
Land degradation affects about 33% of the Earth’s land surface. It leads to the reduction or loss of the biological or economic productivity of land, impacting nearly 2 billion people worldwide with threatened food security and biodiversity, also exacerbates climate change by reducing the land’s ability to sequester carbon.
Contents
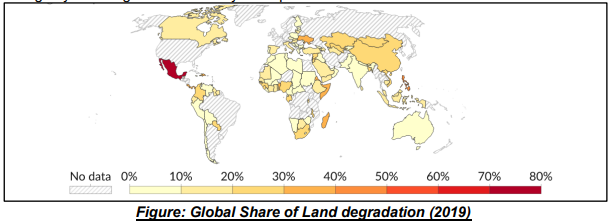
Land Degradation in India
A 2023 report by Down To Earth states that nearly 97 million hectares of land in India are degraded, representing around 29% of the total geographical area. This degradation manifests in various forms, including soil erosion, waterlogging, chemical contamination, and desertification, severely impacting the productivity and sustainability of its resources.
Examples of Land Degradation in India
- Soil Erosion by Water and Wind
- Most common forms of land degradation in India.
- According to studies, water erosion affects 80% of the degraded unirrigated farmland.
- This type of erosion is prevalent in the rainfed areas of the country, which are crucial for India’s food security.
- The northeastern states, known for their biodiversity, have recorded the most rapid increases in land degradation due to these processes.
- Desertification
- The expansion of desert areas, particularly in states like Rajasthan, is a significant example of land degradation.
- Rajasthan accounts for almost 22% of the degraded land in India.
- Desertification results from natural factors like low rainfall and human activities such as unsustainable agricultural practices and overgrazing.
- Chemical Degradation
- Excessive use of chemical fertilizers and pesticides in agriculture has led to the degradation of land quality in India.
- These chemicals can kill beneficial soil microorganisms, reduce soil fertility, and lead to the buildup of harmful salts and minerals in the soil.
- This is particularly evident in the states that were the focus of the Green Revolution, where intensive agriculture has degraded the soil.
- Waterlogging
- Irrigation without adequate drainage leads to waterlogging, which is another significant cause of land degradation in India.
- Waterlogging not only affects the growth of crops by depriving roots of oxygen but also leads to salinization of the soil surface, making the land unfit for agricultural use.
- For example, waterlogging problem in Punjab and rising soil alkalinisation.
National Mission for Sustainable Agriculture, National Watershed Development Project for Rainfed Areas, Integrated Watershed Management Program, National Afforestation Program (NAP), National Mission on Himalayan Studies (NMHS) are some of the important programs by the Indian government to curb land degradation.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here

