
Explore the continued significance of the rimland theory in today’s global landscape. This geopolitical concept, proposed by Nicholas Spykman, emphasizes the strategic importance of coastal regions and their influence on global power dynamics. In the contemporary world, the rimland theory remains relevant as coastal areas continue to serve as crucial hubs for trade, commerce, and military activity. Additionally, advancements in technology and transportation have enhanced the connectivity and strategic value of coastal regions. By examining the enduring relevance of the rimland theory, analysts can gain insights into evolving geopolitical challenges and opportunities, informing strategic decision-making and diplomatic engagements in the modern era. Delve into the complexities of coastal geopolitics to understand the enduring significance of the rimland theory in today’s interconnected world.
Contents
Answer:
Introduction:
The Rimland theory, proposed by Nicholas Spykman in the mid-20th century, posits that the control of the coastal perimeter, or the rimland, surrounding Eurasia is crucial for global domination. This theory contrasts with Mackinder’s Heartland theory, which emphasizes control of the Eurasian landmass. The Rimland includes regions such as Western Europe, the Middle East, South Asia, and East Asia.
Body:
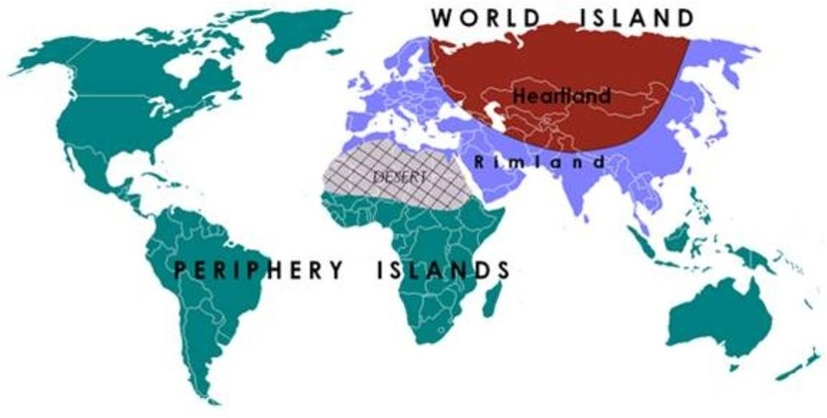
Relevance of the ‘rimland theory’ in the contemporary world
- Geopolitical Significance: The Rimland remains geopolitically significant due to its strategic location and access to maritime trade routes.
- For example, the South China Sea serves as a critical maritime corridor for global trade, making control of its Rimland territories highly contested by countries like China, Vietnam, and the Philippines.
- Security Concerns: In the contemporary world, the Rimland continues to be a focal point for security concerns.
- Issues such as terrorism, piracy, and interstate conflicts persist in regions like the Middle East, East Africa (Horn of Africa), and Southeast Asia, affecting global stability and security.
- Energy Resources: Many Rimland regions possess significant energy resources, particularly oil and natural gas. Control over these resources can influence global energy markets and geopolitical dynamics.
- The Middle East, with its vast oil reserves, remains a critical player in the global energy landscape.
- Maritime Trade and Connectivity: The Rimland facilitates maritime trade and connectivity between regions, contributing to economic interdependence.
- Ports in Southeast Asia, for instance, serve as vital hubs for global shipping and trade, connecting East Asia with Europe, Africa, and the Americas.
- Regional Alliances and Power Dynamics: Countries in the Rimland often form alliances and partnerships to enhance their security and economic interests.
- For instance, NATO (North Atlantic Treaty Organization) in Europe and the Quadrilateral Security Dialogue (Quad) involving the United States, Japan, Australia, and India in the Indo-Pacific region exemplify regional alignments aimed at maintaining stability and countering common threats.
- Technological Advancements: Technological advancements, particularly in transportation and communication, have increased the significance of Rimland regions for global connectivity.
- Projects like China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) aim to enhance infrastructure connectivity across the Rimland and beyond, influencing regional power dynamics.
- Arctic Region: As melting ice caps open up the Arctic for navigation and resource exploitation, the northern rimland gains prominence.
- Countries like Russia, Canada, and Norway are asserting their interests in this emerging geopolitical arena.
- Non-State Actors: The Rimland theory is relevant in understanding the dynamics of non-state actors.
- Such as pirate groups in the Horn of Africa or terrorist organizations operating along coastal regions, who exploit maritime vulnerabilities for their agendas.
Limitations of Rimland theory in the contemporary world:
- Globalization: The Rimland theory overlooks the interconnectedness brought about by globalization, where landlocked regions can still wield significant economic and political power.
- Cybersecurity: In the digital age, the focus on physical geography in the Rimland theory may neglect the importance of cybersecurity and virtual realms in shaping geopolitical dynamics.
- Environmental Concerns: Rising sea levels and climate change pose existential threats to coastal regions, potentially altering the strategic significance of Rimland areas.
Conclusion:
Looking ahead, proactive engagement and multilateral initiatives will be essential to address emerging threats and harness the potential of Rimland regions for sustainable development and peace.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here

