15 and above who missed the opportunity to attend school.
- The mobile application of ULLAS is user-friendly and interactive, available on both Android and iOS platforms.
- It will serve as a digital gateway for learners to access diverse learning resources through the DIKSHA portal of NCERT.
- It allows learners and volunteers to register through self-registration or by surveyors and aims to create a culture of continuous learning and knowledge-sharing in communities across India.
- The initiative focuses on promoting functional literacy, vocational skills, financial literacy, legal literacy, digital literacy, and empowering citizens to participate in nation-building.
- The scheme also encourages volunteers to participate in the ULLAS initiative as a duty towards nation-building.
- Student volunteers will receive incentives such as credits in school/university and appreciation through certificates, letters, and felicitation.
- Overall, the launch of ULLAS will help spreading of knowledge across the nation, empowering citizens with education by using technology and community-driven efforts.
Self-Reliant India Fund for MSMEs
In News:
Recently, the Government of India announced a Rs 50,000 crore Equity infusion for Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) as a part of Aatmanirbhar Bharat package through the Fund of Funds.
Self-Reliant India (SRI) Fund:
- The SRI Fund operates through a mother-fund and daughter-fund structure for equity or quasi-equity investments.
- The National Small Industries Corporation (NSIC) Venture Capital Fund Limited (NVCFL) is registered as the Mother Fund under the SRI Fund implementation.
- It has been registered as a Category-II Alternative Investment Fund (AIF) with SEBI.
- The objective of SRI Fund is to provide equity funding to viable and high-potential MSMEs, fostering their growth and transformation into larger enterprises.
- Rs. 10,000 crores contributed by the Government of India and Rs. 40,000 crores from Private Equity and Venture Capital funds.
Other Initiatives for MSMEs:
- MSME Champions Scheme: This scheme provides financial assistance to MSMEs to enhance their competitiveness and innovation capabilities.
- Infusion in Credit Guarantee Fund: As part of the Budget 2023-24, the government announced an infusion of Rs. 9,000 crores in the corpus of Credit Guarantee Fund Trust for Micro & Small Enterprises.
- Raising and Accelerating MSME Performance (RAMP): This initiative focuses on strengthening institutions and governance of MSME programs at both the central and state levels.
- Amendment in Income Tax Act: The Finance Act 2023 brought about an amendment in Section 43B of the Income Tax Act, 1961, to offer more favourable tax provisions for MSMEs.
Barrier to Women’s Labor Force Participation
In News:
Recently, Tamil Nadu government launched camps to facilitate the registration of applicants for the Kalaignar Magalir Urimai Thogai Thittam, or women’s basic income scheme.
About
The scheme Aimed to “recognize women’s unpaid labour”, the scheme will provide ₹1,000 per month to women in eligible households. In Marriages, the wife bears and rears children and minds the home, and therefore bears the brunt of unpaid care and domestic work, hindering their Participation in Labor Force.
Factors contributing to lower women’s participation in the labor force:
- Patriarchal Social Norms: Deep-rooted societal norms and traditional gender roles often restrict women’s access to education and employment opportunities. Cultural expectations may prioritize women’s roles as caregivers and homemakers, discouraging their active involvement in the workforce.
- Gender Wage Gap: Women frequently encounter wage disparities compared to men, even when performing similar work. This wage gap can demotivate women from seeking formal employment due to the unfair compensation they may receive.
- As per World Inequality Report, 2022, women in India just capture 18% of labor income, while men earn 82%.
- Unpaid Care Work: The unequal distribution of unpaid care and domestic responsibilities falls disproportionately on women, leaving them with limited time and energy for paid employment. This imbalance, where women bear the majority of household duties, acts as a significant barrier to their participation in the labor force.
- Social and Cultural Stigma: In certain societies, there may be negative attitudes or societal resistance towards women working outside the home, leading to lower labor force participation rates among women.
Statistics Regarding Unpaid Care of Women
- Female Labour Force Participation Rate: India’s female labor force participation rate (LFPR) has been declining for more than 20 years, despite the share of educated women surging in this period. In the last two decades, female LFPR has fallen from 30% to 24%, despite the Class 10 enrolment rate among girls increasing from over 46% to 87%.
- Labour Force Participation rate in other countries: India’s female LFPR (24%) was the lowest among all these countries. India had the second-highest female population in the group. In contrast, China, which has the highest female population, had the highest female LFPR of 61%.
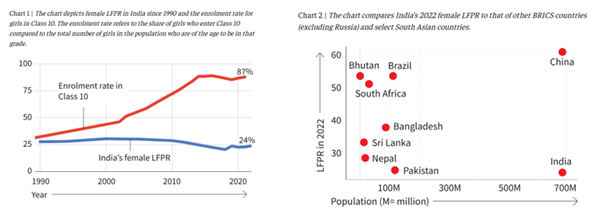
- Time Spending in domestic work by women is more than men: Women who are not in the labour force spend the highest amount of time on unpaid domestic/care work, averaging 457 minutes or 7.5 hours a day. But employed women were not far behind, spending 348 minutes or 5.8 hours a day. Unemployed men spend 3.5 hours per day on such chores, over two hours less than employed women. Employed men spend 2.7 hours a day on such chores, over three hours less than employed women.
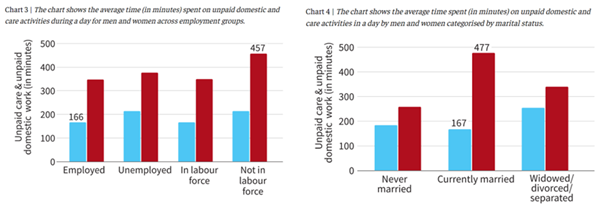
- Married women spend the most amount of time engaged in unpaid work (nearly 8 hours) compared to women who are widowed/divorced/separated (5.7 hours) or have never married (4.3 hours). In contrast, married men spend the least amount of time on unpaid work (2.8 hours) compared to men who are widowed/divorced/separated (4.2 hours) or have never married (3.1 hours).
Corporate Debt Market Development Fund
In News:
Recently, the government of India has approved the Guarantee Scheme for Corporate Debt (GSCD) to provide a guarantee cover for the debt raised by the Corporate Debt Market Development Fund (CDMDF) that aims to stabilize the corporate bond market during times of stress.
Corporate Debt Market Development Fund (CDMDF):
- The CDMDF is an alternative investment fund established to address the needs of the corporate debt market in India.
- It serves as a backstop facility for investment-grade corporate debt securities, providing stability and enhancing investor confidence in the market.
- It provides a backstop facility of Rs 33,000 crore has been established for Mutual Funds. The government will contribute Rs 30,000 crore, and the Asset Management Companies will provide the remaining Rs 3,000 crore.
Guarantee Scheme for Corporate Debt (GSCD):
- It provides a complete guarantee cover for debt raised by the CDMDF.
- Its primary objective is to enhance investor confidence and provide stability to the corporate debt market.
- Guarantee Fund for Corporate Debt (GFCD) will manage the GSCD. The GFCD is a trust fund formed by the Department of Economic Affairs (DEA) and managed by the National Credit Guarantee Trustee Company Ltd (NCGTC).
- NCGTC is a wholly-owned company of the Department of Financial Services under the Ministry of Finance.
- The scheme is designed to support the purchase of investment-grade corporate debt securities by CDMDF during market dislocation.
SEBI Guidelines for CDMDF:
- During normal market conditions, CDMDF focuses on dealing in low duration government securities (G-sec), treasury bills, and guaranteed corporate bond repo with a maturity not exceeding seven days.
- When the market experiences dislocation, CDMDF steps in to purchase investment-grade corporate debt securities, providing a safety net for investors.
- CDMDF is authorized to purchase only listed corporate debt securities with a residual maturity of up to five years.
- CDMDF buys securities at a fair price (not at distress price), factoring in liquidity risk, interest rate risk, and credit risk to ensure transparency and market stability.
- CDMDF will be launched as a closed-ended scheme with an initial tenure of 15 years. The possibility of extension lies at the discretion of the Department of Economic Affairs (DEA) in consultation with SEBI.
RBI’s Digital Payments Index (RBI-DPI)
In News:
Digital payments across the country registered a growth of 13.24% in a year through March 2023, as per RBI’s index that measures the adoption of online transactions.
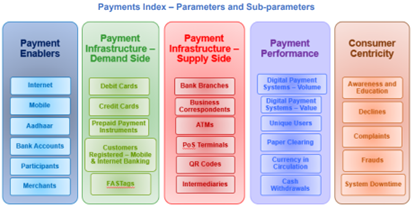
About:
- RBI’s Digital Payments Index (RBI-DPI) stood at 395.57 at end-March 2023 compared to 377.46 in September 2022 and 349.30 in March 2022.
- The increase in the index was attributed to substantial growth in payment infrastructure and performance across the country.
Digital Payments Index
- Digital Payments Index assesses the level of digitalization in payments nationwide and showcases the growth of different digital payment methods.
- It is released semi-annually and consists of five main parameters with varying weights:
- Payment Enablers (weight 25%)
- Payment Infrastructure – Demand-side factors (10%)
- Payment Infrastructure – Supply-side factors (15%)
- Payment Performance (45%)
- Consumer Centricity (5%)
- These parameters enable the measurement of the deepening and penetration of digital payments in the country over different periods.
Resource Efficiency Circular Economy Industry Coalition
In News:
Recently, Resource Efficiency Circular Economy Industry Coalition (RECEIC) was inaugurated by the Union Minister of Environment, Forest and Climate Change.
About Resource Efficiency Circular Economy Industry Coalition (RECEIC)
- A total of 39 multinational corporations (MNCs) hailing from various sectors such as steel, FMCG (Fast-Moving Consumer Goods), and electronics united to form RECEIC.
- Their collective commitment involves embracing resource efficiency and circular economy principles to tackle environmental issues arising from different types of waste, including plastics, microplastics, e-waste, and chemical waste.
- RECEIC is conceptualised by India’s G20 Presidency, it is envisaged to be industry-driven and a self-sustaining initiative continuing to function even beyond India’s G20 Presidency.
Objective of RECEIC
The coalition’s main objectives are to:
- Promote and encourage collaboration between companies,
- Develop advanced capabilities across various sectors and value chains,
- Leverage the diverse global experiences of its members to drive progress,
- Encourage private sector action to enhance resource efficiency and accelerate the transition to a circular economy.
To achieve these goals, the coalition is organized around three key pillars:
- Partnerships for Impact: The coalition aims to forge strategic partnerships between companies, fostering a collaborative approach towards achieving impactful and sustainable outcomes.
- Technology Cooperation: By promoting technology sharing and cooperation among its members, the coalition seeks to drive innovation and enhance capabilities across industries.
- Finance for Scale: The coalition recognizes the importance of financial support to scale up circular economy initiatives. Therefore, it aims to facilitate funding opportunities to accelerate the adoption of sustainable practices in the private sector.
Significance of RECEIC:
- Coalition will have a central role in promoting partnerships, facilitating technological cooperation, knowledge sharing, and fostering innovation. It will also play a key role in enhancing access to finance by enabling the exchange of insights and best practices.
- Coalition’s efforts will significantly contribute to advancing global goals and priorities set by the G20 and other international forums.
- RECEIC will empower industries to address information gaps and coordination challenges across all G20 members, promoting collaboration and collective action towards a more sustainable and efficient global economy.


Challenges for circular economy in India:
- The circular economy model faces challenges in industries due to supply chain limitations and inadequate incentives to invest in recycling and remanufacturing processes.
- In India, there is a lack of awareness among many people about the concept of a circular economy and its associated benefits.
- India’s existing infrastructure may not be adequately prepared to support a circular economy, with issues such as limited recycling facilities and inefficient waste management systems.
- Additionally, there is cultural resistance in India towards the idea of reusing and recycling products, which hinders the widespread adoption of circular practices.
Vivad se Vishwas 2.0
In News:
Union government launches Vivad se Vishwas 2.0 scheme to settle contractual disputes
About Vivad se Vishwas 2.0:
- Ministry of Finance has recently launched the “Vivad se Vishwas 2” scheme to resolve contractual disputes involving the Government of India and government undertakings.
- The scheme was announced in the budget 2022-2023 and covers disputes up to 30 September 2022.
- Key features:
- It offers a voluntary settlement scheme with standardized terms for disputes where an arbitral award is under legal challenge.
- It applies to all domestic contractual disputes involving the government and the deadline for submitting claims under the scheme is 31 October 2023.
- Contractors will be offered settlement amounts up to 85% of the net amount awarded or upheld by the court for awards passed on or before 30 April 2023.
- For arbitral awards passed on or before 31 January 2023, the settlement amount offered will be up to 65% of the net amount awarded.
- The government e-marketplace (GeM) will have a dedicated web-page for the scheme’s implementation where eligible claims will be processed to ensure a smooth and transparent process.
- Contractors with non-GeM contracts of the Ministry of Railways may register their claims on the IREPS platform (www.ireps.gov.in).
- Overall, the scheme will go a long way in ensuring transparency in government contract process and will help promote ease of doing business.
In News:
Government upgrades public sector undertakings Oil companies giving them more flexibility to take decisions on large investments within India and abroad.
- The Ministry of Finance has recently upgraded Oil India to the Maharatna category of central public sector enterprises (CPSEs).
- Maharatna Category:
- The Maharatna category was introduced on May 19, 2010, to empower CPSEs to expand operations and emerge as global giants.
- CPSEs with Maharatna status have greater autonomy in decision-making, especially concerning large investments within India and abroad.
- Some key CPSEs with Maharatna status include BHEL, Indian Oil, ONGC, BPCL, HPCL, and SAIL.
- Criteria for Maharatna status include:
- The CPSE should have Navratna status with significant global presence or international operations.
- It should be listed on the Indian stock exchange with a minimum prescribed public shareholding under SEBI regulations.
- It should have an average annual net profit exceeding Rs 2,500 crore during the last three years.
- Navratna Category:
- The Navratna category is another classification for CPSEs in India which gives more financial and operational autonomy compared to other CPSEs.
- They are allowed to undertake capital expenditure without any monetary ceiling for purchasing new items or replacements.
- Navratna CPSEs can enter into technology joint ventures or strategic alliances and obtain technology and know-how through purchase or other arrangements.
- They have the authority to raise debt from domestic and international capital markets, subject to RBI/Department of Economic Affairs approval.
- These CPSEs can also establish financial joint ventures and wholly-owned subsidiaries in India or abroad within an investment ceiling of Rs 1,000 crore.
- Some important Navratna status companies include:
- Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL), Bharat Heavy Electricals Limited (BHEL), Coal India Limited (CIL), GAIL (India) Limited
- Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL), Hindustan Petroleum Corporation Limited (HPCL), Indian Oil Corporation Limited (IOCL) etc.,
- Overall, the status upgrade reflects the government’s acknowledgment of the CPSE’s achievements and potential for further growth and contribution to the economy.
Restrictions on the import of electronic devices
In News:
The Centre has imposed import restrictions on laptops, tablets, and certain classes of computers, marking a change in the government’s policy of unrestricted trade with regard to these goods.
About the Import Restrictions:
- The import of laptops, tablets, all-in-one personal computers, and ultra-small form factor computers and servers would be restricted, with imports only being allowed for those holding a “valid Licence for Restricted Imports“.
- Companies would be given enough time to apply for licences to import laptops and other devices specified in the list of restrictions.
Exemptions:
- The restrictions will not be applicable to Imports under Baggage Rules.
- Further, the restriction will not be applicable for the import of one such specified device purchased via e-commerce portals, through post or courier.
- Exemptions will also be given for 20 such devices per consignment for the purpose of R&D, testing, benchmarking, evaluation, repair, re-export and product development purposes.
- The policy also provides an exemption for the re-import of such devices that have been repaired abroad.
- Finally, the policy gives another exemption for such devices that form an essential part of a “Capital Good”.
Reasons for Imposing Restrictions:
- WTO Rules: India is obligated to its commitment to zero-duty imports under WTO rules. Thus the inability to check the import of electronic goods, which impacts the domestic manufacturing, restrictions were imposed.
- The China factor: India’s overdependence on China with regard to the import of electronic goods such as laptops, computers etc. needed to be reduced. India’s cumulative imports of electronic goods since 2019 shows that China accounts for a whopping 59% of these imports.
- Boost to indigenous manufacturers: A rise in indigenous manufacturing would not only help India reduce its dependence on its diplomatic and business rival but would also help indigenous manufacturers expand their footprint globally.
- The Security factor: The restrictions had been brought in to guard against electronic hardware coming in with in-built security loopholes that may potentially endanger sensitive personal and enterprise data.
GOBARdhan Initiative
In News:
Recently, The GOBARdhan initiative in India, aimed at converting waste to wealth through biogas and compressed biogas (CBG), has shown promising results and attracted significant investments.
About:
- Galvanizing Organic Bio-Agro Resources Dhan (GOBARdhan) is a crucial umbrella initiative of the Ministry of Jal Shakti, Government of India.
- In 2018, the government launched this scheme as a national priority project under the Swachh Bharat Mission Grameen-Phase II program.
- The government provides technical assistance and up to 50 lakhs of financial support per district for the safe disposal of cattle and organic waste.
- The initiative aims to manage organic waste scientifically while benefiting rural households and involves collaboration between the government, private players, and other stakeholders.
Objectives:
- Safely manage cattle and agricultural waste in villages and make the villages clean.
- Convert organic waste to biogas and organic manure for rural use
- Promote environmental sanitation and curb vector-borne diseases in rural areas
- Create rural employment and income generation opportunities by involving entrepreneurs, SHGs, and youth groups in setting up GOBARdhan units.
More Information
- The Unified Registration Portal for GOBARdhan has received requests for over 1200 biogas plants, including 320 CBG plants in just 60 days since its launch.
Odisha Millets Mission (OMM)
In News:
Recently, Odisha has emerged as one of the forerunners of millets, ensuring the participation of women Self-Help Groups (SHGs) in the millet value chain where they are playing a leading role in processing, value addition, and marketing.
About:
- The initiative is a part of a joint effort led by the Odisha Millets Mission (OMM), a flagship program launched by the Department of Agriculture and Farmers’ Empowerment and the Department of Mission Shakti, to mainstream millet-based food in rural and urban areas.
- The aim is to create sustainable livelihoods and improve nutritional security, involving women SHGs through millet-based enterprises.
- Under the OMM, Millet Shakti Cafés and Outlets have been established in various districts, showcasing a diverse range of millet-based food items.
- OMM has facilitated training in recipe formulation, packaging, quality control, marketing, and other skills, empowering women to participate effectively in the millet industry.
- OMM has demonstrated a unique approach to promoting upskilling and gender equity.
Mahila Samman Savings Certificate Scheme (MSSC)
In News:
Total deposits under the newly launched Mahila Samman Savings Certificate (MSSC) scheme have jumped over Rs 8600 crore and more than 14 lakh accounts have been opened across states.
About:
- MSSC is the newly launched small savings scheme of the Government to commemorate the Azadi ka Amrit Mahotsav.
- It is exclusively for women and girls in India.
- Some of the features of the scheme include:
- MSSC account can be opened by women of any age group including the girl child with a minimum deposit of Rs 1000 and maximum deposit of Rs 2 Lakhs for a period of two years.
- The interest rate for MSSC is 7.5% p.a. which is compounded quarterly.
- The facility of partial withdrawal and premature closure on compassionate grounds are also available under this Scheme.
- The Government of India has authorized the Department of Posts, all Public Sector Banks and four Private Sector Banks to operate MSSC.
- MSSC has been made available for a two-year period up to March 2025.
Data Points
- The highest number of MSSC scheme accounts has been opened in Maharashtra (2,96,771), followed by Tamil Nadu (2,55,125), Andhra Pradesh (1,21,734) and Karnataka (1,05,134).
- Among all states, the lowest number of MSSC accounts have been opened in Arunachal Pradesh (318), Bihar (7482), Goa (2786), Haryana (9247), Jharkhand (8391), Manipur (39), Meghalaya (530), Mizoram (1172), Nagaland (151), Sikkim (305), Tripura (4358).
Urea Gold
In News:
Prime Minister recently launched “Urea Gold”, a new variety of Urea, during an event in Rajasthan’s Sikar.
About:
- It is a new variety of Urea coated with Sulphur.
- It is being introduced to address the Sulphur deficiency in soil and save input costs for the farmers.
- Urea Gold surpasses the existing Neem-coated urea in terms of both economic viability and efficiency.
Urea Gold is said to be better than conventional forms of Urea (including Neem coated urea)
- Sulphur-coated urea facilitates a gradual release of nitrogen, thereby enhancing its availability and uptake by crops.
- The inclusion of humic acid in Urea Gold further extends its lifespan as a fertilizer.
- Reduces overall fertilizer usage: According to the report, 15 kg of Urea Gold provides comparable benefits to 20 kg of conventional urea, making it a more efficient and effective choice for farmers.
| Neem-coated urea |
| Urea is a commonly used nitrogen-based fertilizer that provides essential nutrients to plants to promote healthy growth. It also aids the photosynthesis process of plants. The neem coating on urea slows down the release of nitrogen into the soil. This controlled release helps reduce nitrogen leaching and volatilization, leading to improved nitrogen use efficiency by plants. It would bring down the quantity of urea per acre and consequent reduction in input cost to farmers. |
FAQs on Monthly Current Affairs – August 2023
Q1: What are monthly current affairs?
A1: Monthly current affairs refer to the latest and most significant events, developments, and news stories that have occurred within a particular month. These events encompass a wide range of topics, including politics, economics, science, technology, culture, and more. They are a reflection of the dynamic nature of our world and provide a snapshot of what’s happening globally or within a specific region during a given month.
Q2: Why are monthly current affairs important?
A2: Monthly current affairs are important for several reasons:
- Informed Citizenship: Staying updated with monthly current affairs is crucial for informed citizenship. It empowers individuals to make well-informed decisions, including voting in elections, advocating for causes, and engaging in meaningful discussions about societal issues.
- Professional Relevance: Professionals, such as journalists, policymakers, and business leaders, need to be aware of current affairs to make strategic decisions, create informed content, and respond to changes in their respective fields.
- Academic and Competitive Exams: Many academic institutions and competitive exams assess students’ knowledge of current affairs, making it essential for academic and career success.
- Cultural Awareness: Understanding current events helps individuals appreciate and understand different cultures, societies, and global interconnections.
- Safety and Preparedness: Some current affairs, such as natural disasters or public health emergencies, can directly impact personal safety and require timely awareness and preparedness.
A3: Each month, there are several important events and developments in the field of polity and governance. These may include legislative changes, court rulings, elections, government policies, and more. To stay informed, you can follow reputable news sources, government websites, and organizations specializing in political analysis. Additionally, you can subscribe to monthly political magazines or newsletters that provide summaries of the month’s key events.
Q4: How can I better understand the implications of monthly political developments on governance and policy?
A4: Understanding the implications of monthly political developments on governance and policy requires a multi-faceted approach. Here are a few tips:
- In-depth Analysis: Read articles and analyses from experts and scholars who can provide a deeper understanding of the issues. Academic journals and think tank publications are great sources for this.
- Public Opinion: Pay attention to public opinion and discussions on social media, news forums, and public debates. This can give you insights into how these developments are perceived by the public.
- Policy Implications: Try to connect the dots between political events and potential policy changes. This often requires reading government reports, policy briefs, and expert opinions.
- Legal Implications: If legal matters are involved, consult legal experts or follow court proceedings to understand the legal implications.
- Historical Context: Consider the historical context of political developments. Understanding the history of a specific issue can shed light on its significance.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here


