
The dynamic interplay between land use and land cover has emerged as a pivotal force, precipitating widespread ecological transformations on both global and regional scales. As human societies evolve, so too does the utilization of land, ranging from urban expansion and agricultural intensification to deforestation and industrialization. These sequential changes in land use and land cover have set in motion a cascade of ecological consequences, giving rise to imbalances that reverberate across ecosystems. The intricate relationship between human activities and the environment has become increasingly evident, as alterations in land use patterns contribute to shifts in biodiversity, climate patterns, and overall ecosystem health. This interconnected web of changes underscores the urgent need for a comprehensive understanding of the repercussions of land use modifications and prompts a critical examination of sustainable practices to mitigate the ensuing ecological challenges.
Contents
Answer
Unsustainable population growth along with natural reasons has led to undesirable and sequential changes in land use and land cover patterns. This has resulted in global and regional ecological changes with negative ramifications.
Sequential changes in land use and land cover patterns
- Natural Reasons
- Over time, land cover can change naturally due to factors like erosion, weathering, vegetation growth, and climate change. For Eg. Mont St. Helens’ catastrophic volcanic eruption and destruction of entire ecosystem.
- Anthropogenic Reasons
- Unsustainable growth of agricultural area
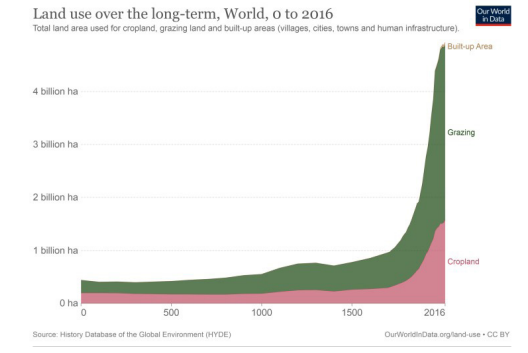

The ever-rising human population has resulted into the conversion of forest areas into agricultural areas. As per FAO estimates, there will be a need to double the agricultural production to feed the growing population.
- Growth of urbanization and urban areas
- Conversion of agricultural area and forest area into urban settlements to house ever growing urban population for eg. In India the growth rate of urban population is close to 31%.
- Conversion of urban area into industrial complexes and industrial area
- Rising need for employment has resulted into conversion of area under urban landscape to be transformed into industrial complexes,leading to morphological changes in the urban settlements.
Global and regional ecological changes and imbalances induced by changing land use pattern
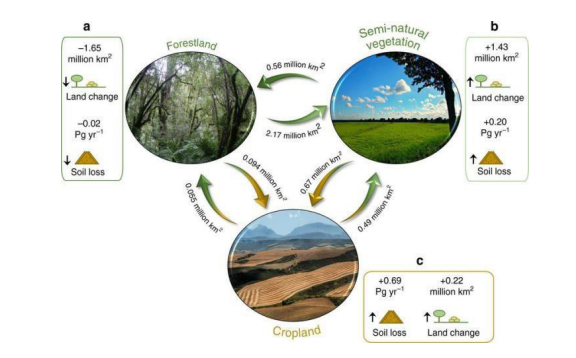
- Simplification of ecosystem and loss of biodiversity and gene pool.
- Loss of ecosystem services like regulating services such as regulation of hydrological cycle and biochemical cycles, provisioning services such as loss of fuel and food resources.
- Reduced ecosystem resilience due to destruction of ecological diversity (Ecosystem stability theory).
- Disruptive changes in the hydrological cycle and changing pattern of precipitation and reduced ground water recharge.
- Habitat fragmentation and increasing edge effect in natural landscapes.
- Man-animal conflicts are rising due to the destruction of natural forests and the encroachment of urban landscapes into forest areas.
- Destruction of natural carbon sinks and release of stored carbon into the atmosphere due to excessive deforestation.

- Changing atmospheric chemistry leads to high levels of pollution across the globe.
- Disruption of hydrosphere balance by way of eutrophication and creation of dead zones
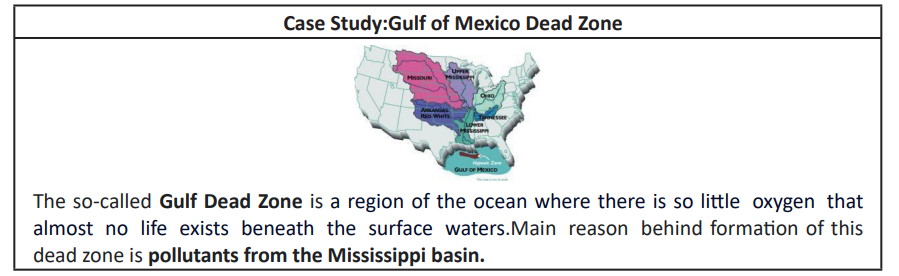
Regional changes
- Land degradation and soil erosion due to excessive deforestation.
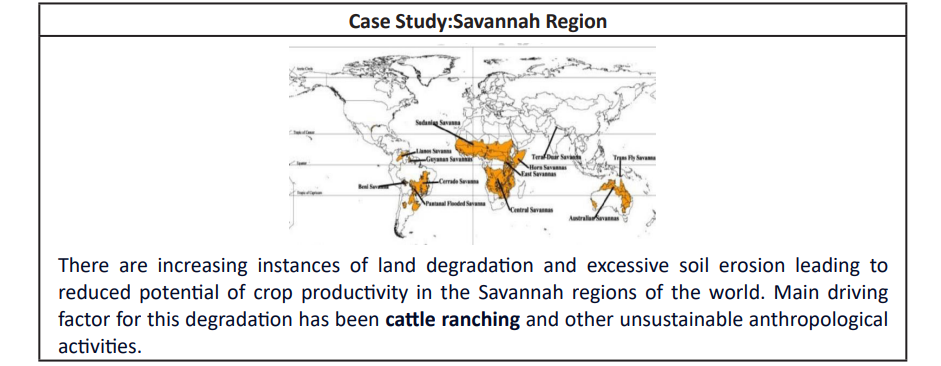
- Habitat fragmentation and rising instances of man- animal conflicts .
- Construction of dams to meet the rising energy requirements resulting into destruction of local biodiversity and ecosystem.
- Rising monoculture have led to increasing susceptibility to forest fires.
- Overgrazing and improper soil management resulted into loss of ecosystem services and soil erosion thus reduced productive capacity of the soil.
Way Forward
- Committing toward fulfilling the Bonn challenge () can prove to be a sustainable solution for solving the land degradation challenges.
- Regional and National NDCs aligned with the overall aim of protecting the ecosystem and ecosystem diversity.
- Adopting sustainable urbanization practices for example adopting urban forestry and social forestry to have more accomodationist policy towards the environment.
- Following One Health concept.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here

