The Andaman Islands, a jewel nestled in the Bay of Bengal, hold a crucial dual role in safeguarding India’s national security and preserving its rich ecological heritage. Situated strategically along key international sea routes, this archipelago serves as a vital outpost for maritime surveillance and defense, ensuring the protection of India’s maritime interests. Simultaneously, the Andaman Islands harbor a unique biodiversity, with lush rainforests and pristine coral reefs that contribute to global ecological balance. Balancing national security imperatives with ecological conservation efforts here is not just a necessity but a testament to responsible stewardship of both natural and strategic resources.

Tags: GS – 2, Government Policies & Interventions- Issues Related to Andaman Islands, Paper – 3 – Growth & Development- Environmental Pollution & Degradation
Contents
- 1 Context:
- 2 Conclusion
- 3 UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
- 4 FAQs
- 4.1 1. How do the Andaman Islands contribute to national security?
- 4.2 2. Why are the Andaman Islands important for ecological conservation?
- 4.3 3. How does national security impact the environment in the Andaman Islands?
- 4.4 4. What are the challenges in balancing national security and ecological preservation in the Andamans?
- 4.5 5. How can individuals contribute to the protection of the Andaman Islands’ national security and ecology?
- 5 To get free counseling/support on UPSC preparation from expert mentors please call 9773890604
Context:
- India’s strategic and economic landscape has been significantly shaped by its geographical features, among which the Andaman and Nicobar (A&N) Islands hold a crucial position.
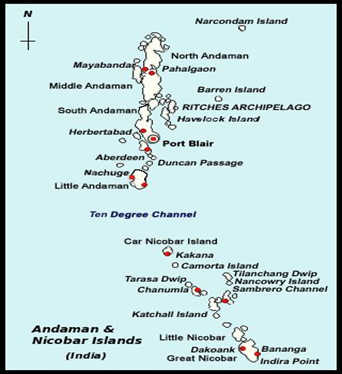
- Despite their strategic importance, these islands have historically been neglected by Indian policymakers.
Historical Context and Strategic Importance of A&N Islands
Early Recognition of Strategic Value:
- Sardar K. M. Panikkar underscored the islands’ significance as early as 1945.
- He argued for establishing advanced bases on the A&N archipelago for control over the Indian Ocean and defence of India’s coastline.
- The islands’ location in the Bay of Bengal provides a strategic vantage point for maritime operations and coastal defence.
Evolution of Strategic Policies:
- India acknowledged the islands’ strategic imperatives later, driven by economic opportunities in Southeast Asia and the ASEAN region.
- Look East and Act East policies aimed at strengthening economic and strategic ties, increasing the islands’ importance.
Military Realisation Post-Kargil:
- The Kargil conflict in 1999 highlighted the gaps in India’s defence preparedness and emphasised the need for a robust military presence in the A&N Islands.
- The Andaman and Nicobar Command (ANC) was established in 2001, integrating defence capabilities in the region.
Renewed Focus and Fortification:
- Recent efforts focus on fortifying the ANC and enhancing infrastructure across the islands.
- Naval and air force bases are being established from Shibpur in the north to Port Blair, Car Nicobar, Kamorta, and Campbell Bay in the south.
Neglect and Complacency Towards A&N Islands:
Post-Independence Neglect:
- Early post-independence years saw significant neglect despite early warnings.
- Focus on western borders and trading links diverted attention from eastern maritime concerns.
Maritime Remoteness and Tenuous Hold:
- Geographical isolation posed logistical challenges for administration and defence.
- Great Nicobar Island, though strategically located, faced difficulties in maintaining a strong presence.
The Holistic Development of Great Nicobar Island, Economic Potential and Development Challenges:
The Holistic Development of Great Nicobar Island:
- A Rs 75,000 crore project aims to establish infrastructure including an international container transshipment terminal, an international airport, power plants, new cities, a coastal transport system, and a free trade zone.
- Faces opposition from environmentalists concerned about its impact on local ecology and indigenous tribes.
Economic Potential and Development Challenges:
- A&N Islands have vast maritime resources with an Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) of 600,000 sq km.
- Sustainable development balancing economic growth and preservation of indigenous tribes is crucial.
Critical Consideration to Balance the Ecology and Development of A&N Islands
Sustainable Development Practices:
- Emphasising sustainable tourism, fisheries, and renewable energy projects is crucial.
- New developments should integrate sustainability principles to maintain ecological balance.
Replicating Successful Models:
- Challenges in replicating duty-free ports and free trade zones due to logistical and industrial support limitations.
- Caution from Sri Lanka’s Hambantota port project serves as a lesson for ambitious developments.
Viability of a New Transshipment Terminal:
- GNI’s proximity to established hubs raises questions about the necessity and economic feasibility of a new terminal.
- Evaluation of similar projects’ success is essential before embarking on new ventures.
Conclusion
- The Andaman and Nicobar Islands hold immense strategic and economic potential for India.
- A balanced approach addressing security and sustainable development can transform them into a strategic asset and model of sustainable development
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q1. Which one of the following pairs of islands is separated from each other by the ‘Ten Degree Channel’? (2014)
- Andaman and Nicobar
- Nicobar and Sumatra
- Maldives and Lakshadweep
- Sumatra and Java
Ans: (a)
Q2. Which of the following have coral reefs? (2014)
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Gulf of Kachchh
- Gulf of Mannar
- Sunderbans
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1, 2 and 3 only
- 2 and 4 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (a)
Q3. In which one of the following places is the Shompen tribe found? (2009)
- Nilgiri Hills
- Nicobar Islands
- Spiti Valley
- Lakshadweep Islands
Ans: (b)
Source:IE
FAQs
1. How do the Andaman Islands contribute to national security?
The Andaman Islands are strategically positioned in the Bay of Bengal, serving as a crucial outpost for monitoring maritime activities. Their location allows India to keep a close watch on international sea routes, ensuring the safety of our borders and maritime interests from potential threats.
2. Why are the Andaman Islands important for ecological conservation?
These islands boast rich biodiversity, including dense rainforests and thriving coral reefs. Protecting these ecosystems is vital not only for preserving unique species but also for maintaining the health of global marine and terrestrial environments. The Andamans thus play a significant role in global ecological balance.
3. How does national security impact the environment in the Andaman Islands?
While ensuring national security, it’s crucial to minimize environmental impact through responsible military and surveillance practices. Efforts are made to balance the needs of defense operations with conservation measures to sustain the islands’ delicate ecosystems and minimize disruption to wildlife habitats.
4. What are the challenges in balancing national security and ecological preservation in the Andamans?
One challenge is managing human activities, such as tourism and development, which can strain natural resources and habitats. Finding sustainable solutions that protect both national security interests and the environment requires careful planning and cooperation between government agencies, local communities, and environmental organizations.
5. How can individuals contribute to the protection of the Andaman Islands’ national security and ecology?
Individuals can support conservation efforts by respecting designated protected areas, minimizing waste and pollution, and supporting eco-friendly tourism practices. Additionally, staying informed about issues affecting the Andaman Islands and advocating for sustainable policies can help ensure these precious resources are safeguarded for future generations.
To get free counseling/support on UPSC preparation from expert mentors please call 9773890604
- Join our Main Telegram Channel and access PYQs, Current Affairs and UPSC Guidance for free – Edukemy for IAS
- Learn Economy for free- Economy for UPSC
- Mains Answer Writing Practice-Mains Answer Writing
- For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here

