
The recent spell of unusually heavy rains in North India has brought to the forefront the pressing issues of urban infrastructure and disaster preparedness. The region, traditionally characterized by a semi-arid climate, is grappling with the aftermath of torrential downpours that have overwhelmed existing drainage systems and led to widespread flooding. This editorial analysis aims to shed light on the apparent gap between urban planning and the challenges posed by climate change, emphasizing the need for adaptive measures to mitigate the impact of extreme weather events. The increasing frequency and intensity of such rainfall in North India underscore the urgency for a holistic approach that integrates climate-resilient infrastructure, sustainable land use planning, and effective disaster response mechanisms. As the region navigates these environmental challenges, policymakers and urban planners must collaboratively address the root causes of vulnerability and work towards fostering greater resilience in the face of evolving climatic patterns.
Tag: GS Paper-1: Important geophysical phenomena.
GS Paper-3: Disaster Management.
Contents
- 1 Exam View:
- 2 Context:
- 3 Decoding the editorial:
- 4 Causes of heavy rains
- 5 Impact of heavy rains
- 6 Measures to mitigate
- 7 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 7.1 1. FAQ: Why is North India experiencing unusually heavy rains?
- 7.2 2. FAQ: How does heavy rainfall impact urban infrastructure in North India?
- 7.3 3. FAQ: Are these heavy rains a new phenomenon in North India?
- 7.4 4. FAQ: How can urban areas in North India better prepare for heavy rains?
- 7.5 5. FAQ: What role does deforestation play in the context of heavy rains in North India?
- 8 In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
Exam View:
Meteorological status; Causes of heavy rains; Impact of heavy rains; Measures to mitigate.
Context:
India has seen a surge in monsoon rainfall due to an interaction between a western disturbance and the monsoon trough, resulting in a 2% excess rainfall over the country causing landslides, flash floods, widespread damage to highways and other infrastructure.
Decoding the editorial:
Meteorological status
- From a 10% deficiency in rainfall till end of June, the monsoon’s surge over the west coast and parts of northern India in the past week has led to a 2% excess rainfall over the country on July 9, according to the India Meteorological Department. There is:
- 59% excess rainfall over northwest India;
- 4% excess over central India;
- 23% deficiency over peninsular India and
- 17% deficiency over east and northeast India.
- Huge amount of rainfall is being received in short bursts.
- The monsoon patterns in India are definitely shifting as a result of climate change with long deficit rainfall periods followed by intermittent short spells of heavy to extremely heavy rains in a few days.
Causes of heavy rains
- The heavy rainfall over Jammu and Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, north Punjab, Haryana and Uttarakhand is due to an interaction between a western disturbance and the monsoon.
- An active monsoon with strong low level easterlies bringing plenty of moisture, supported by upper level divergence due to an east-ward moving trough.
- These heavy rains & flash floods are a reminder of impacts of climate change on monsoon.
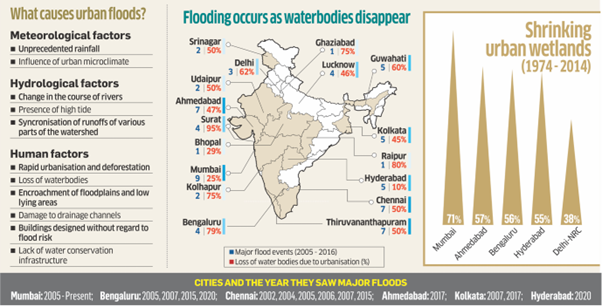
Impact of heavy rains
Impact on hilly areas and surroundings:
- Whether it’s the Himalayan foothills or the Western Ghats, hilly areas are particularly susceptible to heavy rains and landslides.
- Due to global warming, there’s extra moisture, and the hills stop this moisture flow and lift it, which comes down as heavy rains.
- Some of the regions over India where extreme rains have increased are such places where the rains happen due to orographic lifting.
Impact on infrastructure:
- This pounding heavy rain in a short span is resulting in high levels of flooding, infrastructural damage, and property loss all of which can clearly be linked to rising temperatures, and global warming, and this frequency is only going to increase.
- Flash floods due to cloudbursts and extreme rains are difficult to predict.
Measures to mitigate
- Strengthening early warning systems by boosting communication channels and weather forecasting capabilities to be relayed to the people and authorities.
- Investing in sturdy infrastructure that includes flood prevention techniques like building suitable drainage systems and river embankments.
- Adopting sustainable urban design concepts and effective urban planning and land use management practices, such as avoiding building in flood-prone regions and protecting natural drainage systems.
- Identifying areas prone to flash floods using radars.
- Checking the land use changes and development activities that might have aggravated these flash floods.
Source: Hindustan Times
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. FAQ: Why is North India experiencing unusually heavy rains?
Answer: The increased intensity of rainfall in North India can be attributed to various factors, including climate change. Changes in global weather patterns and atmospheric conditions contribute to more erratic and intense precipitation events, leading to instances of unusually heavy rains in the region.
2. FAQ: How does heavy rainfall impact urban infrastructure in North India?
Answer: Heavy rainfall often overwhelms existing urban infrastructure, especially drainage systems, leading to widespread flooding. Inadequate stormwater management and urban planning exacerbate the impact, causing disruptions to transportation, property damage, and posing risks to public safety.
3. FAQ: Are these heavy rains a new phenomenon in North India?
Answer: While the region traditionally experiences a monsoon season, the recent trend of unusually heavy rains is indicative of a changing climate. The frequency and intensity of extreme weather events have increased in recent years, posing new challenges for residents and authorities in North India.
4. FAQ: How can urban areas in North India better prepare for heavy rains?
Answer: Effective disaster preparedness and mitigation strategies are crucial. This includes investing in climate-resilient infrastructure, improving drainage systems, and implementing sustainable urban planning practices. Additionally, public awareness campaigns on disaster preparedness and early warning systems can play a vital role in minimizing the impact of heavy rains.
5. FAQ: What role does deforestation play in the context of heavy rains in North India?
Answer: Deforestation can contribute to the intensity of heavy rains as trees play a crucial role in regulating rainfall patterns. The loss of forests reduces the natural ability of the land to absorb and retain water, leading to increased surface runoff and a higher risk of flooding. Sustainable forest conservation practices are essential to mitigate these effects.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here

