Integrity, often heralded as the cornerstone of virtuous conduct, serves as the bedrock upon which individuals build their character. It empowers humans by aligning their actions with their moral compass, fostering trustworthiness, and cultivating authenticity. Consider the story of Mahatma Gandhi, whose unwavering commitment to truth and non-violence propelled India towards independence from colonial rule. Gandhi’s integrity resonated with millions, inspiring them to join the struggle for freedom. His refusal to compromise on principles, even in the face of adversity, exemplifies how integrity emboldens individuals to stand firm in their convictions, regardless of external pressures. In essence, integrity not only enriches personal ethics but also empowers individuals to lead by example, effecting positive change in society. Thus, it stands as a value that not only shapes character but also empowers human potential.
Contents
Answer:
Approach:
- Start with a brief introduction of the keywords “integrity”.
- Explain how Integrity empowers the human being with suitable examples.
- Conclusion accordingly.
Introduction:
- Integrity is a fundamental ethical value that encompasses honesty, moral uprightness, and adherence to principles and values. It involves having strong moral character, being consistent in one’s actions, and maintaining a high standard of ethics in personal and professional conduct. Integrity is a trait that is highly valued in individuals, organisations, and institutions as it establishes trust, credibility, and accountability. Upholding integrity requires individuals to act with honesty, fairness, and transparency, even in challenging circumstances or when faced with temptations to compromise ethical principles.
Body:
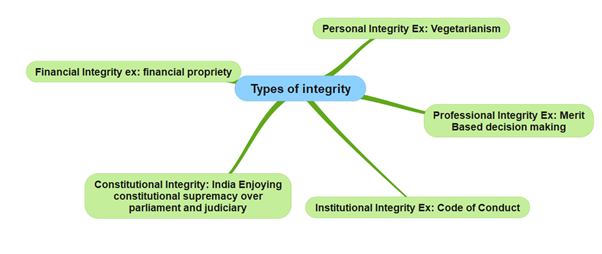
Integrity empowers the human being: In the context, different types of integrity can be observed across various domains. Here are some examples:
- Personal Integrity: Demonstrating consistency and adherence to one’s own values, principles, and beliefs. Example: Mahatma Gandhi’s unwavering commitment to non-violence and truth during India’s struggle for independence.
- Professional Integrity: Acting in accordance with professional ethics, standards, and norms. Example: Dr. Verghese Kurien, the father of the White Revolution in India, displayed professional integrity by revolutionising the dairy industry and ensuring fair practices for farmers.
- Ethical Integrity: Upholding ethical principles and moral values in all aspects of life. Example: Kiran Bedi, the first woman Indian Police Service officer, showcased ethical integrity by implementing various reforms and fighting against corruption during her tenure.
- Intellectual Integrity: Demonstrating consistency and honesty in one’s thinking, reasoning, and pursuit of knowledge. Example: Dr. APJ Abdul Kalam, the former President of India, exhibited intellectual integrity through his lifelong dedication to scientific research and inspiring the younger generation.
- Cultural Integrity: Preserving and promoting the cultural heritage, traditions, and diversity of India. Example: Raja Ravi Varma, the renowned painter, contributed to cultural integrity by depicting Indian mythological stories and capturing the essence of Indian beauty in his artwork.
- Environmental Integrity: Commitment to sustainable practices, conservation, and protection of the environment. Example: Jadav Payeng, known as the “Forest Man of India,” demonstrated environmental integrity by single-handedly planting and nurturing a vast forest ecosystem in Assam.
- Social Integrity: Upholding social justice, equality, and inclusivity. Example: Dr. B.R. Ambedkar, the chief architect of the Indian Constitution, worked tirelessly for social integrity by advocating for the rights and empowerment of marginalised communities.
- Technological Integrity: Adhering to ethical practices in technology development and usage. Example: Nandan Nilekani, the co-founder of Infosys and the architect of Aadhaar, played a crucial role in ensuring technological integrity by implementing a secure and inclusive digital identity system.
- Financial Integrity: Maintaining transparency, honesty, and accountability in financial dealings. Example: Raghuram Rajan, the former Governor of the Reserve Bank of India, emphasised financial integrity by implementing measures to strengthen the banking sector and address systemic issues.
- Political Integrity: Demonstrating honesty, transparency, and accountability in political leadership and governance. Example: Kailash Satyarthi, the Nobel laureate and child rights activist, showcases political integrity by tirelessly advocating for the rights and well-being of children in India and globally.
Conclusion:
- Hence,integrity is indeed a value that empowers individuals. Through examples like Mahatma Gandhi and Dr. APJ Abdul Kalam, we see how integrity fosters trust, credibility, and moral strength, inspiring others to follow their path. Upholding integrity empowers individuals to make ethical choices, build strong relationships, and contribute to the betterment of society. It is a value that not only enhances personal growth and character but also has a profound impact on the collective empowerment of communities and nations.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here


