
India, a diverse and culturally rich nation, unfolds its intricate tapestry through the art and science of mapping. Nestled in South Asia, India’s geographical expanse spans a vast and varied landscape, from the towering peaks of the Himalayas to the sun-kissed beaches of the Indian Ocean. Mapping India is not just about delineating its physical boundaries but delving into its historical, cultural, and demographic nuances. The cartographic journey through India’s map unveils a mosaic of languages, religions, and traditions, encapsulating a nation where ancient history converges with modernity. As the nation progresses, so does the significance of mapping in unraveling the complexities and possibilities that lie within its territorial contours. In this dynamic and ever-evolving landscape, the maps of India serve as indispensable tools, offering insights into its socio-economic dynamics, environmental diversity, and the interplay of tradition and progress.
Contents
- 1 Q: On the outline map of India provided to you, mark the location of all of the following. Write in your QCA Booklet the significance of these locations, whether physical / commercial /economic / ecological/environmental / cultural, in no more than 30 words for each entry: 2×10=20
- 2 Answer
- 3 In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
Q: On the outline map of India provided to you, mark the location of all of the following. Write in your QCA Booklet the significance of these locations, whether physical / commercial /economic / ecological/environmental / cultural, in no more than 30 words for each entry: 2×10=20
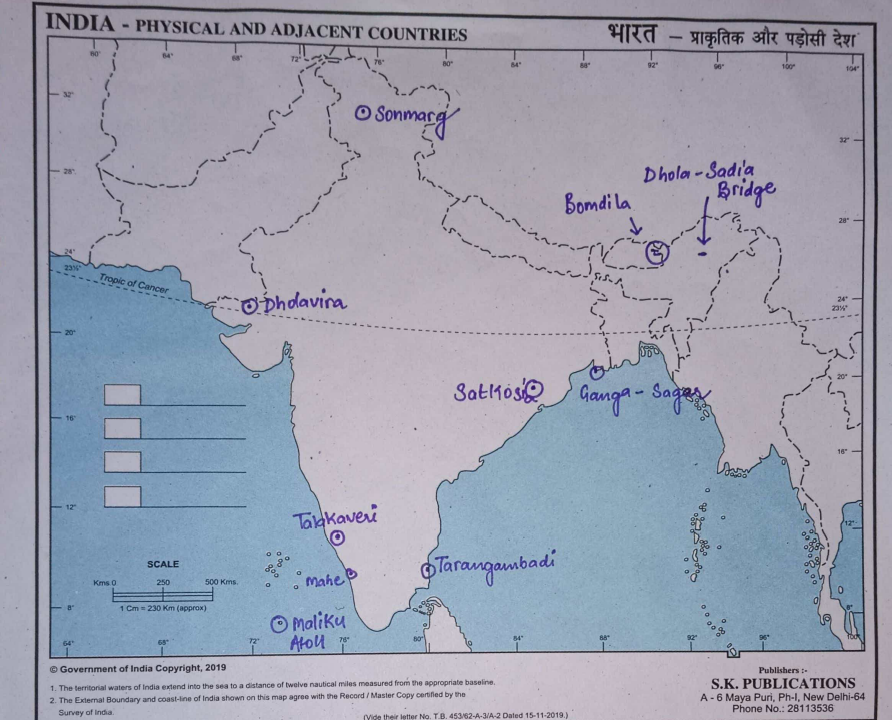
(i) Tarangambadi
(ii) Mahe
(iii) Bomdila
(iv) Dhola Sadiya Bridge
(v) Talakaveri
(vi) Satkosia
(vii) Dholavira
(viii) Sonamarg
(ix) Maliku Atoll
(x) Gangasagar
WITH AFGHANISTAN, BANGLADESH, BHUTAN, NEPAL MYANMAR (BURMA), PAKISTAN AND SRI LANKA
Answer
(i) Tarangambadi
Tarangambadi, formerly Tranquebar, is a town in Nagapattinam district of Tamil Nadu on the Coromandel Coast, it lies north of Karaikal, near the mouth of a distributary named Uppanar of the Kaveri River, Its name means “place of the singing waves”, nearest airport is at Tiruchirappalli international airport and the nearest port is at Karaikal, It is served by Tarangambadi railway station.
(ii) Mahe
One of the four districts of the union territory of Puducherry, smallest district of India by size, surrounded on three sides by Kannur District and one side by Kozhikode District, The Mooppenkunnu is a Hillock which is a Heritage picnic spot in Mahé district, Hinduism is the majority religion, The walkway on the banks of Mahé River is a major tourist attraction.
(iii) Bom Dila
Bom Dila is the headquarters of West Kameng district in the state of Arunachal Pradesh in India, wet season is cool and mostly cloudy and the dry season is cold and clear, The Eaglenest Wildlife Sanctuary is near Bom Dila, Tourism has become a big source of income in Bom Dila because of infrastructure developments, The Bom Dila pass offers views of Kangto and Gorichen Peaks, the highest in the state.
(iv) Dhola Sadiya Bridge
Officially known as Bhupen Hazarika Bridge, is a beam bridge in India, connecting the northeast states of Assam and Arunachal Pradesh, bridge spans the Lohit River, a major tributary of the Brahmaputra, connecting the village of Dhola in the south to the village of Sadiya to the north, both in Tinsukia district of Assam, first permanent road connection between the northern Assam and eastern Arunachal Pradesh, At 9.15 kilometers in length, it is the longest bridge in India over water.
(v) Talakaveri
Generally considered to be the source of the river Kaveri and a holy place for many Hindus, located on Brahmagiri hills near Bhagamandala in Kodagu district (Coorg), in the South Indian state of Karnataka, close to the border with Kasaragod district, Kerala, Talakaveri is about 8 km away from Bhagamandala, 36 km from Panathur (Kerala) and 48 km from Madikeri, the
headquarters of Kodagu district, temple here is dedicated to Goddess Kaveramma.
(vi) Satkosia
Satkosia is a famous place in Odisha, Satkosia tiger reserve and the Satkosia gorge are the most famous attractions, Satkosia Tiger Reserve comprises of two adjoining sanctuaries of central Odisha named as Satkosia Gorge Sanctuary and Baisipalli Sanctuary, Lying in transitional zone between Chhota Nagpur Plateau and Deccan Plateau, it exhibits endemic life forms of both biotic provinces, area supports moist deciduous forest, dry deciduous forest and moist peninsular Sal
forest, area is the home for Tiger, Leopard, Elephant, Gaur etc.
(vii) Dholavira
An archaeological site at Khadirbet in Bhachau Taluka of Kutch District, in the state of Gujarat in western India, Also known locally as Kotada timba, the site contains ruins of a city of the ancient Indus Valley civilization, Earthquakes have repeatedly affected Dholavira, including a particularly severe one around 2600 BC, location is on the Tropic of Cancer, site was
“officially” discovered in 1967-68 by J. P. Joshi, of the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) and is one of the five largest Harappan sites and the most prominent of archaeological sites in India belonging to the Indus Valley Civilization.
(viii) Sonamarg
A hill station located in the Ganderbal District of Jammu and Kashmir, had historical significance as a gateway on the ancient Silk Road, connecting Kashmir with Tibet, situated in the Kashmir Valley, a notable tourist destination, experiences the regionally-rare humid continental climate, with significant rainfall, average temperature in is 6.5 °C and nearly 932 mm of precipitation falls annually.
(ix) Maliku Atoll
An island in Lakshadweep, India, southernmost atoll of Lakshadweep archipelago, situated west of Trivandrum, the capital city of Kerala, The atoll is 10 km in length, having a maximum breadth of about 6 km. The closest geographic feature is the Investigator Bank, a submerged shoal located 31 km to the northeast, Maliku Atoll has a lagoon with two entrances in its northern side, Saalu Magu on the northeast and Kandimma Magu on the northwest, Its western side is fringed by a narrow reef and coral rocks awash.
(x) Ganga Sagar
A village and a gram panchayat in the Indian state of West Bengal, The entire district is situated in the Delta, The southern part of the delta has numerous channels and islands such as the Henry Island, Sagar Island, a place of Hindu pilgrimage, The Ganga Sagar Mela and pilgrimage is held annually on Sagar Island’s southern tip, where the Ganges enters the Bay of Bengal, This
confluence is also called Ganga Sagar, Near the confluence is the Kapila Temple, The Ganga Sagar pilgrimage and fair is the second largest congregation of mankind after Kumbha Mela.

In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here

