
In the intricate tapestry of Earth’s ecosystems, the plants and animals that thrive are those that have demonstrated a remarkable ability to adapt and flourish within their specific habitats and environmental niches. Evolutionary forces have sculpted an array of species, each uniquely equipped to navigate the challenges presented by their surroundings. Whether it be the resilient flora that transforms arid deserts into vibrant landscapes or the diverse fauna that has honed specialized behaviors for survival in dense rainforests, the success of these organisms lies in their capacity to adjust to the dynamic conditions of their environment. Examining examples across different ecosystem provides a fascinating insight into the intricate dance of adaptation that has allowed life to persist and diversify across the planet.
Contents
Answer
Plants and animals adapt to their environment and habitat over time by way of ecological adaptations. These adaptations allow them to survive, thrive, and reproduce in their specific ecological niche. The importance of adaptations and survival instincts was well appreciated and documented by Charles Darwin in his book ‘On the Origin of Species (1859).
Different kinds of adaptation as per the requirements of different ecosystems are as follows:
- Behavioral adaptations
- Morphological adaptations
- Physiological adaptations
- Mutualistic relationship
- Competition
Behavioral adaptations
Plants and Animals adapt to their peculiar environmental conditions by adapting certain behavioral tendencies.
- Animals in desert regions, like Desert Fox, are primarily nocturnal to avoid harsh
- temperatures of the day time, they come out in the night when temperatures are comparatively cooler, thus reducing the water loss through sweating.
- Migration in Birds to avoid harsh climates for eg. Arctic Tern migrate thousands of miles to find suitable breeding and feeding ground.
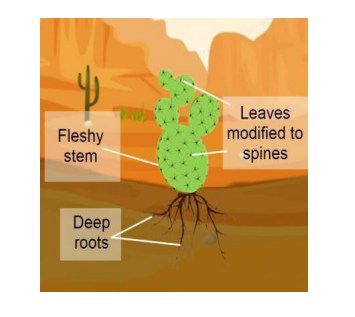
Similarly plants adapt to harsh conditions of desert by certain modifications such as
- Small leaves on desert plants help reduce moisture loss during photosynthesis. Small leaves mean less evaporative surface per leaf. In addition, a small leaf in the sun doesn’t reach as high a temperature as a large leaf.
- Leaves and stems of many desert plants have a thick, waxy covering, keeping the plants cooler and reducing evaporative loss.
- Some plants, such as Ephedra (Mormon tea) and cacti, carry out most or all of their photosynthesis in their green stems.
- Leaves are modified into Spines. Spines shade plants and break up drying winds across the leaf/stem surface.
- The roots of desert plants are also adapted to help them survive. Some plants have shallow, widespread roots to absorb a maximum of rainfall moisture. Others have deep taproots to get water that is deep underground.

Morphological adaptations
- Many insects and animals have evolved to resemble the color of their surrounding habitats to avoid predators and increase their survival chances for eg. Stick insects have come to resemble closely with twigs, providing them camouflage against predators.
- Cacti plants have adapted to the desert ecosystem by modifying their leaves into spines (to deter herbivores) and by developing a thick waxy coating over their leaves to avoid excessive water loss.
Physiological adaptations
- Birds like pelicans and seagulls have salt glands near their eyes that help them to excrete excess salt ingested while consuming sea water or prey from seawater.
- Some frog species can switch to anaerobic respiration during periods of oxygen deprivation, such as when they hibernate underwater. These adaptations help them to survive harsh weather conditions.
- Thermoregulation is carried out by many organisms to regulate their body temperature for eg. mammals like polar bears have a thick layers of insulating blubber under their skin to keep them warm in winter environments.
Mutualistic relationship
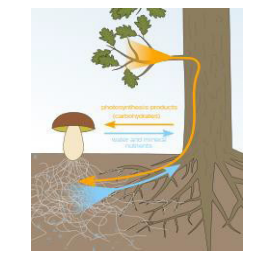
- Many plants form Mutualistic relationships to cope with their environmental limitations for eg. corals live in a symbiotic relationship with algae (Zooxanthellae)
- Plants live in a Mutualistic relationship with mycorrhizal fungi. These fungi help plants to access nutrients from the sol.
- Bees, butterflies, and other pollinator species have co-evolved with flowering plants. They obtain nectar and pollen from flowers while facilitating pollination and reproduction.

Competition
- The famous experiment by Charles Darwin in the Galapagos Islands illustrates how different flinch species evolved beak shapes that allowed them to access different food sources.
Thus, the success of plants and animals in a particular ecosystem is a result of their ability to evolve and adapt to their habitat’s environmental conditions over time. These adaptations enhance their chances of survival and reproduction in their specific ecological niche.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here

