
The Great Nicobar Project is an ambitious initiative aimed at fostering sustainable development in the ecologically sensitive and strategically significant Great Nicobar Island, part of the Andaman and Nicobar archipelago in India. The project encompasses a range of infrastructural developments including a transshipment port, an airport, and a township, all designed to enhance connectivity and economic growth while ensuring the preservation of the island’s unique biodiversity. Balancing development with environmental conservation, the Great Nicobar Project aims to transform the region into a hub of trade and tourism, contributing to regional security and economic stability.
Tags: GS Paper – 3, Ecology & Environment — Great Nicobar Island Project — Government Policies & Interventions
Contents
- 0.1 Contex:
- 0.2 What is the Great Nicobar Island Project?
- 0.3 Purpose:
- 0.4 Criticism of the Great Nicobar Island Project:
- 0.5 Conclusion:
- 1 UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
- 2 FAQs
- 2.1 1. What is the Great Nicobar Project?
- 2.2 2. What are the primary objectives of the Great Nicobar Project?
- 2.3 3. What are the potential environmental impacts of the Great Nicobar Project?
- 2.4 4. How is the government addressing the concerns of indigenous communities on Great Nicobar Island?
- 2.5 5. What are the expected economic benefits of the Great Nicobar Project?
- 3 To get free counseling/support on UPSC preparation from expert mentors please call 9773890604
Contex:
- Recently, the National Green Tribunal (NGT) has issued a stay on the Great Nicobar Island project worth ₹72,000 crore and created a committee to review the environmental clearance granted by the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change.
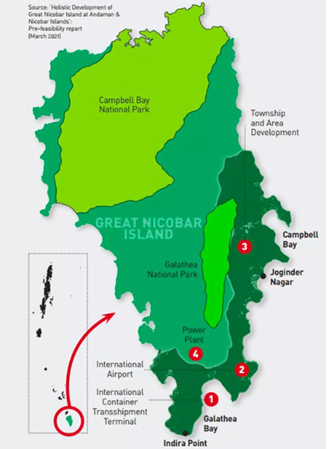
What is the Great Nicobar Island Project?
About:
- The Great Nicobar Island (GNI) Project is a significant development initiative planned for the southern end of the Andaman and Nicobar islands.
Key components of the project include:
- An international container transshipment terminal
- A greenfield international airport
- Township development
- A 450 MVA gas and solar-based power plant
- The project spans an area of 16,610 hectares on the island.
Purpose:
Economic Reasons:
- According to a NITI Aayog report, the proposed port aims to integrate Great Nicobar into the regional and global maritime economy, transforming it into a crucial hub for cargo transshipment.
- The island is strategically located, equidistant from Colombo (southwest), Port Klang (Malaysia), and Singapore (southeast), and near the East-West international shipping corridor, which handles a substantial portion of global shipping trade.
Strategic Reasons:
- The idea to develop Great Nicobar dates back to the 1970s, emphasising its significance for national security and the consolidation of India’s presence in the Indian Ocean Region.
- The increasing assertiveness of China in the Indian Ocean has amplified the urgency of developing Great Nicobar to bolster India’s strategic interests in the region.
Criticism of the Great Nicobar Island Project:
Impact on Biodiversity:
- The project has been criticised for its potential adverse effects on the rich biodiversity of the area and the habitats of endangered species.
- The project site falls within Coastal Regulation Zones-IA and IB, and includes Galathea Bay, a crucial nesting ground for birds.
- The construction and development activities, including dredging, pose a threat to turtle nesting sites, dolphins, and other species in the region.
Impact on Tree Cover and Mangroves:
- Loss of Tree Cover: Environmentalists warn that the project will result in significant deforestation, affecting the island’s flora and fauna.
- Increased Runoff: The reduction in tree cover is expected to increase runoff and sediment deposits in the ocean, which could harm nearby coral reefs.
- Mangrove Destruction: The development will also lead to the loss of vital mangrove ecosystems, further impacting local biodiversity.
Lack of Adequate Assessment:
- Inadequate Data Collection: Critics point out that environmental impact assessments (EIAs) have relied on data from only one season, whereas comprehensive assessments require data from three seasons.
- Non-compliance with Terms of Reference (ToR): The EIA reports are alleged to have been conducted without adhering to the prescribed ToR, undermining the validity of the assessments.
Encroachment in Tribal Space:
- Challenges for PVTGs: Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs), who are supposed to receive the highest level of protection, are facing encroachments into their territories under the guise of development.
- Impact on Tribal Communities: These encroachments pose significant challenges to the traditional lifestyles and well-being of the indigenous communities on the island.
Conclusion:
Thus, the National Green Tribunal (NGT) has issued a stay order on the Great Nicobar Island project and directed the formation of a committee to reassess its environmental clearance. This decision seeks to guarantee adherence to the Island Coastal Regulation Zone 2019 guidelines and uphold the rights of tribal communities affected by the project.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q1. Which one of the following pairs of islands is separated from each other by the ‘Ten Degree Channel’? (2014)
(a) Andaman and Nicobar
(b) Nicobar and Sumatra
(c) Maldives and Lakshadweep
(d) Sumatra and Java
Ans: (a)
Q2. Which of the following have coral reefs? (2014)
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Gulf of Kachchh
- Gulf of Mannar
- Sunderbans
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1, 2 and 3 only
- 2 and 4 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (a)
Q3. In which one of the following places is the Shompen tribe found? (2009)
(a) Nilgiri Hills
(b) Nicobar Islands
(c) Spiti Valley
(d) Lakshadweep Islands
Ans: (b)
Source: IE
FAQs
1. What is the Great Nicobar Project?
Answer: The Great Nicobar Project is an ambitious development initiative proposed by the Indian government to transform Great Nicobar Island into a major hub for trade, tourism, and strategic military operations. The project includes the construction of a transshipment port, an international airport, a power plant, and a township, among other infrastructure developments.
2. What are the primary objectives of the Great Nicobar Project?
Answer: The primary objectives of the Great Nicobar Project are to:
- Enhance India’s strategic presence in the Indian Ocean region.
- Boost economic growth through the development of a major transshipment port.
- Promote tourism and increase connectivity with the rest of the country.
- Improve the living standards of the local population by providing modern amenities and infrastructure.
3. What are the potential environmental impacts of the Great Nicobar Project?
Answer: The potential environmental impacts of the Great Nicobar Project include:
- Deforestation and loss of biodiversity due to large-scale construction activities.
- Disruption of the natural habitat of several endemic and endangered species.
- Potential pollution from construction and operational activities affecting the pristine marine and terrestrial ecosystems.
- Changes to the coastal and marine environment, which could affect coral reefs and other marine life.
4. How is the government addressing the concerns of indigenous communities on Great Nicobar Island?
Answer: The government has stated that it will ensure the protection of the rights and livelihood of indigenous communities on Great Nicobar Island. Measures include:
- Conducting detailed social impact assessments.
- Providing adequate compensation and resettlement options.
- Ensuring that indigenous people have a role in decision-making processes.
- Implementing programs to preserve and promote the cultural heritage of the local tribes.
5. What are the expected economic benefits of the Great Nicobar Project?
Answer: The expected economic benefits of the Great Nicobar Project include:
- Creation of thousands of direct and indirect jobs during and after the construction phase.
- Increased trade and commerce due to the development of the transshipment port.
- Boost to the tourism sector, attracting both domestic and international tourists.
- Overall economic growth of the region, contributing to the national economy.
- Enhanced connectivity and infrastructure, leading to improved quality of life for residents.
To get free counseling/support on UPSC preparation from expert mentors please call 9773890604
- Join our Main Telegram Channel and access PYQs, Current Affairs and UPSC Guidance for free – Edukemy for IAS
- Learn Economy for free- Economy for UPSC
- Mains Answer Writing Practice-Mains Answer Writing
- For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here

