
Welcome to our monthly current affairs update for August 2023. In this ever-changing world, staying informed about the latest events, trends, and developments is crucial. This month, we’ll take you on a journey through the most significant and noteworthy happenings across the globe. From politics to technology, from culture to the environment, we’ll cover it all. Join us as we explore the stories shaping our world and the issues that demand our attention. Our goal is to provide you with a concise and insightful overview of the events that are shaping our times, enabling you to engage in informed conversations and make well-informed decisions. So, without further ado, let’s dive into the whirlwind of current affairs for this month.
Contents
- 1 Lithium Extraction
- 2 Graphene-Aurora Program
- 3 Somatic genetic variants
- 4 Project Worldcoin
- 5 ASTRA Beyond Visual Range air-to-air missile
- 6 C.R. Rao (1920-2023)
- 7 Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV)
- 8 ISRO’s Chandrayaan-3 mission
- 9 Agnibaan SubOrbital Technological Demonstrator (SOrTeD)
- 10 Namoh 108
- 11 In News:
- 12 Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
- 13 Acoustic Side Channel Attacks
- 14 Definition of Green Hydrogen
- 15 DRDO’s UAV Tapas
- 16 Demon particle
- 17 Gene-edited mustard
- 18 ‘Microplastics’ in the human Heart
- 19 India’s first drone common testing centre
- 20 STEREO (Solar TErrestrial RElations Observatory) mission
- 21 Aditya-L1 Mission
- 22 Zayed Talwar
- 23 First-ever 2D composite quantum material
- 24 Neerakshi
- 25 IMS-1 Satellite Bus Technology
- 26 Genetic Diversity in the Indian Population
- 27 Einstein cross
- 28 Fediverse
- 29 NIDHI program
- 30 Finger Minutiae Record – Finger Image Record (FMR-FIR) modality
- 31 Akira ransomware
- 32 Room-temperature superconductor
- 33 Cell-Free DNA
- 34 Space Debris
- 35 Worldcoin
- 36 GEMINI Blood Test
- 37 Scrub Typhus
- 38 Hepatitis
- 39 Post-quantum Cryptography
- 40 Ureilite
- 41 Trachoma
- 42 Nuclear Medicine
- 43 Eastern Equine Encephalitis
- 44 FAQs on Monthly Current Affairs – August 2023
- 45 In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
Lithium Extraction
In News:
Recently, India has successfully extracted lithium from the mineral concentrate on a laboratory scale.
About:
- India has recently identified a comprehensive list of 30 critical minerals, including lithium, as part of its mineral security strategy.
- The country has demonstrated its capability to develop technologies for the beneficiation of lithium ore to lithium mineral concentrate.
Lithium
- Lithium is a chemical element with the symbol Li and atomic number 3.
- It is a soft and silvery-white metal.
- It is sometimes also referred to as ‘White gold’ due to its high demand for rechargeable batteries.
- Like all alkali metals, lithium is highly reactive and flammable, and must be stored in vacuum, inert atmosphere, or inert liquid such as purified kerosene or mineral oil.
- Major Global Lithium Reserves:
- Chile > Australia > and Argentina are the top countries with Li reserves.
- Lithium Triangle: Chile, Argentina, Bolivia.
Graphene-Aurora Program
In News:
Recently, The Ministry of Electronics & Information Technology (MeitY) Secretary has launched the ‘Graphene-Aurora program’ at a function in Maker Village Kochi, Kerala.
About:
- The program shall be implemented by Digital University Kerala with joint funding from MeitY and Government of Kerala and Industry partners.
- The establishment of the India Graphene Engineering and Innovation Centre (I-GEIC) will play a pivotal role in this effort.
- This initiative aims to bridge the gap between graphene research and commercialization.
- Purpose:
- The centre shall fill the gap between R&D and commercialization by providing a complete facility to startup and industry.
- It shall also nurture the deep/emerging Graphene technology & innovation ecosystem that can guide, develop, implement and support SMEs and startups to commercialize developed graphene technologies for scale adoption.
Graphene:
- Graphene is a single layer of carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice, forming a two-dimensional structure.
- It is the world’s thinnest, strongest, and most conductive material of both electricity and heat.
- It conducts electricity better than copper.
- It is 200 times stronger than steel but six times lighter.
- It is almost perfectly transparent as it absorbs only 2% of light.
- It is impermeable to gases, even those as light as hydrogen and helium.
- It is used in electronics for creating faster and more efficient devices, in materials science for reinforcing composites, in energy storage for enhancing battery performance, and in medical fields for drug delivery and biosensors, among other uses.
Maker Village
- Maker Village is a pioneering startup initiative of the MeitY, Government of India with Indian Institute of Information Technology, Trivandrum as the implementation agency and Kerala Startup Mission as the supporting partner.
- It is India’s largest electronic hardware incubator and Electronics System Design & Manufacturing facility.
Somatic genetic variants
In News:
Scientists have known of somatic variants for many years, but recently there has been an explosion in the amount of data.
About:
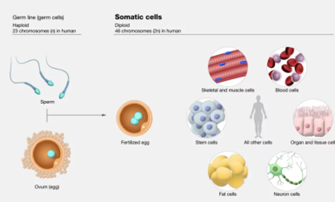
- Somatic genetic variants also known as somatic mutations refer to alterations in the DNA sequence that occur specifically within the cells of an individual’s body (somatic cells), excluding the germline cells (sperm and egg cells).
- Somatic genetic mutations occur after birth during development and are not inherited from parents.
- Somatic mutations can occur for various reasons, such as errors during DNA replication, exposure to environmental factors (like radiation or chemicals), or simply as a natural consequence of cellular.
- Somatic mutations can have different effects depending on where they occur in the genome and which genes are affected.
- Some somatic mutations are harmless and have no discernible impact on the cell or individual. However, others can lead to the development of diseases, including cancer.
Somatic Mutation Progression:
- Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes, one from each parent, which carry our genetic information or blueprint.
- After fertilization, a single cell with 23 chromosomes begins dividing, ultimately creating nearly a trillion cells in the human body.
- While DNA replication during cell division is generally accurate, errors occur at an estimated rate of 0.64-0.78 mutations per billion base pairs per division.
- These mutations are more common during development and are referred to as somatic genetic mutations.
- These errors, often arising from the repeated copying of the genome, increase with age and tissue turnover.
- Turnover is the replacement of old cells with new ones.
- Some of these mutations can confer advantages to cells, leading to the development of tumours known as driver mutations.
Project Worldcoin
In News:
Recently, a project called Worldcoin has been launched by OpenAI, an Artificial intelligence company.
About:
- The project claims to be building the world’s largest identity and financial public network.
Project Worldcoin:
- Worldcoin is an initiative to create a digital network in which everyone can claim some kind of stake and join the digital economy.
- The initiative uses a device called “Orb” to collect biometric (iris) data and help participants get a World ID through the World app.
- With the app, participants can collect a cryptocurrency called Worldcoin [WLD].
- Users need to be willing to scan irises and/or get their own irises scanned to make the Worldcoin network possible.
- Those who have their irises scanned and collect a World ID can use this to claim the WLD crypto, which they may use for transactions (if possible and legal) or hold on to the asset in the hope that its price might rise.
- Worldcoin claims that using biometric information to avoid duplication is a valid method for including everyone in its network.
- This process is called “proof of personhood” and makes sure that people do not sign themselves up multiple times in exchange for crypto.
More Information:
- Worldcoin lists 18 locations in India — largely in Delhi, Noida, and Bangalore — where Orb operators are scanning people’s eyes.
ASTRA Beyond Visual Range air-to-air missile
In News:
Recently, Light Combat Aircraft (LCA) LSP-7, known as “Tejas,” successfully launched the indigenous Beyond Visual Range (BVR) air-to-air missile called ASTRA.

About:
- The missile was fired from the aircraft at an altitude of approximately 20,000 feet and achieved all test objectives flawlessly.
ASTRA Missile:
- ASTRA is an indigenous Beyond Visual Range (BVR) air-to-air missile.
- It is to engage and destroy highly maneuvering supersonic aerial targets.
- It is designed and developed by Defence Research and Development Laboratory (DRDL), Research Centre Imarat (RCI) and other laboratories of DRDO.
- The indigenous Astra BVR firing from home grown Tejas fighters is a major step towards ‘Aatmanirbhar Bharat’.
| LCA Tejas |
| It is the lightest, smallest and tailless multi-role supersonic fighter aircraft in its class. This aircraft is designed to carry a range of air-to-air, air-to-surface, precision-guided, weapons. It has the air-to-air refueling capability. The maximum payload capacity of Tejas is 4000 kg. Speed: Mach 1.8. |
C.R. Rao (1920-2023)
In News:
Recently, Renowned statistician Calyampudi Radhakrishnan Rao, known as C.R. Rao, has passed away at the age of 102.
About:

- C.R. Rao was among the world’s most eminent statisticians and spent a significant part of his career in India.
- C.R. Rao was born in 1920, in Hadagali, Bellary district in a Telugu family.
- Various theorems: Rao-Blackwell Theorem, Cramér–Rao inequality, Fisher–Rao theorem, Orthogonal arrays, Multivariate statistical analysis, Biometry etc.
- Rao formulated the Cramer-Rao bound in 1945, setting a benchmark for assessing statistical techniques. His Rao-Blackwellisation concept in 1948 improved estimator efficiency.
- Rao’s work in multivariate analysis, estimation theory, and differential geometry was groundbreaking. His Fisher-Rao metric is widely used in probability and physics.
- Over his career, Rao authored roughly 500 papers and 14 books, addressing complex statistical problems.
- He played a key role in developing statistical education and research in India, serving on various government committees and contributing to the field’s growth.
- He received numerous awards, including India’s Padma Bhushan and Padma Vibhushan.
- He served as chairman of the Committee on Statistics and Demographic and Communication for Population Control.
- His famous book is “Statistics and Truth: Putting Chance to Work”.
- Ethical values: C.R. Rao’s life embodied ethical values such as dedication to education, professionalism, pioneering statistical concepts, and contributing to society through his work in statistics.
Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV)
In News:
Recently, The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved the first vaccine (ABRYSVO), that protects newborns from Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV).
About:
- ABRYSVO’s approval is the first and only maternal immunization to help protect newborns immediately at birth through six months.
- It is made by Pfizers.
- Abrysvo has been authorized for use in adults aged 60 and above to protect them from RSV.
- The vaccine generates passive immunity by producing antibodies against RSV in pregnant individuals, which are then passed on to their foetuses in the uterus.
Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV)
- Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) belongs to the family of viruses called Paramyxoviridae and is a leading cause of lower respiratory tract infections, such as bronchiolitis and pneumonia, especially in children under the age of two.
- It is a negative-sense, single-stranded RNA virus.
- It usually causes mild, cold-like symptoms.
- But infants, young children and people older than 65 can develop severe disease and potentially die from the virus.
- These infections include bronchiolitis, an inflammation of the small airways in the lung, and pneumonia, an infection of the lungs.
- Transmission:
- The virus spreads through respiratory droplets when an infected person coughs or sneezes, and it can also be transmitted through direct contact with contaminated surfaces.
- Symptoms:
- The symptoms of RSV infection usually start about 4 to 6 days after infection.
- They include Runny nose, Decrease in appetite, Cough, Sneezing, Fever, Wheezing.
ISRO’s Chandrayaan-3 mission
In News:
The Chandrayaan-3 lander made a successful soft landing on the surface of the moon, making India the first country to reach close to the lunar south pole. India has also become the fourth nation to land on the lunar surface, after the United States, the erstwhile Soviet Union, and China.
About Chandrayaan Mission:
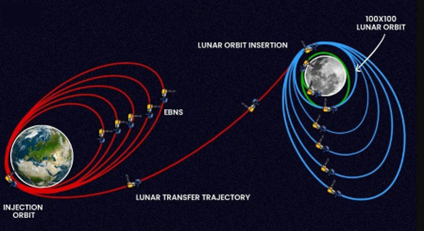
- The Chandrayaan-1 mission was launched in 2008. The Moon Impact Probe was made to crash land on the lunar surface to leave India’s mark on the Moon. Chandrayaan-1’s orbiter also detected evidence of water on the Moon.
- Chandrayaan-2 was launched in 2019 with a lander, called Vikram. It was scheduled to make a soft-landing on the lunar surface but minutes before the scheduled touchdown, ISRO lost contact with the spacecraft. However, the Chandrayaan-2 orbiter continued to work fine.
- Chandrayaan-3 mission’s successful soft landing on the Moon marks India becoming the fourth nation after the United States, Russia, and China to reach the lunar surface and first to reach the South Pole.
- There were various instruments on Chandrayaan-3 to carry out several experiments:
- Lander Payloads:
- Radio Anatomy of Moon Bound Hypersensitive Ionosphere and Atmosphere (RAMBHA) to study the electrons and ions near the moon’s surface, and changes over time.
- Chandra’s Surface Thermo Physical Experiment (ChaSTE) focuses on thermal properties of the lunar surface near the polar region assisting in understanding temperature variations.
- Instrument for Lunar Seismic Activity (ILSA) measures lunar quakes near the landing site, analysing the composition of the Moon’s crust and mantle through seismic activity.
- LASER Retroreflector Array (LRA) provided by NASA, acts as a target for lasers, enabling precise measurements for future missions.
- Rover Payloads:
- LASER-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy (LIBS) determines the chemical and mineral composition of the lunar surface, offering insights into its geological makeup.
- Alpha Particle X-ray Spectrometer (APXS) identifies elements on the lunar surface.
Reasons for exploring Moon’s South Pole:
- Focus on Equatorial region: All the previous spacecraft to have landed on the Moon have landed in the equatorial region, because:
- The terrain & temperature are more hospitable and conducive
- Presence of Sunlight offers a regular supply of energy to solar-powered instruments.
- Unexplored region: The polar regions of the Moon have difficult terrain with many parts lying in completely dark regions, and temperatures can go below 230 degrees Celsius.
- Insights into early history of the Solar System: Extreme cold temperatures in Polar Regions of the moon preserves objects as they remain frozen and undergo minimal change. Thus rocks and soil in the Moon’s poles offer valuable insights into early stages of the Solar System.
- Presence of water: These specific areas referred to as Permanently Shadowed Regions of the moon can have evidence for presence of water in the region at the surface.
- Technological Advancements: Undertaking missions to the lunar South Pole allows ISRO to develop and showcase innovative technologies.
Significance of Chandrayaan Mission:
- Progress in India’s space programme: The Chandrayaan and Mangalyaan signal a shift in India’s space science strategy. Earlier, ISRO focused on utilitarian objectives like satellite launches on enabling telecommunications, telemedicine etc. But now there is push towards space exploration.
- Future space exploration: The demonstration of India’s capability to launch, and successfully soft land on a planetary body can impact IRSO’s ability to carry out, or participate in, other space missions.
- Boost to the Indian space-tech ecosystem: The successful launch of Chandrayaan-3 could bolster investor confidence and attract more private investment in space technology to promote cost-efficient and highly reliable space-grade hardware.
- Confidence in LMV’s capability for Gaganyaan: With a human-rated Launch Vehicle Mark (LVM) to be used for the upcoming Gaganyaan mission, LVM-3’s success in Chandrayaan-3 has enhanced confidence over the launch vehicle.
- Nurturing startups: Success of ISRO’s mission also depended on contributions of private players and startups which provided critical components for the mission. This has increased reliability in the private sector and could attract business opportunities for Indian startups to in the global market.
- Strengthening international reputation: Success of Chandrayaan-3 could earn global recognition and lead to the cost-effective adoption of spacecraft manufactured by Indian companies and proof of its reliability.
- Strategic Positioning: The mission positions India as an important player in the international space race, potentially matching China’s influence. Together with Artemis Accords, it will enhance India’s ever-increasing space footprints.
Agnibaan SubOrbital Technological Demonstrator (SOrTeD)
In News:
Recently, AgniKul Cosmos, a space tech start-up based in Chennai, set to launch their groundbreaking Agnibaan SubOrbital Technological Demonstrator (SOrTeD), the world’s first 3D-printed rocket into space.
About:
- The Agnibaan SOrTeD is a customisable launch vehicle that could be launched in one or two stages.
- It is powered by AgniKul’s patented Agnilet engine.
- Agnilet, is a 3D-printed, 6 kilonewton (kN) semi-cryogenic engine that uses liquid oxygen and kerosene as propellants.
- Unlike traditional sounding rockets that launch from guide rails, Agnibaan SOrTeD will lift off vertically and follow a predetermined trajectory to perform a precisely orchestrated set of manoeuvres during flight.

Features:
- It is capable of carrying payloads up to 100 kg to an altitude of 700 km in five different configurations.
- The rocket has a mass of 14,000 kg.
- The rocket’s first stage could have up to seven Agnilet engines, depending on the mission, which are powered by Liquid Oxygen and Kerosene.
- The rocket is also designed for launch from more than 10 different launch ports.
- To ensure its compatibility with multiple launch ports, AgniKul has built a launch pedestal named ‘Dhanush’ that will support the rocket’s mobility across all its configurations.
- The Agnilet engine, which powers the entire operation, is the world’s sole single-piece 3D-printed engine.
More Information:
- AgniKul Cosmos’ journey is supported by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) and Indian National Space Promotion and Authorisation Centre (IN-SPACe).
| 3D Printing |
| 3D printing is also known as additive manufacturing which uses materials such as plastics and metals to convert products envisaged on computer-aided design to real three-dimensional items. 3D printing traditionally has been used for prototyping and has a lot of scope in making artificial limbs, stents, dental crowns, parts of automobiles and consumer goods, among others. |
Namoh 108
In News:
Recently, The Lucknow-based CSIR-NBRI (National Botanical Research Institute) has reportedly developed a new variety of lotus flowers called ‘Namoh 108,’ characterized by having 108 petals.

About:
- The name “Namoh 108” is a combination of the religious significance of the ‘lotus flower’ and the digit ‘108,’ which holds importance in Hinduism.
Features of Namoh 108:
- The Namoh 108 lotus variety flowers from March to December “and is rich in nutrients.
- The flower’s genome was sequenced, making it the only Indian lotus variety with a sequenced genome.
- The release also included products derived from the lotus, such as apparel made from lotus fibre and a perfume called ‘Frotus’ extracted from lotus flowers.
More Information:
- The flower’s characteristics were modified to facilitate cultivation outside Manipur.
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
In News:
Medical fraternity deliberates on challenges to live with ALS and need to care for patients
About Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS)
- Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) also known as Lou Gehrig’s disease or motor neuron disease is a neurodegenerative disease affecting motor neurons in brain and spine.
- Living with it takes a toll on patients and caregivers due to delayed diagnosis, infrastructural gaps, and invisible labor.
- Major highlights:
- Motor Neuron Degeneration of Special nerve cells affects control voluntary functions: walking, talking, chewing, arm movement.
- Progressive death of motor neurons leads to muscle atrophy leading to muscle weakness and twitching (fasciculations).
- It also leads to difficulty in speaking, swallowing, breathing and gradual loss of voluntary muscle control.
- There is no single test available at present and the disease is diagnosed through clinical examination and ruling out other conditions.
- Motor cell failure is detected in multiple body regions through a diagnostic process which may take 8 to 15 months from symptom onset.
- Although there is no clear cause available at present since most cases sporadic with around 5-10% cases have genetic link (familial ALS).
- The average survival time is 3 years as breathing muscles involvement leads to respiratory failure due to no definitive cure except treatments to manage symptoms and extend life.
- At present, treatment involves multidisciplinary approach involving neurologists, therapists, caregivers and medications to manage symptoms and slow progression.
- Breathing support devices and feeding tubes are inserted as the disease progresses with physical and occupational therapy used to maintain functionality.
- There is need to pursue more research to understand causes and develop treatments besides awareness campaigns to educate public about ALS and support for patients.
- Companies can also take fundraising for research and patient care through initiatives like Ice Bucket Challenge.
- Overall, ALS is a debilitating neurodegenerative disease whose early diagnosis, comprehensive care, and research efforts are essential to improve the quality of life for those affected by ALS.
Acoustic Side Channel Attacks
In News:
Recently, a research paper titled “A Practical Deep Learning-Based Acoustic Side Channel Attack on Keyboards”, was published and supported by the ethics committee of Durham University.
About Side Channel Attacks (SCA)
- SCAs are a method of hacking a cryptographic algorithm based on the analysis of auxiliary systems used in the encryption method.
- These can be performed using a collection of signals emitted by devices, including electromagnetic waves, power consumption, mobile sensors as well as sound from keyboards and printers to target devices.
- These collected signals are used to interpret signals that can be then used to compromise the security of a device.
About Acoustic Side Channel Attacks (SCA)
- ASCA, the sound of clicks generated by a keyboard is used to analyze keystrokes and interpret what is being typed to leak sensitive information.
- These attacks are particularly dangerous as the acoustic sounds from a keyboard are not only readily available but also because their misuse is underestimated by users.
- Users take no precautionary steps are taken to hide the sound of the keystrokes.
- The use of laptops has increased the scope of ASCAs as laptop models have the same keyboard making it easier for AI-enabled deep learning models to pick up and interpret the acoustics.
How can users protect against ASCAs?
- Using touch-based typing can reduce the chances of successful keystroke recognition making it more difficult for threat actors to leak sensitive information.
- Changes in typing style and creating stronger passwords that use a combination of upper- and lower-case alphabets can make it more difficult for criminals to launch successful ASCA attacks
Definition of Green Hydrogen
In News:
Recently, In a significant move for the progress of the National Green Hydrogen Mission, the government has notified the Green Hydrogen Standard for India.
About:
“Green Hydrogen” shall mean Hydrogen produced using -renewable energy, including, but not limited to, production through electrolysis or conversion of biomass. Renewable energy also includes such electricity generated from renewable sources which is stored in an energy storage system or banked with the grid in accordance with applicable regulations.
For Green Hydrogen produced through electrolysis:-
- The non-biogenic greenhouse gas emissions arising from water treatment, electrolysis, gas purification and drying and compression of hydrogen shall not be greater than 2 kilogram of carbon dioxide equivalent per kilogram of Hydrogen (kg CO₂ eq/kg Hydrogen), taken as an average over last 12-month period.
For Green Hydrogen produced through conversion of biomass:-
- The non-biogenic greenhouse gas emissions arising from biomass processing, heat/steam generation, conversion of blomass to hydrogen, gas purification and drying and compression of hydrogen shall not be greater than 2 kilogram of carbon dioxide equivalent per kilogram of Hydrogen (kg CO2 eq/kg Hydrogen) taken as an average over last 12-month period.
Additional Information
- Detailed methodology for measurement, reporting, monitoring, on-site verification, and certification of green hydrogen and its derivatives shall be specified by the Ministry of New & Renewable Energy.
- Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE), Ministry of Power shall be the Nodal Authority for accreditation of agencies for the monitoring, verification and certification for Green Hydrogen production projects.
DRDO’s UAV Tapas
In News:
After the crash of Tapas unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) in Karnataka, during its experimental flight trial, Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) informed that there was no collateral damage.
About the Unmanned Aerial Vehicle TAPAS:
- Tactical Airborne Platform for Aerial Surveillance (TAPAS)-Beyond Horizon-201 or Tapas BH-201 is a long-endurance unmanned aerial vehicle that used to be previously referred to as Rustom-II.
- The drone has a 20.6-meter wingspan and a maximum speed of 225 kmph. It can cover a range of more than 250 km using the C Band frequency data link developed by Defence Electronics Application Laboratory (DEAL) at DRDO.
- It’s range can also be enhanced to more than1000 km via SATCOM using the Kᵤ Band frequency and GAGAN system.
- TAPAS BH 201 is being developed in India by Aeronautical Development Establishment.
- The medium-altitude, long-endurance drone has an impressive flight endurance of several hours and successfully completed its maiden flight in November 2016.
- The TAPAS BH 201 drone has the capability to fly autonomously or via remote control, allowing for pre-programmed flight plans and operational use in daylight or darkness.
- Its compact, lightweight design makes it easily transportable and deployable to remote locations, while its real-time data collection and transmission provide valuable intelligence for decision-making.
- With a range of over 18 hours and altitude capabilities of up to 28,000 feet, the TAPAS BH 201 has already completed more than 180 flights and will be live-streaming aerial and static displays at Aero India 2023.
Significance of UAV-TAPAS:
- Tapas-BH is the answer to India’s quest for ISTAR (Intelligence, Surveillance, Target Acquisition, Tracking, and Reconnaissance) requirements.
- TAPAS incorporates the highest-grade military EO Electro-Optical (EO) and Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) payloads which will improve the images dramatically for the ISTAR range of operations for the military across the terrain.
- The development of TAPAS is also crucial for the next phase of armed drones with greater capabilities which will reduce the dependency on importing ISTAR drones.
- The long-endurance capabilities of drones are vital for border surveillance amid escalating Chinese build-up across the border.
Demon particle
In News:
Researchers at the University of Illinois recently discovered a demon particle that could lead to the making of superconductors that can operate at room temperature.
About the Superconductors:
- Superconductivity is the property of certain materials to conduct direct current electricity without energy loss when they are cooled below a critical temperature. These materials also expel magnetic fields as they transition to the superconducting state.
- Such metals or alloys can conduct electricity without resistance, but for that to happen, the temperature of such material needs to be below 100 degrees Fahrenheit.
- Superconductors are used in operations such as levitating trains and highly accurate magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) machines.
Demon Particles:
- These are massless particles, termed as the holy grail of superconductors, which were discovered nearly 70 years after ‘demon particles’ were first predicted.
- The prediction of the demon particle was first made by theoretical physicist David Pines in 1956, who believed that electrons would behave strangely when passed through a solid.
- Electric interactions make electrons combine to form collective units i.e. plasmons. This can make electrons lose individuality in solids. However, with such a large mass, plasmons cannot form with energies available at room temperature.
- But Pines pointed out that there is an exception. Since demons do not contain mass, they can form plasmons with any energy and at room temperatures as well, thus giving rise to the idea of superconductors working at room temperatures.
- With the discovery of materials capable of operating at room temperature, emergence of more powerful computers could come into being.
About the Research:
- The team at University of Illinois, identified the potential existence of the demon particle while investigating the properties of the metal strontium ruthenate, which is similar to high-temperature superconductors.
- The team of researchers were conducting the first survey on the electronic properties of the metal by blasting it with electrons, which led to the summoning of the demon through the metal’s features.
- The final GE lines of mustard contain no Cas9 protein and are transgene-free.
Gene-edited mustard
In News:
Recently, Indian scientists have developed the first-ever low-pungent mustard.
About GTR Gene-Edited Mustard
- Mustard (Brassica juncea) dry seed contain 120-130 parts per million (ppm or mg/kg) of glucosinolates. This is as against the sub-30 ppm levels in canola seeds.
- By lowering the glucosinolate content to the dry seed weight concentration, the scientists have bred mustard lines whose oil and meal match the standard of canola-quality rapeseed (Brassica napus) in terms of pungency.
- In this seed glucosinolates are synthesized in mustard leaves and pod walls before translocation to seeds.
- New GTR genes-edited mustard lines are transgene-free or non-genetically modified (GM). It is low-pungent mustard that is pest and disease-resistant.

- It does not contain any foreign genes like Bar-Barnase-Barstar (isolated from other soil bacteria) in the GM hybrid mustard (DMH-11)
About Glucosinolates:
- Glucosinolates are synthesized in the leaves and pod walls of mustard plants. Its translocation and accumulation in the seeds happens through the action of glucosinolate transporter or GTR genes.
- Mustard seeds have high levels of glucosinolates, a group of sulphur and nitrogen-containing compounds contributing to the characteristic pungency of their oil and meal.
- High glucosinolates are also known to cause goiter (swelling of the neck) and internal organ abnormalities in livestock.
- High glucosinolates reduce the feed intake of livestock.
- Glucosinolates limit the palatability of the meal and the exploitation of its true protein potential are also key arsenals of the Brassicaceae family crops – from mustard and canola to cabbage, cauliflower and broccoli – against invading pests, pathogens and termites.
Importance of the Gene-Edited Mustard
- India is a huge importer of edible oils, In the fiscal year 2022-2023 India imports were valued at $20.84 billion that only meet 60% of the country’s consumption requirement.
- There is a dire need to boost domestic oilseed production through focused breeding to improve crop yields, pest and disease resistance, and product quality. So, it can l help to save the foreign exchange and reduce import dependency.
- Mustard and soyabean are India’s most widely-cultivated oilseed crops, planted annually on 9 million and 12.5 million hectares area respectively.
- Mustard’s higher average oil extractable content (38% versus 18% for soyabean) makes mustard the bigger “oilseed” crop, while a source of both fats for humans and protein for animals.
‘Microplastics’ in the human Heart
In News:
Recent research from China’s Beijing Anzhen Hospital, published by the American Chemical Society, has discovered microplastics in the human heart for the first time.

About:
- The researchers found numerous individual microplastic pieces in most tissue samples, and plastic particles were also present in all blood samples.
- The study also identified specific types of plastics, such as polyethylene terephthalate (used in clothing and food containers) and polyvinyl chloride (common in window frames and pipes), in the samples.
Microplastics:
- Microplastics are tiny bits of various types of plastic found in the environment.
- They are a result of the fragmentation and degradation of larger plastic items, as well as the direct release of tiny plastic particles, often intentionally added to consumer products like cosmetics and cleaning agents.
- Microplastics, which are less than 5 millimetres in size, can enter the human body through various openings and have been linked to health issues like obesity, diabetes, and chronic liver disease due to their impact on the gastrointestinal tract.
- The name is used to differentiate them from “macroplastics” such as bottles and bags made of plastic.
- There are two categories of microplastics:
- Primary microplastics: They are tiny particles designed for commercial use, such as cosmetics, as well as microfibers shed from clothing and other textiles, such as fishing nets.
- Secondary microplastics: They are particles that result from the breakdown of larger plastic items, such as water bottles.
India’s first drone common testing centre
In News:
India’s first Unmanned Aerial Systems (Drone) Common Testing Centre under Defence Testing Infrastructure Scheme (DTIS) will be established in Tamil Nadu.
About:
- The initiative is led by the Tamil Nadu Industrial Development Corporation (TIDCO) as part of the Tamil Nadu Defence Industrial Corridor (TNDIC), aimed at nurturing the aerospace and defence industry ecosystem.
- It will be established under Defence Testing Infrastructure Scheme (DTIS).
- As part of the implementation of the TNDIC, the government is about to create an enabling ecosystem including Common Testing Centres for the Aerospace and Defence Industry.
- Location – The Unmanned Aerial Systems (UAS) Common Testing Centre would be established at the SIPCOT Industrial Park, Vallam Vadagal near Sriperumbudur in Tamil Nadu.
- It will enable the State to be a significant contributor to the self-reliance of the country in the aerospace & defence sector.
- More Information:
- An integrated facility for testing for UAS (Drone) is available only with DRDO at Chitradurga, Karnataka.
| Defence Testing Infrastructure Scheme (DTIS) |
| Aim – To boost domestic defence & aerospace manufacturing. Launch – May 2020. Ministry – Ministry of Defence (MoD). Duration – 5 years. It envisages setting up of 6-8 greenfield defence testing infrastructure facilities that are required for defence and aerospace related production. Funding Pattern – 75% Government funding in the form of ‘Grant-in-Aid’ + 25% to be borne by the Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV) constituents. |
STEREO (Solar TErrestrial RElations Observatory) mission
In News:
Nasa’s Solar Terrestrial Relations Observatory (STEREO-A) spacecraft made its first Earth flyby nearly 17 years after its launch.
About:
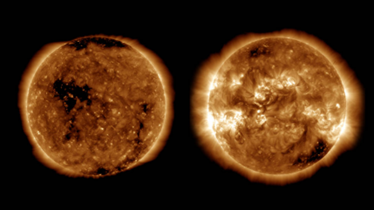
- The pair of STEREO (Solar Terrestrial Relations Observatory) spacecraft were launched on October 25, 2006, from Florida’s Cape Canaveral Air Force Station.
- STEREO-A (A stands for Ahead), along with its twin STEREO-B (B stands for Behind), was launched to study the Sun’s Behavior by charting Earth-like orbits around it.
- Their primary goal was to provide a stereoscopic view of the Sun, enabling researchers to study it from multiple perspectives.
- In 2011, another significant milestone was achieved as both STEREO-A and -B reached a remarkable 180-degree separation in their orbits, which gave us the full sphere image of the Sun.
Significance of STEREO-A:
- STEREO-A’s recent approach to Earth offers a unique opportunity for scientific observations. By combining its views with other spacecraft, including the Solar and Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO) and Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO), STEREO-A will provide 3D views of the Sun.
- This stereoscopic vision allows scientists to gain depth perception and explore features like active regions and coronal loops in unprecedented detail.
- STEREO-A’s passage through Earth’s vicinity also allows for an in-depth study of solar eruptions, known as coronal mass ejections (CMEs), which can impact Earth’s technology.
- This approach provides multipoint measurements to understand the evolution of CMEs’ magnetic fields.
Aditya-L1 Mission
In News:
ISRO is ready to launch its first solar mission Aditya-L1, after the successful launch of Chandrayaan-3. The satellite realized at the UR Rao Satellite Centre Bengaluru has arrived at SDSC-SHAR (spaceport) in Sriharikota.
About Aditya-L1 mission:
- Aditya-L1 is the first Indian space mission to observe the Sun and the solar corona. It will be launched by the PSLV-XL launch vehicle.
- The objective of the mission is to study solar upper atmospheric (chromosphere and corona) dynamics and understand the physics of the solar corona and its heating mechanism.
- The mission will be launched to the halo orbit around the L1 point (first Lagrangian point of the Sun-Earth system) which is 1.5 million km from the Earth. L1 orbit allows Aditya-L1 to continuously view the Sun without any occultation or eclipses.
- The spacecraft carries seven payloads of which the primary payload is the Visible Emission Line Coronagraph(VELC), to observe the photosphere, chromosphere and the outermost layers of the Sun (the corona) using electromagnetic and particle and magnetic field detectors.
Significance of Aditya-L1 mission:
- Understand the impact of space weather on earth: Evolution of every planet, including Earth is governed by its parent star. Variations in this weather can change the orbits of satellites or shorten their lives, interfere with on board electronics, cause power blackouts and other disturbances.
- Observe Earth directed solar storms: The mission helps to observe, track and predict the impacts of Earth-directed storms. Since every solar storm heading towards the Earth passes through L1, a satellite placed in the halo orbit around L1 helps observe the sun without any eclipses.
- Fillip to the Indian space industry as many of the instruments and their components for this mission are being manufactured for the first time in the country.

What is a Lagrange Point?
- Lagrangian points, also known as Lagrange points or liberation points, are specific locations in space where the gravitational forces of two large bodies, such as a planet and its moon or a planet and the Sun, produce enhanced regions of gravitational equilibrium.
- L1 refers to Lagrange Point 1, one of five points in the orbital plane of the Earth-Sun system, which is 1.5 million kilometres inside Earth’s orbit, between the Sun and the Earth.
- These can be used by spacecraft to reduce fuel consumption needed to remain in position. The L1 point is home to the Solar and Heliospheric Observatory Satellite (SOHO), an international collaboration project of NASA and the European Space Agency (ESA).
Zayed Talwar
In News:
Two ships of the Indian Navy, INS Visakhapatnam, and INS Trikand have arrived in Dubai to conduct the bilateral exercise ‘Zayed Talwar’ with the UAE Navy.

About:
- Zayed Talwar is a Bilateral Exercise between India and UAE Navy.
- The aim of the exercise is to enhance interoperability and synergy between the two navies.
- The ships will undertake professional interactions with the UAE Naval Force on multiple elements of maritime operations during their visit.
- The visit seeks to strengthen the maritime partnership, share best practices, and foster a common understanding of security challenges in the region.
INS Visakhapatnam:
- It is the lead ship and the first of the Indian Navy’s Visakhapatnam-class stealth guided-missile destroyers.
- It was commissioned on November 21, 2021, is one of the largest destroyers in Indian Navy service.
- Features:
- Displacement: 7,400 tonnes.
- Propulsion: It is propelled by four powerful Gas Turbines, in a Combined Gas and Gas (COGAG) configuration.
- Speed: It is capable of achieving speeds in excess of 30 knots.
- The ship is equipped to fight under Nuclear, Biological and Chemical (NBC) warfare conditions.
| Other exercises between India and UAE: |
| Exercise Desert Flag (Air Force) In-UAE BILAT (bilateral naval exercise) Desert Eagle (bilateral air force exercise) |
First-ever 2D composite quantum material
In News:
2-D carbides or nitrides of transition metals were used by a team of scientists to develop a new composite quantum material using computer simulations, that exhibits an exotic quantum property called Rashba splitting, in colossal scale, in a metallic environment.
About the 2D composite quantum material
- 2-D materials are materials with confined geometry in one of the directions.
- Quantum materials are compounds with exotic physical properties that arise due to quantum effects like quantum fluctuations, quantum coherence, and quantum entanglement, having no counterpart in the classical world.
- They hold the promise of revolutionising quantum technology, such as quantum computing, communication, sensors, and memory devices.
- Composite 2-D quantum materials, are quantum materials exhibiting two apparently different quantum properties, but connected by the basic requirement of symmetries.
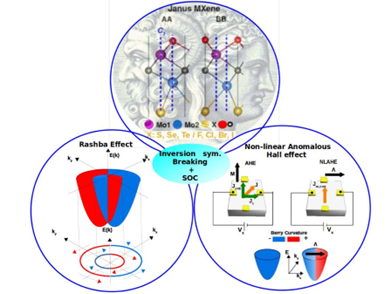
- This material can help interfacing with other substrates in spintronic devices like spin transistors, spin diodes, and spin filters.
About Spintronics and Rashba effect:
- Spintronics is a technology (used on next-generation nanoelectronic devices) that exploits the intrinsic spin of electrons alongside their charge for innovative electronic devices.
- An example is a spin transistor, where electron spin is used for information storage and processing, potentially leading to more energy-efficient and faster electronic devices.
- Rashba splitting is a quantum phenomenon in materials where spin-up and spin-down electrons separate due to interactions with an electric field.
- For instance, in a 2-D carbide material, Rashba splitting causes momentum-dependent separation of electron spin bands, enabling novel spintronic device applications.
About the research:
- The study has led to the first-ever discovery of a 2-D composite quantum material.
- In their study, by proper choice of materials ingredients, the scientists managed to demonstrate the existence of two distinct quantum phenomena Rashba effect and Nonlinear anomalous Hall effect.
- The team chose two dimensional carbides or nitrides of transition metals technically called MXenes and zeroed down on Mo2CO2.
- Starting with this parent material, they computationally designed a Janus structure Mo2COX, named after the two-faced Roman God.
- Even as Rashba splitting in the designed 2-D material was being computed for different X atoms in the Janus structure, the material under study was found to also have the ability to display another quantum property called the anomalous Hall Effect under the effect of longitudinal DC electric field along a particular direction.
Neerakshi
In News:
Recently, India has launched an Autonomous Underwater Vehicle called ‘Neerakshi’ for detecting underwater mines.
About:

- Neerakshi is an autonomous underwater vehicle (AUV) designed to detect mines.
- Developed by: It is a collaboration of Kolkata-based warshipmaker Garden Reach Shipbuilders and Engineers (GRSE) Ltd and MSME entity Aerospace Engineering Private Ltd (AEPL).
- Features:
- It is a 2.1-metre-long cylindrical unmanned vehicle about a foot in diameter and weighing around 45 kg.
- It has an endurance of nearly 4 hours and is capable of operating up to a depth of 300m.
- It can be used for a variety of functions ranging from mine detection to mine disposal to underwater survey.
- Significance:
- It is the first of its kind in India and will be tested by the Navy, Coast Guard, and Army before being available commercially.
- It is part of GRSE’s broader ambitions to create autonomous sea surface vehicles, sea-based drones and explore green propulsion technologies.
IMS-1 Satellite Bus Technology
In News:
Recently, ISRO has transferred its IMS-1 Satellite Bus Technology to Alpha Design Technologies Pvt Ltd., promoting private industry participation in India’s space sector.

About:
- Indian Mini Satellite-1 Satellite Bus was developed by the UR Rao Satellite Centre of Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO).
- It is a small satellite platform designed to enable low-cost access to space.
- It would enable low-cost access to space by providing a dedicated platform for payloads for earth imaging, ocean and atmospheric studies, microwave remote sensing and space science missions with a quick turnaround time.
- Features
- The IMS-1 bus weighs about 100 kilograms and can carry a 30-kilogram payload.
- The solar arrays onboard generate 330 watts of power.
- It comes with four reaction wheels with a 1 Newton thruster that is good for pointing accuracy with an accuracy threshold of 0.1 Degrees.
- Used in: The bus was used in previous ISRO missions like IMS-1, Youthsat and Microsat-2D.
Genetic Diversity in the Indian Population
In News:
Study links Endogamy to persistence of harmful Genetic Variants in India
About Genetic Diversity in the Indian Population:
- Jeffrey Wall and colleagues from the University of California has recently conducted a study involving around 5,000 individuals from India, Pakistan, and Bangladesh.
- Whole-genome sequencing was performed to detect genetic changes, including deletions, insertions, and alterations.
- India is known for its remarkable cultural and linguistic diversity, and this diversity extends to its genetic makeup consisting of a multitude of ethnicities, languages, religions, and cultural practices.
- This diversity is reflected in the genetic composition of the population, with distinct genetic variations across different regions and communities.
- Major findings:
- Genetic differences exist between various regions of India due to historical and geographical factors as different ethnic groups within India have unique genetic traits and variations.
- These variations can influence susceptibility to diseases, responses to medications, and overall health profiles.
- Endogamy has led to genetic isolation in many Indian communities resulting in the preservation of specific genetic traits and the emergence of unique genetic variants within these communities.
- Endogamy and consanguineous marriages contribute to higher levels of inbreeding within some Indian communities.
- It has increased the likelihood of individuals carrying two identical genetic variants for a gene (homozygosity), which can lead to the expression of recessive genetic disorders.
- The unique genetic makeup of the Indian population influences the occurrence of disorders such as diabetes, heart diseases, and certain types of cancers.
- Many health traits and disorders are influenced by multiple genes and environmental factors, making their genetic analysis complex.
- Genetic studies provide insights into the genetic basis of diseases, leading to personalized medicine approaches and will help in tailoring healthcare interventions for different population groups.
- Genetic research can also contribute to disease prevention, early diagnosis, and more effective treatments.
- However, Studying the genetic diversity of India’s population requires comprehensive data collection from diverse communities.
- Other issues include ethical considerations, privacy concerns, and the need for informed consent which are critical aspects of genetic research.
- Overall, Genetic diversity studies in India will go a long way to contribute to the global understanding of human genetics and its implications for health and wellness.
Einstein cross
In News:
Recently, Astronomers have discovered a stunning, rare example of an “Einstein cross” splitting and magnifying light from the far depths of the universe.
About:
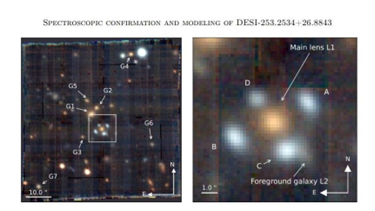
- Einstein predicted the existence of these crosses back in 1915.
- In this case, a foreground elliptical galaxy, located around 6 billion light-years from Earth, has distorted and split a beam of light from a background galaxy about 11 billion light-years away.
- The result is a pattern of four blue smudges around the orange glow of the foreground galaxy.
- The background light likely originates from a quasar, a young galaxy with a supermassive black hole at its core emitting intense radiation.
Einstein’s theory of general relativity
- Einstein’s theory of general relativity describes the way massive objects warp the fabric of the universe, called space-time.
- Gravity, Einstein discovered, isn’t produced by an unseen force; rather, it’s simply our experience of space-time curving and distorting in the presence of matter and energy.
- It explains how massive objects warp space-time, and the strong gravity of the foreground galaxy curved the light from the quasar, creating the Einstein cross pattern.
Fediverse
In News:
Meta, the parent company for Facebook, Instagram, and WhatsApp, recently launched its Twitter, now X, rival Threads.
About:
- Threads will be the company’s first app to join the fediverse – a network of servers operated by third parties.
Fediverse
- The fediverse is a group of federated social networking services that work on decentralised networks operated using open-source standards.
- In this system, a network of servers, managed by third parties, facilitates communication between users of various social media platforms, enabling seamless cross-platform interaction.
- Meta, the parent company of Facebook, Instagram, and WhatsApp, is planning to include its new Threads app in the fediverse.
- This approach allows users to communicate across different social media platforms without creating separate accounts for each one.
- Platforms like Pixelfed, PeerTube, Lemmy, Diaspora, Movim, Prismo WriteFreely, and others already utilize the fediverse.
More Information:
- For example, if a user on Threads, once it enables use of the fediverse, is unable to use their profile for some reason, they can transport all their data to another platform.
- This data would include their follower list, profile information, and posts.
- This kind of cross-platform communication is not facilitated by traditional social media platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter.
- Additionally, if the servers for an existing platform go down, users of platforms on the fediverse can retain and shift their data to another platform that is part of it.
NIDHI program
In News:
Recently, Union Minister said NIDHI (National Initiative for Developing and Harnessing Innovations) program under DST has various components to support innovations, startups, and startup incubation ecosystem in the country.
About:
- The National Initiative for Developing and Harnessing Innovations (NIDHI) program was initiated in 2016 as a comprehensive framework by the Department of Science & Technology’s Innovation & Entrepreneurship division.
- NIDHI primary objective is to foster the growth of startups by identifying, supporting, and amplifying innovative endeavors.
- The program’s core stakeholders encompass various arms of the central government, state governments, academic and research institutions, mentors, financial entities, angel investors, venture capitalists, and private sectors.
- Funding for the program is channeled through the National Science & Technology Entrepreneurship Development Board (NSTEDB).
Key Elements of the NIDHI Program:
- NIDHI-PRAYAS (Promoting and Accelerating Young and Aspiring Innovators and Startups): This initiative operates at the Proof-of-Concept level, providing both mentorship and financial backing to innovators to translate their ideas into functional prototypes.
- NIDHI Entrepreneurs-In-Residence (EIR) Program: The program extends fellowships to students who are inclined towards entrepreneurship. This facilitates their immersion in the startup ecosystem.
- NIDHI Seed Support Program: This component ensures that startups receive essential early-stage seed funding, enabling them to initiate their ventures.
- NIDHI Accelerator Program: Designed to expedite startups’ preparedness for investment, the accelerator program is a structured fast-track process spanning 3-6 months. It aids in propelling startup ideas to higher levels.
Finger Minutiae Record – Finger Image Record (FMR-FIR) modality
In News:
Recently, the Unique Identification Authority of India (UIDAI) has rolled out an in-house Artificial Intelligence/Machine Learning (AI/ML) technology-based Finger Minutiae Record – Finger Image Record (FMR-FIR) modality.
About:
- The Finger Minutiae Record–Finger Image Record (FMR-FIR) modality is an Artificial Intelligence / Machine Learning technology used by UIDAI to prevent fraud in Aadhaar-enabled Payment System (AePS).
- It verifies the authenticity of fingerprints during authentication by combining finger minutiae (distinct ridge characteristics) and finger images.
- The modality’s primary function lies in assessing the liveness of the captured fingerprint.
- It can differentiate between a genuine, “live” finger and a cloned or fake fingerprint, thereby preventing spoofing attempts.
- FMR-FIR operates in real-time, providing instant verification results during the authentication process.
- This technology, specifically designed to enhance Aadhaar-enabled Payment System (AePS) transactions, aims to tackle fraudulent activities, including the misuse of cloned fingerprints.
- Need of FMR-FIR modality
- In FY2023, the total number of fraud cases in the banking system was 13,530. Of this, almost 49 per cent or 6,659 cases were in the digital payment – card/internet – category.
| AePS: |
| The AePS is a bank-led model that allows online interoperable financial transactions at Point of Sale (PoS) or micro-ATMs through the Business Correspondent (BC) of any bank using the Aadhaar authentication. It was taken up by the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI) – a joint initiative of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and the Indian Banks’ Association (IBA). The AePS is meant to provide easy and secure access to banking services for the poor and marginalized sections of society, especially in rural and remote areas. It eliminates the need for OTPs, bank account details, and other financial information. Transactions can be carried out with only the bank name, Aadhaar number, and captured fingerprint during Aadhaar enrollment. |
Akira ransomware
In News:
Computer Emergency Response Team of India issues an alert for ransomware “Akira”
About Akira ransomware
- Akira ransomware is a type of malicious software that encrypts data on infected both Windows and Linux devices.
- It is named “Akira” due to its ability to modify filenames by appending them with the “.akira” extension.
- It uses VPN services to trick users into downloading malicious files and once data is encrypted, victims are forced to pay a ransom to get the decryption key.
- They operate an active leak site where they publish information about their victims and their recent data leaks.
- It is designed to delete Windows Shadow Volume copies on affected devices, making data recovery difficult.
- The ransomware terminates active Windows services to prevent interference during the encryption process.
- Victims are given a unique negotiation password to communicate with the ransomware gang through their Tor site.
- The ransomware spreads through spear-phishing emails with malicious attachments, drive-by-download attacks, and insecure Remote Desktop connections.
- It targets corporate networks in various domains, including education, finance, real estate, manufacturing, and consulting.
- To protect against Akira ransomware, users should maintain up-to-date offline backups, update OS and networks, enforce strong password policies, and use multi-factor authentication (MFA).
- Besides, implementing Domain-based Message Authentication, Domain Keys Identified Mail (DKIM), and Sender policy for email validation can also help prevent email spoofing and spam.
- Overall, users should avoid clicking on suspicious links and conduct regular security audits of critical systems to avoid unforeseen ransomware incidences in their systems.
Room-temperature superconductor
In News:
Recently, Korean researchers claimed to have developed a superconductor named LK-99 that can operate at room temperature and ambient pressure.
About:

- Superconductor LK-99 is a mix of powdered compounds of lead, oxygen, sulphur and phosphorus. When heated at very high temperatures, it forms a dark grey solid.
Superconductor:
- A superconductor is a material that exhibits zero electrical resistance to the flow of electric current.
- Superconductors transmit electricity with almost 100% efficiency.
- The temperature of a superconductor, known as the critical temperature, is typically below 10 Kelvin (-263 degrees Celsius).
- Room temperature is 20-22°C. Superconductors at room temperature can cut the cost of electricity grids, computer chips, magnets for maglev trains, energy-storage devices and fusion reactors by saving electricity and money on coolants.
More Information:
- Superconductors are essential for quantum computing, where quantum bits (qubits) process information simultaneously, providing immense computational power.
- Currently, physical qubits require super-cooling to avoid errors, but room-temperature superconductors could eliminate the need for elaborate cooling systems, making quantum computing more practical and accessible.
- Note: Conductors like copper, gold, silver and aluminium heat up because they resist electricity flow when it passes through them.
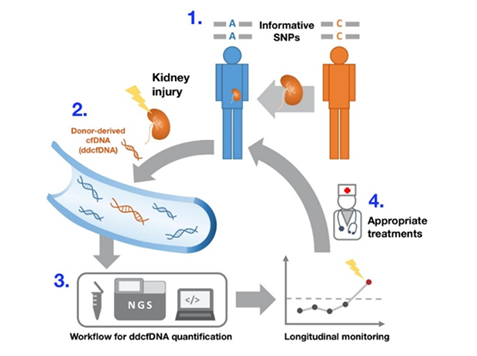
Cell-Free DNA
In News:
Scientists have been aware of such degraded fragments of nucleic acids in body fluids since 1948. But only in the last two decades or so, since genome sequencing technologies started to become more accessible, have they really figured out what to do with that knowledge.
cell-free DNA (cfDNA):
- cfDNA refers to fragments of DNA that exist outside of cells, specifically in various body fluids.
- Scientists have been aware of cfDNA since 1948, but only in the last two decades have they figured out what to do with it.
- It is not enclosed within the cell like majority of DNA.
- These cfDNA fragments contain genetic information and can offer insights into a person’s health status, potential diseases, and genetic variations.
How cfDNA is produced:
- cfDNA is released into the extracellular environment under different circumstances, including cell death or other cellular processes.
- The degradation is influenced by multiple processes causing variations in the amount, size, and origin of cfDNA.
- The release of cfDNA could occur together with a variety of processes, including those required for normal development, those related to the development of certain cancers and those associated with several other diseases.
Applications of cfDNA:
- There are a number of emerging applications of cfDNA, including in understanding why a body is rejecting a transplanted organ. cfDNA obtained from the donor who is donating the organ – called donor-derived cfDNA (dd-cfDNA) – could provide an early yet accurate estimate of how well the organ is being taken up.
- In screening foetuses for specific chromosomal abnormalities, an application known as Non-Invasive Prenatal Testing (NIPT). Analysis of cfDNA in maternal blood provides crucial information about the foetus’s genetic health.
- In the early detection, diagnosis, and treatment of cancers. The ‘GEMINI‘ test uses cfDNA sequencing to detect lung cancer with high accuracy.
- Aiding in the diagnosis and monitoring of conditions like Alzheimer’s disease, neuronal tumours, and stroke.
- Detection and management of conditions such as type-2 diabetes and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
Space Debris
In News:
Australian Space Agency confirms space debris from ISRO Rocket on Australian Shore
About Space debris:
- The Australian Space Agency has recently confirmed that a space junk on its shore is most likely debris from an expended third-stage of a Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) operated by ISRO.
- Space debris consists of non-functional, abandoned, or defunct objects in Earth’s orbit including old satellites, spent rocket stages, fragments from collisions, and discarded spacecraft components.
- There are thousands of trackable space debris objects and millions of smaller, untraceable pieces which poses a significant threat to operational satellites and future space missions
- Collisions between space debris and operational satellites can create more debris in a cascading effect known as the Kessler syndrome.
- The Kessler syndrome could lead to a dense cloud of debris that could make certain orbits unusable for decades or even centuries.
- Falling space debris poses a threat to life and property being a threat to marine life and cause pollution.
- Space agencies and organizations track space debris to predict potential collisions and manoeuvre satellites to avoid them.
- Efforts are being made to mitigate space debris, including satellite deorbiting, designing satellites with less debris-generating components, and implementing guidelines for space activities.
- In this regard, the United Nations Office for Outer Space Affairs (UNOOSA) plays a role in promoting space debris mitigation and cooperation among space-faring nations.
- Overall, International cooperation is essential to address the growing problem of space debris and ensure the sustainability of space activities.
Historical Compensation Case
- Most space-faring countries are signatories to the Convention on International Liability for Damage Caused by Space Objects.
- It makes launching countries “absolutely liable” for compensation in case of damage caused by their space objects on Earth or to a flight in air.
- The country where the debris falls can claim compensation if it has been damaged by the falling object which is determined based on international law and principles of justice and equity.
- The Convention resulted in compensation being paid once when Canada sought damages from the Soviet Union in 1978.
- The Soviet Union reportedly paid 3 million Canadian dollars in compensation for a satellite with radioactive substance falling into an uninhabited region in Canada.
Worldcoin
In News:
Recently, OpenAI CEO formally re-introduced a Worldcoin project of his that was eclipsed by the popularity of ChatGPT.
About:

- Worldcoin is an initiative to create a digital network where individuals can claim a stake and join the digital economy.
- This venture runs on a simple model, allow your eyes to be scanned in order to prove your human uniqueness and receive some crypto and an ID (called a World ID) in exchange.
- Using a device called “Orb,” Worldcoin volunteers known as ‘Orb operators’ scan a person’s iris pattern to collect their biometric data and help them get a World ID through the World app.
- In exchange, participants receive a cryptocurrency called Worldcoin [WLD]. The goal is to build the “world’s largest identity and financial public network” accessible globally.
- This process is called “proof of personhood” and makes sure that people do not sign themselves up multiple times in exchange for crypto.
Key features:
- Worldcoin uses biometric data to ensure unique participation and avoid duplications. The company claims to use zero-knowledge proofs (ZKPs) to maintain users’ privacy and comply with Europe’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
- Worldcoin has been introduced in with Orb operators scanning people’s eyes at various locations in cities like Delhi, Noida, and Bangalore.
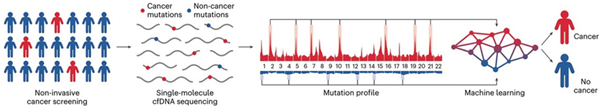
GEMINI Blood Test
In News:
Recently, researchers have developed a new blood testing technology called GEMINI which uses genome-wide sequencing of single molecules of DNA combined with machine learning.
GEMINI (Genome-wide Mutational Incidence for Non-Invasive Detection of Cancer):
- This technology has the potential to enable earlier detection of lung and other cancers.
- The test starts by collecting a blood sample from individuals at risk of cancer. From this sample, cell-free DNA (cfDNA) shed by tumours is sequenced using cost-efficient whole genome sequencing.
- Cell-free DNA (cfDNA) refers to small fragments of DNA that are released into the bloodstream or other bodily fluids when cells in the body die and break down. These fragments of DNA are not enclosed within cells, hence the term “cell-free.”
- Single molecules of DNA are analyzed for sequence alterations, providing mutation profiles across the genome.
- A machine learning model then identifies changes in cancer and non-cancer mutation frequencies, generating a score indicating the likelihood of having cancer.
- In laboratory tests, the GEMINI test, when combined with computerized tomography imaging, detected over 90% of lung cancers, including early-stage diseases.
- The test also identified altered mutation profiles in cfDNA from patients with other cancers, such as liver cancer, melanoma, and lymphoma, suggesting broader applications.
Scrub Typhus
In News:
Recently, the Health department has issued an alert against scrub typhus in Alappuzha.
About:

- Scrub Typhus is a life-threatening infection caused by Orientia tsutsugamushi bacteria which is a major public health threat in South and Southeast Asia.
- Spread: Through bites of Larval Mites of family trombiculid, also called Chiggers.
- It will not spread from person to person.
- Symptoms: fever, chills, headache, body aches, muscle pain, a dark scab-like region at the site of the chigger bite, enlarged lymph nodes, dry cough, skin rashes, red eyes and in some cases mental changes, ranging from confusion to coma.
- Treatment: Scrub typhus should be treated with the antibiotic doxycycline. Doxycycline can be used in persons of any age.
- There is no vaccine available for this disease.
- India is one of the hotspots with at least 25% of the disease burden.
| Typhus |
| Typhus is a group of bacterial infectious diseases that include epidemic typhus, scrub typhus, and murine typhus. Epidemic typhus is due to Rickettsia prowazekii spread by body lice. Scrub typhus is due to Orientia tsutsugamushi spread by chiggers. Murine typhus is due to Rickettsia typhi spread by fleas. |
Hepatitis
In News:
World Hepatitis Day is observed recently.
About:
- The day is an opportunity to step up national and international efforts on hepatitis, encourage individual actions and engagement and highlight the need for a greater global response.
- 2023 Theme: ‘We’re not waiting’ — a call to people around the world to take action because Hepatitis Can’t Wait.
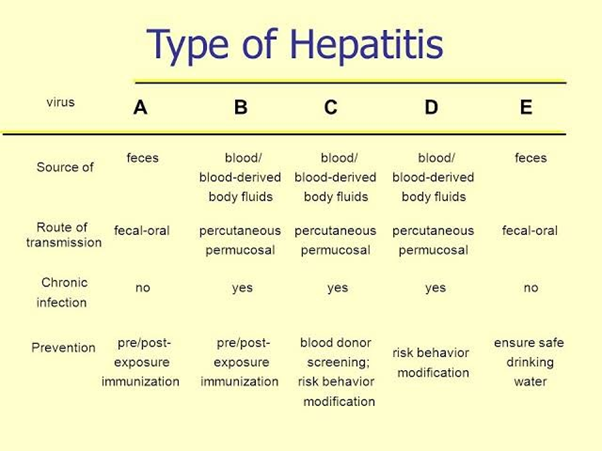
Hepatitis:
- Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver.
- Problem causing agents: Heavy alcohol use, toxins, some medications, and certain medical conditions can cause hepatitis.
- However, hepatitis is often caused by a virus.
- There are five main strains of the hepatitis virus, referred to as types A, B, C, D and E.
- While they all cause liver disease, they differ in important ways including modes of transmission, severity of the illness, geographical distribution and prevention methods.
- In particular, types B and C lead to chronic disease in hundreds of millions of people and together are the most common cause of liver cirrhosis, liver cancer and viral hepatitis-related deaths.
- Some common risk factors associated with hepatitis infection, including:
- Poor sanitation and hygiene practices
- Consumption of contaminated food or water
- Being in contact with the infected person
- Having unprotected sex with an infected partner
- Sharing needles or other drug-injection equipment with an infected person
- Pregnant women and babies born to mothers with Hepatitis B
- Symptoms: Fatigue, Jaundice, Loss of appetite, Nausea and vomiting, Abdominal pain, Dark urine, Clay-coloured stools, Joint pain, Fever, Unexplained Weight Loss and Flu-Like Symptoms
- Treatment:
- Hepatitis A: Hepatitis A is a short-term illness and may not require treatment.
- Hepatitis B: There is no specific treatment program for acute hepatitis B.
- Hepatitis C: Antiviral medications can treat both acute and chronic forms of hepatitis C.
- Hepatitis D: The WHO trusted Source lists pegylated interferon alpha as a treatment for hepatitis D. However, this medication can have severe side effects.
- Hepatitis E: Currently, no specific medical therapies are available to treat hepatitis E. However, pregnant women who develop this infection require close monitoring and care.
- Autoimmune hepatitis: Corticosteroids, like prednisone or budesonide, are extremely important in the early treatment of autoimmune hepatitis. They’re effective in about 80 per cent of people with this condition.
Post-quantum Cryptography
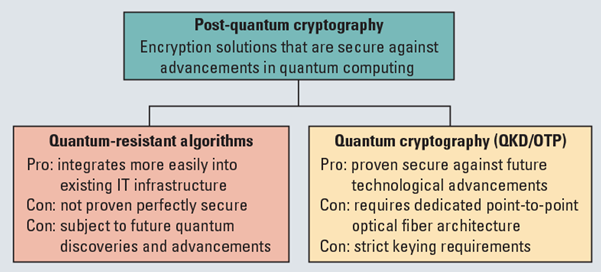
In News:
There has been a lot of worry about quantum computing and its potential impact on computer security. Post-quantum cryptography involves exploring alternative techniques to counter vulnerabilities against quantum attacks.
About quantum computing:
- Modern digital computers are all based on the idea of making electricity do certain things using clever circuitry, and pretend that logical operations are occurring.
- When these circuits or gates are built using lasers, all new kinds of gates can be built in addition to the basic ones.
- The principles of quantum mechanics enabled a set of gates that were utterly impossible to build using electronics.
- In other words, using quantum states to represent logic (instead of high and low voltages) allows us to compute very differently.
- For example, one common classical gate is a “not” gate: this simply outputs the opposite of the input. On a quantum computer, one could have a “square root of not” gate.
- This new, different kind of computation is very powerful.
- Many things that were complex and cumbersome when run on electronic logic become incredibly simple on a quantum system.
What is the need for post-quantum cryptography?
- Governments and organisations across the world are rushing to develop quantum computing platforms and advanced security algorithms to defend against such machines.
- One prominent example of the latter is the U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology’s Post-Quantum Cryptography Standardisation project.
- India has recently announced collaborations with the U.S. in quantum computing and launched the National Quantum Mission.
- Much of our current security is based on techniques such as RSA, elliptic curves, Diffie-Hellman key exchange.
- Unfortunately, in 1994, Peter Shor developed a quantum algorithm that (with certain modifications) can break all of these with ease.
- Quantum computing is a fast-changing field. One promising technique, supersingular isogeny Diffie-Hellman key exchange, was considered secure by many until it was utterly broken by Wouter Castryck and Thomas Decru last year.
- We are probably decades away from a quantum computer powerful enough to do anything meaningful or dangerous.
- However, it is important that we quickly and carefully transition to technologies secure against quantum attacks.
Ureilite
In News:
Scientists discovers the Ureilite meteorite’s role in the formation of the Dhala crater.
About Ureilite:
- Ureilite is an extraordinarily rare and ancient type of meteorite and constitute only a tiny fraction of all known meteorites on Earth.
- These meteorites are classified as a rare class of primitive meteorites and are composed of a silicate rock, primarily containing olivine and pyroxene minerals.
- They also contain less than 10% of carbon, in the form of either diamond or graphite, along with metal sulfides and some fine-grained silicates.
- The study of rare meteorite and their impacts offers insights into the early history and processes of our solar system.
- There is need for researchers to focus on further uncovering the secrets of ureilite impacts to better understand the dynamics of our infant solar system.
- In this regard, exploration of Dhala impact will help understanding possible role meteors in bringing water to Earth and its impact on the development of life on our planet.
Meteor impact:
- India has three ancient meteor impact craters: Ramgarh (Rajasthan), Lonar (Maharashtra), and Dhala (Madhya Pradesh).
- The Dhala impact structure was created when meteor crashed into Earth around 2500-1700 million years ago at an extraordinary speed of 15 km/s forming impact crater in Madhya Pradesh.
- The Ureilite meteorite responsible for the Dhala crater impact is estimated to be around one kilometer in diameter and is Asia’s largest and the world’s seventh-largest impact crater.
Trachoma
In News:
Recently, World Health Organization (WHO) announced that Iraq has joined the league of 17 other countries that have eliminated trachoma.
About:
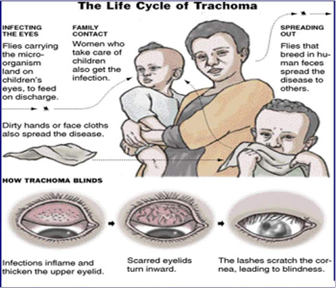
- Trachoma is a neglected tropical disease and the world’s leading infectious cause of blindness.
- It is a disease of the eye caused by infection with the bacterium Chlamydia trachomatis.
- Disease thrives in areas with water shortages, poor sanitation, and fly infestations.
- WHO recommends the SAFE strategy (Surgery, Antibiotics, Facial cleanliness, and Environmental improvement) to eliminate trachoma.
More Information:
- The WHO has recognized Iraq as the 50th country to eliminate at least one neglected tropical disease.
- Despite substantial progress, trachoma is still endemic in six countries in the WHO’s Eastern Mediterranean Region.
- The 17 other countries that have eliminated trachoma are: Benin, Cambodia, China, Gambia, Ghana, Islamic Republic of Iran, Lao People’s Democratic Republic, Malawi, Mali, Mexico, Morocco, Myanmar, Nepal, Oman, Saudi Arabia, Togo and Vanuatu.
Nuclear Medicine
In News:
Recently, India has expressed its support for South Africa’s Integrated Early Warning systems and Russia’s BRICS Collaboration in Nuclear Medicine.
About:
- Nuclear medicine uses radioactive material inside the body to see how organs or tissue are functioning (for diagnosis) or to target and destroy damaged or diseased organs or tissue (for treatment).
- It involves the use of small amounts of radioactive materials, known as radiopharmaceuticals, which are introduced into the body.
- These substances emit gamma rays that can be detected by specialized cameras to create images of organs and tissues.
- This imaging technique helps in diagnosing various conditions, such as cancer, heart disease, and bone disorders, by providing detailed information about the functioning and structure of internal organs.
- Nuclear medicine treatments involve using radioactive substances to target and destroy specific cells or tissues, such as cancer cells.
Eastern Equine Encephalitis
Eastern Equine encephalitis (EEE) virus has been reported in Alabama and New York, with serious implications for public health. Mosquito borne illness continue to pose a significant threat across various parts of the world.
Eastern Equine Encephalitis (EEE):
- It is an extremely rare but serious and often fatal infection that causes encephalitis or inflammation of the brain.
- It spreads to people and animals by the bite of an infected mosquito.
- It was first identified in horses in Massachusetts, United States, in 1831.
- It is caused by the Eastern Equine Encephalitis Virus (EEEV), which belongs to the genus Alphavirus and the family Togaviridae.
- EEE virus has a single-stranded, positive-sense RNA genome.
- The virus does not spread between humans or from animals like horses to humans.
- About 30% of people bitten by an EEE-infected mosquito develop encephalitis and die from the infection.
Symptoms:
- EEEV infections in humans can vary in severity. Many people infected with the virus do not develop any symptoms (asymptomatic).
- However, when symptoms do occur, they can include fever, headache, vomiting, diarrhea, and various neurological symptoms such as encephalitis (inflammation of the brain), which can lead to seizures, coma, and, in some cases, death.
- Severe cases are more common in infants and the elderly.
Treatment:
- Currently, there are no vaccines available to directly treat Eastern equine encephalitis.
- To mitigate the risk of infection, individuals are advised to take several precautionary steps, including avoiding mosquito bites by using repellents and wearing protective clothing.
FAQs on Monthly Current Affairs – August 2023
Q1: What are monthly current affairs?
A1: Monthly current affairs refer to the latest and most significant events, developments, and news stories that have occurred within a particular month. These events encompass a wide range of topics, including politics, economics, science, technology, culture, and more. They are a reflection of the dynamic nature of our world and provide a snapshot of what’s happening globally or within a specific region during a given month.
Q2: Why are monthly current affairs important?
A2: Monthly current affairs are important for several reasons:
- Informed Citizenship: Staying updated with monthly current affairs is crucial for informed citizenship. It empowers individuals to make well-informed decisions, including voting in elections, advocating for causes, and engaging in meaningful discussions about societal issues.
- Professional Relevance: Professionals, such as journalists, policymakers, and business leaders, need to be aware of current affairs to make strategic decisions, create informed content, and respond to changes in their respective fields.
- Academic and Competitive Exams: Many academic institutions and competitive exams assess students’ knowledge of current affairs, making it essential for academic and career success.
- Cultural Awareness: Understanding current events helps individuals appreciate and understand different cultures, societies, and global interconnections.
- Safety and Preparedness: Some current affairs, such as natural disasters or public health emergencies, can directly impact personal safety and require timely awareness and preparedness.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here

