Money laundering presents a grave threat to the economic sovereignty of any nation, including India. As one of the fastest-growing economies globally, India’s financial system is particularly vulnerable to the adverse effects of money laundering activities. The significance of combating money laundering in India cannot be overstated, as it not only undermines the integrity of the financial sector but also facilitates various other criminal activities such as terrorism financing, drug trafficking, and corruption. The illicit flow of funds destabilizes the economy, erodes public trust in financial institutions, and hampers economic growth and development efforts. To effectively address this menace, concerted efforts from both government agencies and private sector entities are imperative. Strengthening regulatory frameworks, enhancing cross-border cooperation, promoting transparency in financial transactions, leveraging technology for monitoring and detection, and raising public awareness about the consequences of money laundering are among the key steps required to control this illicit practice in India. Additionally, building capacity within law enforcement agencies, improving international cooperation through mutual legal assistance treaties, and imposing stringent penalties on offenders are essential measures to deter and combat money laundering effectively. By implementing a comprehensive strategy that combines preventive measures, enforcement actions, and international cooperation, India can safeguard its economic sovereignty and preserve the integrity of its financial system.
Tag: Money laundering and its prevention.
Contents
Decoding the Question:
- In Intro try to write definition money laundering
- In Body,
- Justifying how money laundering poses a serious threat to a country’s economic sovereignty.
- In the second part of the answer, discuss the significance of identifying it as a threat
- Write steps required to control money laundering.
- Try to Conclude answers with suggestions.
Answer:
Money laundering is concealing or disguising the identity of illegally obtained proceeds so that they appear to have originated from legitimate sources. It is frequently a component of other, much more serious, crimes such as drug trafficking, robbery or extortion. According to the IMF, global Money Laundering is estimated between 2 to 5% of World GDP.
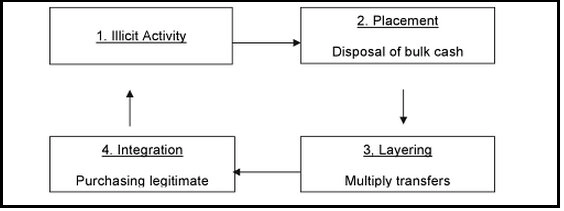

Threat to Countries Economic Sovereignty:
- In Mohammad Arif Case, High Court of Orissa held that the offence of Money Laundering is nothing but an act of financial terrorism that poses a serious threat not only to the financial system of the country but also to the integrity and sovereignty of a nation.
- The Supreme Court of India has constantly held that economic offences are sui generis in nature as they stifle the delicate economic fabric of a society.
- The abuse of the financial system has great potential to negatively impact a country’s macro-economic performance and may also adversely impact its cross-border externalities.
- Further, such actions can inflict reputational damage on the country in the world of business and commerce both inside the country and abroad.
- Money laundering is done in an exotic fashion encompassing a series of actions by the proverbial renting of credibility from the innocent investors.
- The offenders often target the unsuspecting, rural, and economically distressed populations of our state who while hoping for a dreamy return, part with their hard-earned money.
Steps Taken by Government of India to Prevent Money Laundering:
- Criminal Law Amendment Ordinance (XXXVIII of 1944): It covers proceeds of only certain crimes such corruption, breach of trust and cheating and not all the crimes under the Indian Penal Code.
- The Smugglers and Foreign Exchange Manipulators (Forfeiture of Property) Act, 1976: It covers penalty of illegally acquired properties of smugglers and foreign exchange manipulators and for matters connected therewith and incidental thereto.
- Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances Act, 1985: It provides for the penalty of property derived from, or used in illegal traffic in narcotic drugs.
- PMLA (Amendment) Act, 2012: Adds the concept of ‘reporting entity’ which would include a banking company, financial institution, intermediary etc. It has provided for provisional attachment and confiscation of property of any person involved in such activities.
- Financial Intelligence Unit-IND: It is an independent body reporting directly to the Economic Intelligence Council (EIC) headed by the Finance Minister.
- Enforcement Directorate (ED): It can take actions like confiscation of property if the same is determined to be proceeds of crime derived from a Scheduled Offence under PMLA, and to prosecute the persons involved in the offence of money laundering.
Tackling money laundering is a very critical and dynamic challenge. As organised crime groups, businesses and even individuals can make money laundering, hence controlling money laundering is very much needed.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here


