The concept of geo-economics has gained significant prominence in the context of the evolving landscape of global geopolitics. In this editorial analysis, we will delve into the intricate interplay between geo-economics and geopolitics in the contemporary world, exploring how economic interests and strategies have become integral to the power dynamics among nations. As countries seek to advance their national interests and influence on the international stage, the fusion of economics and geopolitics has emerged as a defining feature of the new age of geopolitics. We will examine key drivers, challenges, and implications of this paradigm shift and discuss how it is shaping the policies and strategies of nations in an increasingly interconnected and interdependent world.
Tags: GS Paper – 2: Government Policies & Interventions; Effect of Policies & Politics of Countries on India’s Interests.
GS Paper – 3: Inclusive Growth; Role of External State & Non-State Actors.
Contents
- 1 Exam view:
- 2 Context:
- 3 Decoding the editorial:
- 4 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 4.1 1: What is geo-economics, and how does it differ from geopolitics?
- 4.2 2: What are the key drivers behind the rise of geo-economics in the new age of geopolitics?
- 4.3 3: How does geo-economics impact international trade and commerce?
- 4.4 4: What challenges does the fusion of geo-economics and geopolitics present for countries?
- 4.5 5: How can countries effectively navigate the complexities of geo-economics in the new age of geopolitics?
- 5 In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
Exam view:
Use of rupee for international payments; Challenges; Agreements in the past; A new financial architecture.
Context:
Currencies of the South are ready to replace the hegemonic order enjoyed by currencies of the North. That India is a favoured trading partner, has been quite evident, since March 2018 when 23 advanced and developing countries agreed to have currency swap arrangements with India.
Decoding the editorial:
Use of rupee for international payments
Russia-India agreement
- The Ukraine-Russia war began in early 2022 led to sanctions imposed by the United States and the European Union on Russia.
- An alternative route was chosen to settle payments between India and Russia by using the Indian rupee in transactions related to trade between the two countries.
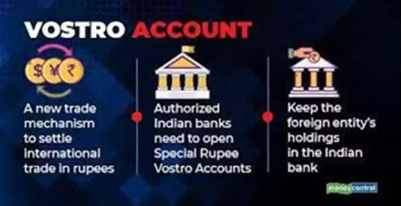
- When it comes to the modalities, payments from either India or Russia now go to the Rupee Vostro accounts, opened in Russian banks by the authorised dealer banks in India, which take care of settling payments between the two countries.
Rupee-Dirham agreement
- It is meant to cover transactions in trade, remittances and capital flows.
- The process will help to avoid exchange risks for both trade partners and save, for India, dollar payments for its imports of crude oil and minerals from the UAE.
- In addition the agreement provides for interlinking their payment and messaging systems.
- It makes for quick and cost-effective transfers of money for an estimated 3.5 million Indian community in the UAE, an 18% share in terms of the total remittance flows into India.
- Negotiations are on with Indonesia to launch a similar agreement using the rupiah for transactions with India.
Challenges
- The rupee has a low rank in the global currency hierarchy
- It may be subject to depreciation.
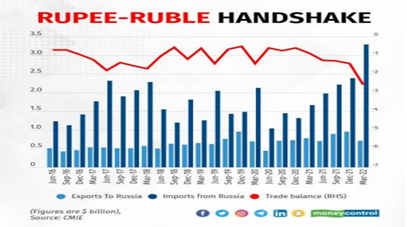
- Russia continuing with a trade surplus
- The sum in 2020-21 amounted to $3.42 billion, followed by similar surpluses in the following years.
- Russia is reluctant to hold more of the Indian rupee as an asset in the Vostro account.
- The sanctions prevent some Russian banks from making or receiving international payments using SWIFT.
- Arranging for payments on Russia’s reluctance
- The options were few, with the dollar or the Euro not permissible or by purchasing the rouble at an exchange rate which is too volatile in the market.
- Indian refiners for instance have settled some payments for Russian oil imports using the Chinese yuan, which seems to be acceptable to Russia.
- This is in the backdrop of Russia selling oil to China and accepting yuan payments.
Agreements in the past
- India had initiated similar bilateral trade and clearing arrangements in the 1950s.
- This was a major tool used in conducting trade with the former Soviet Union and countries in the Soviet bloc.
- It began in the 1950s, with the Soviet Union setting up a steel plant in Bhilai, defying the opposition from western nations.
- Problems similar to concerns now
- The choice of a suitable currency to settle trade surpluses when the Soviet Union began having trade surpluses on a consistent basis.
- The floating of the dollar in 1971 led to a turmoil in the currency market.
- The Balkanisation of the former Soviet Union left Russia standing separate.
- The India-Soviet Agreement had a natural ending at that stage.
A new financial architecture
- Problems in the past, in settling payments on trade surpluses relate to a different geopolitical scenario if one compares the situation prevalent now.
- While the purchase of the yuan to settle Russian surpluses in the prevailing rupee account is currently approved as a convenient step by Russia, there is a history of opposition, in the context of BRICS, to similar use of the Chinese currency by the non-Chinese members of BRICS.
- The Indian rupee, the Russian rouble, China’s yuan, the UAE’s dirham and even Indonesia’s rupiah share the common goal of local currency transactions.
- There is a visible geo-economic and political turn with countries in the South getting ready to trade and settle their payments with one another without the use of the hegemonic currencies from the advanced economies in the North.
- The set up will also avoid seeking the help of institutions in the advanced countries, which include the International Monetary Fund and the World Bank as well as private capital.
Source: The Hindu
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1: What is geo-economics, and how does it differ from geopolitics?
Answer: Geo-economics is the study of how economic factors and strategies influence and interact with geopolitical decisions and power dynamics among nations. While geopolitics primarily concerns political and military aspects, geo-economics focuses on economic interests, trade, investments, and their impact on international relations.
2: What are the key drivers behind the rise of geo-economics in the new age of geopolitics?
Answer: The rise of geo-economics can be attributed to globalization, technological advancements, and the increased interdependence of nations. Economic power and competition for resources have become essential components of a country’s influence, prompting the integration of economic considerations into geopolitical strategies.
3: How does geo-economics impact international trade and commerce?
Answer: Geo-economics plays a significant role in international trade by influencing trade policies, tariffs, and trade agreements. Nations often use economic leverage as a tool to achieve political objectives or secure their interests, which can impact the flow of goods and services globally.
4: What challenges does the fusion of geo-economics and geopolitics present for countries?
Answer: One of the primary challenges is striking a balance between economic interests and political objectives. Countries may face dilemmas when their economic relations with certain nations conflict with their political goals. Additionally, economic coercion and trade disputes can strain international relations.
Answer: Effective navigation involves comprehensive strategic planning, diversification of economic partnerships, and maintaining a clear understanding of the potential consequences of economic decisions on geopolitics. International cooperation and diplomacy play crucial roles in managing and resolving geo-economic conflicts and tensions.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here


